Page 858 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 858
Chapter 53 Lysosomal Storage Diseases: Perspectives and Principles 741
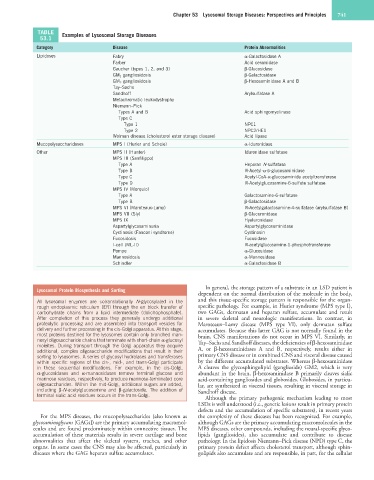
TABLE Examples of Lysosomal Storage Diseases
53.1
Category Disease Protein Abnormalities
Lipidoses Fabry α-Galactosidase A
Farber Acid ceramidase
Gaucher (types 1, 2, and 3) β-Glucosidase
GM 1 gangliosidosis β-Galactosidase
GM 2 gangliosidosis β-Hexosaminidase A and B
Tay–Sachs
Sandhoff Arylsulfatase A
Metachromatic leukodystrophy
Niemann–Pick
Types A and B Acid sphingomyelinase
Type C
Type 1 NPC1
Type 2 NPC2/HE1
Wolman disease (cholesterol ester storage disease) Acid lipase
Mucopolysaccharidoses MPS I (Hurler and Scheie) α-Iduronidase
Other MPS II (Hunter) Iduronidase sulfatase
MPS III (Sanfilippo)
Type A Heparan N-sulfatase
Type B N-Acetyl-α-D-glucosaminidase
Type C Acetyl-CoA-α-glucosaminide acetyltransferase
Type D N-Acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase
MPS IV (Morquio)
Type A Galactosamine-6-sulfatase
Type B β-Galactosidase
MPS VI (Maroteaux-Lamy) N-Acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase (arylsulfatase B)
MPS VII (Sly) β-Glucuronidase
MPS IX Hyaluronidase
Aspartylglycosaminuria Aspartylglycosaminidase
Cystinosis (Fanconi syndrome) Cystinosin
Fucosidosis Fucosidase
I-cell (ML-II) N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase
Pompe α-Glucosidase
Mannosidosis α-Mannosidase
Schindler α-Galactosidase B
In general, the storage pattern of a substrate in an LSD patient is
Lysosomal Protein Biosynthesis and Sorting
dependent on the normal distribution of the molecule in the body,
All lysosomal enzymes are cotranslationally N-glycosylated in the and this tissue-specific storage pattern is responsible for the organ-
rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) through the en block transfer of specific pathology. For example, in Hurler syndrome (MPS type I),
carbohydrate chains from a lipid intermediate (dolichophosphate). two GAGs, dermatan and heparan sulfate, accumulate and result
After completion of this process they generally undergo additional in severe skeletal and neurologic manifestations. In contrast, in
proteolytic processing and are assembled into transport vesicles for Maroteaux–Lamy disease (MPS type VI), only dermatan sulfate
delivery and further processing in the cis-Golgi apparatus. At this stage, accumulates. Because this latter GAG is not normally found in the
most proteins destined for the lysosomes contain only branched man- brain, CNS manifestations do not occur in MPS VI. Similarly, in
nosyl oligosaccharide chains that terminate with short-chain α-glucosyl Tay–Sachs and Sandhoff diseases, the deficiencies of β-hexosaminidase
moieites. During transport through the Golgi apparatus they acquire
additional, complex oligosaccharide modifications that result in their A, or β-hexosaminidases A and B, respectively, results either in
sorting to lysosomes. A series of glycosyl hydrolases and transferases primary CNS disease or in combined CNS and visceral disease caused
within specific regions of the cis-, mid-, and trans-Golgi participate by the different accumulated substrates. Whereas β-hexosaminidase
in these sequential modifications. For example, in the cis-Golgi, A cleaves the glycosphingolipid (ganglioside) GM2, which is very
α-glucosidases and α-mannosidases remove terminal glucose and abundant in the brain, β-hexosaminidase B primarily cleaves sialic
mannose residues, respectively, to produce mannose-terminated core acid-containing gangliosides and globosides. Globosides, in particu-
oligosaccharides. Within the mid-Golgi, additional sugars are added, lar, are synthesized in visceral tissues, resulting in visceral storage in
including β-N-acetylglucosamine and β-galactoside. The addition of Sandhoff disease.
terminal sialic acid residues occurs in the trans-Golgi. Although the primary pathogenic mechanism leading to most
LSDs is well understood (i.e., genetic lesions result in primary protein
defects and the accumulation of specific substrates), in recent years
For the MPS diseases, the mucopolysaccharides (also known as the complexity of these diseases has been recognized. For example,
glycosaminoglycans [GAGs]) are the primary accumulating macromol- although GAGs are the primary accumulating macromolecules in the
ecules and are found predominately within connective tissues. The MPS diseases, other compounds, including the neural-specific glyco-
accumulation of these materials results in severe cartilage and bone lipids (gangliosides), also accumulate and contribute to disease
abnormalities that affect the skeletal system, trachea, and other pathology. In the lipidosis Niemann–Pick disease (NPD) type C, the
organs. In some cases the CNS may also be affected, particularly in primary protein defect affects cholesterol transport, although sphin-
diseases where the GAG heparan sulfate accumulates. golipids also accumulate and are responsible, in part, for the cellular