Page 241 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 241
Chapter 18 Cell Death 193
Cytochrome c
Release
MOMP
Active
BAX/BAK
Proapoptotic
BAX/BAK
Activator BH3-only
MITOCHONDRION
Antiapoptotic
Sensitizer BH3-only
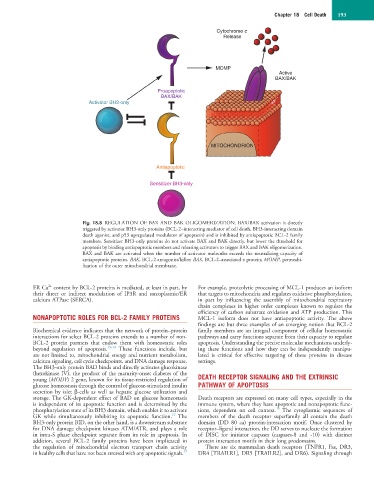
Fig. 18.8 REGULATION OF BAX AND BAK OLIGOMERIZATION. BAX/BAK activation is directly
triggered by activator BH3-only proteins (BCL-2–interacting mediator of cell death, BH3-interacting domain
death agonist, and p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis) and is inhibited by antiapoptotic BCL-2 family
members. Sensitizer BH3-only proteins do not activate BAX and BAK directly, but lower the threshold for
apoptosis by binding antiapoptotic members and releasing activators to trigger BAX and BAK oligomerization.
BAX and BAK are activated when the number of activator molecules exceeds the neutralizing capacity of
antiapoptotic proteins. BAK, BCL-2 antagonist/killer; BAX, BCL-2–associated x protein; MOMP, permeabi-
lization of the outer mitochondrial membrane.
2+
ER Ca content by BCL-2 proteins is mediated, at least in part, by For example, proteolytic processing of MCL-1 produces an isoform
their direct or indirect modulation of IP3R and sarcoplasmic/ER that targets to mitochondria and regulates oxidative phosphorylation,
calcium ATPase (SERCA). in part by influencing the assembly of mitochondrial respiratory
chain complexes in higher order complexes known to regulate the
efficiency of carbon substrate oxidation and ATP production. This
NONAPOPTOTIC ROLES FOR BCL-2 FAMILY PROTEINS MCL-1 isoform does not have antiapoptotic activity. The above
findings are but three examples of an emerging notion that BCL-2
Biochemical evidence indicates that the network of protein–protein family members are an integral component of cellular homeostatic
interactions for select BCL-2 proteins extends to a number of non- pathways and carry functions separate from their capacity to regulate
BCL-2 protein partners that endow them with homeostatic roles apoptosis. Understanding the precise molecular mechanisms underly-
beyond regulation of apoptosis. 15–18 These functions include, but ing these functions and how they can be independently manipu-
are not limited to, mitochondrial energy and nutrient metabolism, lated is critical for effective targeting of these proteins in disease
calcium signaling, cell cycle checkpoints, and DNA damage response. settings.
The BH3-only protein BAD binds and directly activates glucokinase
(hexokinase IV), the product of the maturity-onset diabetes of the
young (MODY) 2 gene, known for its tissue-restricted regulation of DEATH RECEPTOR SIGNALING AND THE EXTRINSIC
glucose homeostasis through the control of glucose-stimulated insulin PATHWAY OF APOPTOSIS
secretion by islet β-cells as well as hepatic glucose utilization and
storage. The GK-dependent effect of BAD on glucose homeostasis Death receptors are expressed on many cell types, especially in the
is independent of its apoptotic function and is determined by the immune system, where they have apoptotic and nonapoptotic func-
19
phosphorylation state of its BH3 domain, which enables it to activate tions, dependent on cell context. The cytoplasmic sequences of
17
GK while simultaneously inhibiting its apoptotic function. The members of the death receptor superfamily all contain the death
BH3-only protein BID, on the other hand, is a downstream substrate domain (DD 80 aa) protein-interaction motif. Once clustered by
for DNA damage checkpoint kinases ATM/ATR, and plays a role receptor–ligand interaction, the DD serves to nucleate the formation
in intra-S phase checkpoint separate from its role in apoptosis. In of DISC for initiator caspases (caspases-8 and -10) with distinct
addition, several BCL-2 family proteins have been implicated in protein interaction motifs in their long prodomains.
the regulation of mitochondrial electron transport chain activity There are six mammalian death receptors (TNFR1, Fas, DR3,
17
in healthy cells that have not been stressed with any apoptotic signals. DR4 [TRAILR1], DR5 [TRAILR2], and DR6). Signaling through