Page 235 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 235
Chapter 18 Cell Death 187
of a proapoptotic BCL-2 family member, BID, also features caspase-
mediated processing to a truncated factor, tBID, which then traffics
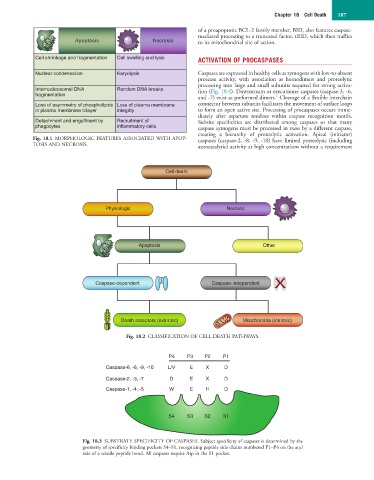
Apoptosis Necrosis to its mitochondrial site of action.
Cell shrinkage and fragmentation Cell swelling and lysis ACTIVATION OF PROCASPASES
Nuclear condensation Karyolysis Caspases are expressed in healthy cells as zymogens with low-to-absent
protease activity, with association as homodimers and proteolytic
processing into large and small subunits required for strong activa-
Internucleosomal DNA Random DNA breaks tion (Fig. 18.4). Downstream or executioner caspases (caspase-3, -6,
fragmentation 1
and -7) exist as preformed dimers. Cleavage of a flexible interchain
Loss of asymmetry of phospholipids Loss of plasma membrane connector between subunits facilitates the movement of surface loops
in plasma membrane bilayer integrity to form an open active site. Processing of procaspases occurs imme-
diately after aspartate residues within caspase recognition motifs.
Detachment and engulfment by Recruitment of Subsite specificities are distributed among caspases so that many
phagocytes inflammatory cells caspase zymogens must be processed in trans by a different caspase,
creating a hierarchy of proteolytic activation. Apical (initiator)
Fig. 18.1 MORPHOLOGIC FEATURES ASSOCIATED WITH APOP- caspases (caspase-2, -8, -9, -10) have limited proteolytic (including
TOSIS AND NECROSIS. autocatalytic) activity at high concentrations without a requirement
Cell death
Physiologic Necrotic
Apoptosis Other
X
Caspase-dependent Caspase-independent
Death receptors (extrinsic) Mitochondria (intrinsic)
Fig. 18.2 CLASSIFICATION OF CELL DEATH PATHWAYS.
P4 P3 P2 P1
Caspase-6, -8, -9, -10 L/V E X D
Caspase-2, -3, -7 D E X D
Caspase-1, -4, -5 W E H D
S4 S3 S2 S1
Fig. 18.3 SUBSTRATE SPECIFICITY OF CASPASES. Subject specificity of caspases is determined by the
geometry of specificity binding pockets S4–S1, recognizing peptide side chains numbered P1–P4 on the acyl
side of a scissile peptide bond. All caspases require Asp in the S1 pocket.