Page 1715 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1715
Chapter 95 Practical Aspects of Hematologic Stem Cell Harvesting and Mobilization 1525
500 Physician Prescription for Apheresis and Peripheral Blood Stem Cell
CD34 + cells/component × 10 6 350 The attending physician should be aware of apheresis and laboratory
450
Processing
400
procedures in order to maximize the value of peripheral blood stem
300
cell (PBSC) products. The choices of venous access, anticoagulant(s),
+
250
blood volume processed, target dose of CD34 cells, and cryopreserva-
tion volumes can be individualized. Apheresis unit staff may ask for
200
guidance regarding pain medications, concurrent medications, and
150
blood transfusions (although it is advisable to avoid transfusion during
100
because changes in the hematocrit may affect the efficiency of the
50
+
collection). Adequate numbers of CD34 cells can be collected for
0 the apheresis procedure because of citrate or other reactions, and
more than one cycle of chemotherapy. It is important to communicate
0 10 20 30 40 50 with the cryopreservation facility if PBSC components will be used to
+
CD34 cells/µL support more than one cycle of chemotherapy or if dimethyl sulfoxide
toxicity is of concern, in order to facilitate appropriate packaging of
+
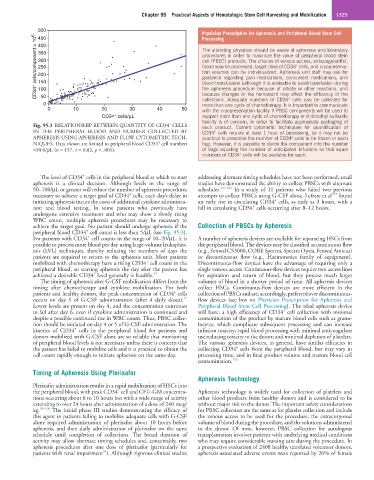
Fig. 95.3 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN QUANTITY OF CD34 CELLS each product. Current cytometric techniques for quantification of
IN THE PERIPHERAL BLOOD AND NUMBER COLLECTED BY CD34 cells require at least 1 hour of processing, so it may not be
+
APHERESIS USING APHERESIS AND FLOW CYTOMETRIC TECH- practical to prescribe the number of CD34 cells to be frozen in each
+
+
NIQUES. Data shown are limited to peripheral blood CD34 cell numbers bag. However, it is possible to divide the component into the number
<50.0/µL (n = 157, r = 0.82, p < .001). of bags equaling the number of anticipated infusions so that equal
+
numbers of CD34 cells will be available for each.
+
The level of CD34 cells in the peripheral blood at which to start addressing alternate timing schedules have not been performed, small
apheresis is a clinical decision. Although levels in the range of studies have demonstrated the ability to collect PBSCs with alternate
50–100/µL or greater will reduce the number of apheresis procedures schedules. 101,102 In a study of 11 patients who failed two previous
+
102
necessary to achieve a target goal of CD34 cells, each day’s delay in attempts to collect PBSCs using G-CSF alone, Lefrere et al found
+
initiating apheresis incurs the costs of additional cytokine administra- an early rise in circulating CD34 cells, as early as 3 hours, with a
+
tion and blood testing. In some patients who previously have fall in circulating CD34 cells occurring after 8–12 hours.
undergone extensive treatment and who may show a slowly rising
WBC count, multiple apheresis procedures may be necessary to
achieve the target goal. No patient should undergo apheresis if the Collection of PBSCs by Apheresis
+
peripheral blood CD34 cell count is less than 5/µL (see Fig. 95.3).
+
For patients with CD34 cell counts in the range of 10–20/µL, it is A number of apheresis devices are available for separating HSCs from
possible to process more blood per day using large-volume leukapher- the peripheral blood. The devices may be classified as continuous flow
esis (LVL) techniques, thereby reducing the numbers of days the (e.g., Fenwal CS3000, COBE Spectra, Spectra Optia, Fenwal Amicus)
patients are required to return to the apheresis unit. Most patients or discontinuous flow (e.g., Haemonetics family of equipment).
+
mobilized with chemotherapy have a rising CD34 cell count in the Discontinuous-flow devices have the advantage of requiring only a
peripheral blood, so starting apheresis the day after the patient has single venous access. Continuous-flow devices require two access lines
+
achieved a desirable CD34 level generally is feasible. 97 for aspiration and return of blood, but they process much larger
The timing of apheresis after G-CSF mobilization differs from the volumes of blood in a shorter period of time. All apheresis devices
timing after chemotherapy and cytokine mobilization. For both collect HSCs. Continuous-flow devices are more efficient in the
+
patients and healthy donors, the peak concentration of CD34 cells collection of PBSCs and are, accordingly, preferred over discontinuous-
71
occurs on day 5 of G-CSF administration (after 4 daily doses). flow devices (see box on Physician Prescription for Apheresis and
Lower levels are present on day 4, and the concentration continues Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Processing). The ideal apheresis device
+
to fall after day 6, even if cytokine administration is continued and will have: a high efficiency of CD34 cell collection with minimal
despite a possible continued rise in WBC count. Thus, PBSC collec- contamination of the product by mature blood cells such as granu-
tion should be initiated on day 4 or 5 of G-CSF administration. The locytes, which complicate subsequent processing and can increase
+
kinetics of CD34 cells in the peripheral blood for patients and infusion toxicity; rapid blood processing with minimal anticoagulant
donors mobilized with G-CSF alone are so reliable that monitoring use reducing toxicity to the donor; and minimal depletion of platelets.
of peripheral blood levels is not necessary unless there is concern that The various apheresis devices, in general, have similar efficacies in
+
the patient has failed to mobilize cells and it is practical to obtain the collecting CD34 cells from the peripheral blood, but may vary in
cell count rapidly enough to initiate apheresis on the same day. processing time, and in final product volume and mature blood cell
contamination. 103
Timing of Apheresis Using Plerixafor
Apheresis Technology
Plerixafor administration results in a rapid mobilization of HSCs into
+
the peripheral blood, with peak CD34 cell and CFU-GM concentra- Apheresis technology is widely used for collection of platelets and
tions occurring about 6 to 10 hours but with a wide range of activity other blood products from healthy donors and is considered to be
extending to over 24 hours after administration of a dose of 240 mcg/ without major risk to the donor. The important safety considerations
kg. 98–100 The initial phase III studies demonstrating the efficacy of for PBSC collection are the same as for platelet collection and include
this agent in patients failing to mobilize adequate cells with G-CSF the venous access to be used for the procedure, the extracorporeal
alone required administration of plerixafor about 10 hours before volume of blood during the procedure, and the solutions administered
apheresis, and then daily administration of plerixafor on the same to the donor. Of note, however, PBSC collection for autologous
schedule until completion of collections. The broad duration of transplantation involves patients with underlying medical conditions
activity may allow alternate timing schedules and, conceivably, two who may require considerable nursing care during the procedure. In
apheresis procedures after one dose of plerixafor (particularly for a prospective evaluation of 2408 healthy unrelated volunteer donors,
94
patients with renal impairment ). Although rigorous clinical studies apheresis-associated adverse events were reported by 20% of female