Page 239 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 239
Chapter 18 Cell Death 191
BH4 BH3 BH1 BH2 TM
MCL-1
BCL-2
Antiapoptotic BCL-X L
multidomain
BCL-B
BCL-w
BFL-1/A1
BOK/MTD
Proapoptotic
multidomain BAK
BAX
BCL-Rambo
BCL-G
BIM
BID
PUMA
BH3-only
BMF
BAD
BIK
HRK
NOXA
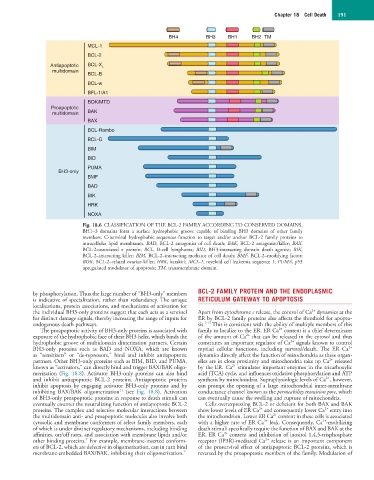
Fig. 18.6 CLASSIFICATION OF THE BCL-2 FAMILY ACCORDING TO CONSERVED DOMAINS.
BH1–3 domains form a surface hydrophobic groove capable of binding BH3 domains of other family
members. C-terminal hydrophobic sequences function to target and/or anchor BCL-2 family proteins to
intracellular lipid membranes. BAD, BCL-2 antagonist of cell death; BAK, BCL-2 antagonist/killer; BAX,
BCL-2–associated x protein; BCL, B-cell lymphoma; BID, BH3-interacting domain death agonist; BIK,
BCL-2–interacting killer; BIM, BCL-2–interacting mediator of cell death; BMF, BCL-2–modifying factor;
BOK, BCL-2–related ovarian killer; HRK, harakiri; MCL-1, myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1; PUMA, p53
upregulated modulator of apoptosis; TM, transmembrane domain.
BCL-2 FAMILY PROTEIN AND THE ENDOPLASMIC
by phosphorylation. Thus the large number of “BH3-only” members
is indicative of specialization, rather than redundancy. The unique RETICULUM GATEWAY TO APOPTOSIS
localizations, protein associations, and mechanisms of activation for
2+
the individual BH3-only proteins suggest that each acts as a sentinel Apart from cytochrome c release, the control of Ca dynamics at the
for distinct damage signals, thereby increasing the range of inputs for ER by BCL-2 family proteins also affects the threshold for apopto-
endogenous death pathways. sis. 9,14 This is consistent with the ability of multiple members of this
2+
The proapoptotic activity of BH3-only proteins is associated with family to localize to the ER. ER Ca content is a chief determinant
2+
exposure of the hydrophobic face of their BH3 helix, which binds the of the amount of Ca that can be released in the cytosol and thus
2+
hydrophobic groove of multidomain dimerization partners. Certain constitutes an important regulator of Ca signals known to control
2+
BH3-only proteins such as BAD and NOXA, which are known myriad cellular functions, including survival/death. The ER Ca
as “sensitizers” or “de-repressors,” bind and inhibit antiapoptotic dynamics directly affect the function of mitochondria as these organ-
2+
partners. Other BH3-only proteins such as BIM, BID, and PUMA, elles are in close proximity and mitochondria take up Ca released
2+
known as “activators,” can directly bind and trigger BAX/BAK oligo- by the ER. Ca stimulates important enzymes in the tricarboxylic
merization (Fig. 18.8). Activator BH3-only proteins can also bind acid (TCA) cycle, and influences oxidative phosphorylation and ATP
2+
and inhibit antiapoptotic BCL-2 proteins. Antiapoptotic proteins synthesis by mitochondria. Supraphysiologic levels of Ca , however,
inhibit apoptosis by engaging activator BH3-only proteins and by can prompt the opening of a large mitochondrial inner-membrane
11
inhibiting BAX/BAK oligomerization (see Fig. 18.8). Activation conductance channel known as the permeability transition pore, which
of BH3-only proapoptotic proteins in response to death stimuli can can eventually cause the swelling and rupture of mitochondria.
eventually counter the neutralizing function of antiapoptotic BCL-2 Cells overexpressing BCL-2 or deficient for both BAX and BAK
2+
2+
proteins. The complex and selective molecular interactions between show lower levels of ER Ca and consequently lower Ca entry into
2+
the multidomain anti- and proapoptotic molecules also involve both the mitochondrion. Lower ER Ca content in these cells is associated
2+
2+
cytosolic and membrane conformers of select family members, each with a higher rate of ER Ca leak. Consequently, Ca -mobilizing
of which is under distinct regulatory mechanisms, including binding death stimuli specifically require the function of BAX and BAK at the
2+
affinities, on/off rates, and association with membrane lipids and/or ER. ER Ca content and inhibition of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
2+
9
other binding proteins. For example, membrane-inserted conform- receptor (IP3R)-mediated Ca release is an important component
ers of BCL-2, which are defective in oligomerization, can in turn bind of the prosurvival effect of antiapoptotic BCL-2 proteins, which is
membrane-embedded BAX/BAK, inhibiting their oligomerization. 9 reversed by the proapoptotic members of the family. Modulation of