Page 1923 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1923
Chapter 111 Principles of Red Blood Cell Transfusion 1703
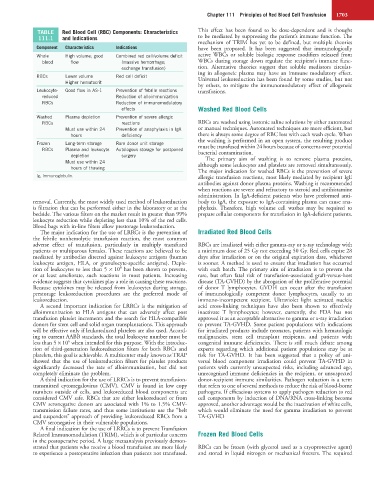
TABLE Red Blood Cell (RBC) Components: Characteristics This effect has been found to be dose-dependent and is thought
111.1 and Indications to be mediated by suppressing the patient’s immune function. The
mechanism of TRIM has yet to be defined, but multiple theories
Component Characteristics Indications have been proposed. It has been suggested that immunologically
Whole High volume; good Combined red cell/volume deficit active WBCs or soluble biologic response modifiers released from
blood flow (massive hemorrhage; WBCs during storage down regulate the recipient’s immune func-
exchange transfusion) tion. Alternative theories suggest that soluble mediators circulat-
ing in allogeneic plasma may have an immune modulatory effect.
RBCs Lower volume Red cell deficit Universal leukoreduction has been found by some studies, but not
Higher hematocrit
by others, to mitigate the immunomodulatory effect of allogeneic
Leukocyte- Good flow in AS-1 Prevention of febrile reactions transfusions.
reduced Reduction of alloimmunization
RBCs Reduction of immunomodulatory
effects Washed Red Blood Cells
Washed Plasma depletion Prevention of severe allergic
RBCs reactions RBCs are washed using isotonic saline solutions by either automated
Must use within 24 Prevention of anaphylaxis in IgA or manual techniques. Automated techniques are more efficient, but
hours deficiency there is always some degree of RBC loss with each wash cycle. When
the washing is performed in an open system, the resulting product
Frozen Long-term storage Rare donor unit storage must be transfused within 24 hours because of concerns over potential
RBCs Plasma and leukocyte Autologous storage for postponed bacterial contamination.
depletion surgery
The primary aim of washing is to remove plasma proteins,
Must use within 24 although some leukocytes and platelets are removed simultaneously.
hours of thawing The major indication for washed RBCs is the prevention of severe
Ig, Immunoglobulin. allergic transfusion reactions, most likely mediated by recipient IgE
antibodies against donor plasma proteins. Washing is recommended
when reactions are severe and refractory to steroid and antihistamine
administration. In IgA-deficient patients who have preformed anti-
removal. Currently, the most widely used method of leukoreduction body to IgA, the exposure to IgA-containing plasma can cause ana-
is filtration that can be performed either in the laboratory or at the phylaxis. Therefore, high volume cell washes may be required to
bedside. The various filters on the market result in greater than 99% prepare cellular components for transfusion in IgA-deficient patients.
leukocyte reduction while depleting less than 10% of the red cells.
Blood bags with in-line filters allow prestorage leukoreduction.
The major indication for the use of LRRCs is the prevention of Irradiated Red Blood Cells
the febrile nonhemolytic transfusion reaction, the most common
adverse effect of transfusion, particularly in multiply transfused RBCs are irradiated with either gamma-ray or x-ray technology with
patients or multiparous females. These reactions are believed to be a minimum dose of 25 Gy not exceeding 50 Gy. Red cells expire 28
mediated by antibodies directed against leukocyte antigens (human days after irradiation or on the original expiration date, whichever
leukocyte antigen, HLA, or granulocyte-specific antigens). Deple- is sooner. A method is used to ensure that irradiation has occurred
6
tion of leukocytes to less than 5 × 10 has been shown to prevent, with each batch. The primary aim of irradiation is to prevent the
or at least ameliorate, such reactions in most patients. Increasing rare, but often fatal risk of transfusion-associated graft-versus-host
evidence suggests that cytokines play a role in causing these reactions. disease (TA-GVHD) by the abrogation of the proliferative potential
Because cytokines may be released from leukocytes during storage, of donor T lymphocytes. GVDH can occur after the transfusion
prestorage leukoreduction procedures are the preferred mode of of immunologically competent donor lymphocytes, usually to an
leukoreduction. immuno-incompetent recipient. Ultraviolet light activated nucleic
A second important indication for LRRCs is the mitigation of acid cross-linking techniques have also been shown to effectively
alloimmunization to HLA antigens that can adversely affect post inactivate T lymphocytes; however, currently, the FDA has not
transfusion platelet increments and the search for HLA-compatible approved it as an acceptable alternative to gamma or x-ray irradiation
donors for stem cell and solid organ transplantations. This approach to prevent TA-GVHD. Some patient populations with indications
will be effective only if leukoreduced platelets are also used. Accord- for irradiated products include neonates, patients with hematologic
ing to current AABB standards, the total leukocyte number must be malignancies, stem cell transplant recipients, and patients with
6
less than 5 × 10 when intended for this purpose. With the introduc- congenital immune deficiencies. There is still much debate among
tion of third-generation leukoreduction filters for both RBCs and experts regarding which additional patient populations may be at
platelets, this goal is achievable. A multicenter study known as TRAP risk for TA-GVHD. It has been suggested that a policy of uni-
showed that the use of leukoreduction filters for platelet products versal blood component irradiation could prevent TA-GVHD in
significantly decreased the rate of alloimmunization, but did not patients with currently unsuspected risks, including advanced age,
completely eliminate the problem. unrecognized immune deficiencies in the recipient, or unsuspected
A third indication for the use of LRRCs is to prevent transfusion- donor-recipient immune similarities. Pathogen reduction is a term
transmitted cytomegalovirus (CMV). CMV is found in low copy that refers to one of several methods to reduce the risk of blood-borne
numbers outside of cells, and leukoreduced blood components are pathogens. If efficacious systems to apply pathogen reduction to red
considered CMV safe. RBCs that are either leukoreduced or from cell components by induction of DNA/RNA cross-linking become
CMV seronegative donors are associated with 1% to 1.5% CMV- approved, another advantage would be the inactivation of white cells,
transmission failure rates, and thus some institutions use the “belt which would eliminate the need for gamma irradiation to prevent
and suspenders” approach of providing leukoreduced RBCs from a TA-GVHD
CMV seronegative in their vulnerable populations.
A final indication for the use of LRRCs is to prevent Transfusion
Related Immunomodulation (TRIM), which is of particular concern Frozen Red Blood Cells
in the postoperative period. A large metaanalysis previously demon-
strated that patients who receive a blood transfusion are more likely RBCs can be frozen (with glycerol used as a cryoprotective agent)
to experience a postoperative infection than patients not transfused. and stored in liquid nitrogen or mechanical freezers. The required