Page 797 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 797
Chapter 49 Lymphocytosis, Lymphocytopenia, Hypergammaglobulinemia, and Hypogammaglobulinemia 683
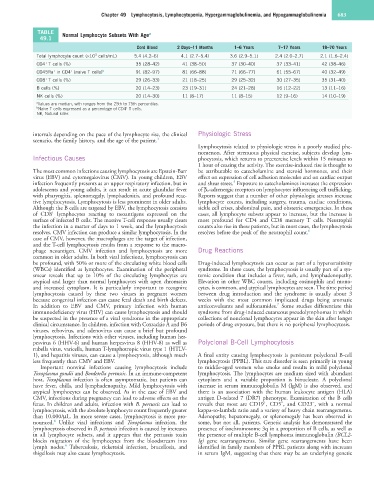
TABLE Normal Lymphocyte Subsets With Age a
49.1
Cord Blood 2 Days–11 Months 1–6 Years 7–17 Years 18–70 Years
3
Total lymphocyte count (×10 cells/mL) 5.4 (4.2–6) 4.1 (2.7–5.4) 3.6 (2.9–5.1) 2.4 (2.0–2.7) 2.1 (1.6–2.4)
+
CD4 T cells (%) 35 (28–42) 41 (38–50) 37 (30–40) 37 (33–41) 42 (38–46)
+
+
CD45Ra in CD4 (naive T cells) b 91 (82–97) 81 (66–88) 71 (66–77) 61 (55–67) 40 (32–49)
+
CD8 T cells (%) 29 (26–33) 21 (18–25) 29 (25–32) 30 (27–35) 35 (31–40)
B cells (%) 20 (14–23) 23 (19–31) 24 (21–28) 16 (12–22) 13 (11–16)
NK cells (%) 20 (14–30) 11 (8–17) 11 (8–15) 12 (9–16) 14 (10–19)
a Values are median, with ranges from the 25th to 75th percentiles.
b Naive T cells expressed as a percentage of CD4 T cells.
+
NK, Natural killer.
intervals depending on the pace of the lymphocyte rise, the clinical Physiologic Stress
scenario, the family history, and the age of the patient. 3
Lymphocytosis related to physiologic stress is a poorly studied phe-
nomenon. After strenuous physical exercise, subjects develop lym-
Infectious Causes phocytosis, which returns to preexercise levels within 15 minutes to
1 hour of ceasing the activity. The exercise-induced rise is thought to
The most common infections causing lymphocytosis are Epstein-Barr be attributable to catecholamine and steroid hormones, and their
virus (EBV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV). In young children, EBV effect on expression of cell adhesion molecules and on cardiac output
5
infection frequently presents as an upper respiratory infection, but in and shear stress. Exposure to catecholamines increases the expression
adolescents and young adults, it can result in acute glandular fever of β 2 -adrenergic receptors on lymphocytes influencing cell trafficking.
with pharyngitis, splenomegaly, lymphadenitis, and profound reac- Reports suggest that a number of other physiologic stresses increase
tive lymphocytosis. Lymphocytosis is less prominent in older adults. lymphocyte counts, including surgery, trauma, cardiac conditions,
Although the B cells are targeted by EBV, the lymphocytosis consists sickle cell crises, abdominal pain, and obstetric emergencies. In these
+
of CD8 lymphocytes reacting to neoantigens expressed on the cases, all lymphocyte subsets appear to increase, but the increase is
surface of infected B cells. The massive T-cell response usually clears most profound for CD4 and CD8 memory T cells. Neutrophil
the infection in a matter of days to 1 week, and the lymphocytosis counts also rise in these patients, but in most cases, the lymphocytosis
resolves. CMV infection can produce a similar lymphocytosis. In the resolves before the peak of the neutrophil count. 6
case of CMV, however, the macrophages are the target of infection,
and the T-cell lymphocytosis results from a response to the macro-
phage neoantigen. CMV infection and lymphocytosis are more Drug Reactions
common in older adults. In both viral infections, lymphocytosis can
be profound, with 50% or more of the circulating white blood cells Drug-induced lymphocytosis can occur as part of a hypersensitivity
(WBCs) identified as lymphocytes. Examination of the peripheral syndrome. In these cases, the lymphocytosis is usually part of a sys-
smear reveals that up to 10% of the circulating lymphocytes are temic condition that includes a fever, rash, and lymphadenopathy.
atypical and larger than normal lymphocytes with open chromatin Elevation in other WBC counts, including eosinophils and mono-
and increased cytoplasm. It is particularly important to recognize cytes, is common, and atypical lymphocytes are seen. The time period
lymphocytosis caused by these two viruses in pregnant women between drug introduction and the syndrome is usually about 3
because congenital infection can cause fetal death and birth defects. weeks with the most common implicated drugs being aromatic
7
In addition to EBV and CMV, primary infection with human anticonvulsants and sulfonamides. Some studies differentiate this
immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can cause lymphocytosis and should syndrome from drug-induced cutaneous pseudolymphomas in which
be suspected in the presence of a viral syndrome in the appropriate collections of nonclonal lymphocytes appear in the skin after longer
clinical circumstance. In children, infection with Coxsackie A and B6 periods of drug exposure, but there is no peripheral lymphocytosis.
viruses, echovirus, and adenovirus can cause a brief but profound
lymphocytosis. Infections with other viruses, including human her-
pesvirus 6 (HHV-6) and human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) as well as Polyclonal B-Cell Lymphocytosis
rubella virus, varicella, human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-
1), and hepatitis viruses, can cause a lymphocytosis, although much A final entity causing lymphocytosis is persistent polyclonal B-cell
less frequently than CMV and EBV. lymphocytosis (PPBL). This rare disorder is seen primarily in young
Important nonviral infections causing lymphocytosis include to middle-aged women who smoke and results in mild polyclonal
Toxoplasma gondii and Bordetella pertussis. In an immune-competent lymphocytosis. The lymphocytes are medium sized with abundant
host, Toxoplasma infection is often asymptomatic, but patients can cytoplasm and a variable proportion is binucleate. A polyclonal
have fever, chills, and lymphadenopathy. Mild lymphocytosis with increase in serum immunoglobulin M (IgM) is also observed, and
atypical lymphocytes can be observed. As in the case of EBV and there is an association with the human leukocyte antigen (HLA)
CMV, infections during pregnancy can lead to adverse effects on the antigen D-related 7 (DR7) phenotype. Examination of the B cells
+
−
−
fetus. In children and adults, infection with B. pertussis can lead to reveals that most are CD19 , CD5 , and CD23 , with a normal
lymphocytosis, with the absolute lymphocyte count frequently greater kappa-to-lambda ratio and a variety of heavy chain rearrangements.
than 10,000/µL. In more severe cases, lymphocytosis is more pro- Adenopathy, hepatomegaly, or splenomegaly has been observed in
4
nounced. Unlike viral infections and Toxoplasma infection, the some, but not all, patients. Genetic analysis has demonstrated the
lymphocytosis observed in B. pertussis infection is caused by increases presence of isochromosome 3q in a proportion of B cells, as well as
in all lymphocyte subsets, and it appears that the pertussis toxin the presence of multiple B-cell lymphoma immunoglobulin (BCL2-
blocks migration of the lymphocytes from the bloodstream into Ig) gene rearrangements. Similar gene rearrangements have been
4
lymph nodes. Tuberculosis, rickettsial infection, brucellosis, and identified in family members of PPBL patients along with increases
shigellosis may also cause lymphocytosis. in serum IgM, suggesting that there may be an underlying genetic