Page 1201 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1201
1176 Part IX: Lymphocytes and Plasma Cells Chapter 76: Functions of T Lymphocytes: T-cell Receptors for Antigen 1177
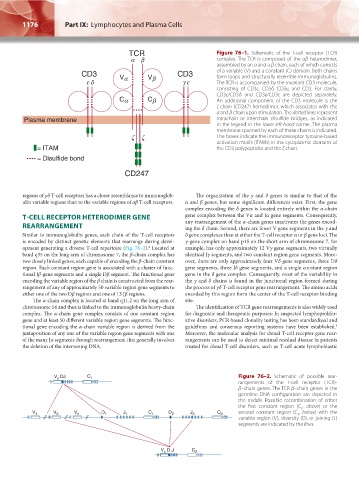
Figure 76–1. Schematic of the T-cell receptor (TCR)
complex. The TCR is composed of the αβ heterodimer,
assembled by an α and a β chain, each of which consists
of a variable (V) and a constant (C) domain. Both chains
form loops and structurally resemble immunoglobulins.
The TCR is accompanied by the invariant CD3 molecule,
consisting of CD3ε, CD3δ, CD3γ, and CD3. For clarity,
CD3ε/CD3δ and CD3γ/CD3ε are depicted separately.
An additional component of the CD3 molecule is the
ζ chain (CD247) homodimer, which associates with the
α and β chain upon stimulation. The dotted lines represent
intrachain or interchain disulfide bridges, as indicated
in the legend in the lower left-hand corner. The plasma
membrane spanned by each of these chains is indicated.
The boxes indicate the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based
activation motifs (ITAMs) in the cytoplasmic domains of
the CD3 polypeptides and the ζ chain.
regions of γδ T-cell receptors has a closer resemblance to immunoglob- The organization of the γ and δ genes is similar to that of the
ulin variable regions than to the variable regions of αβ T-cell receptors. α and β genes, but some significant differences exist. First, the gene
complex encoding the δ genes is located entirely within the α-chain
T-CELL RECEPTOR HETERODIMER GENE gene complex between the Vα and Jα gene segments. Consequently,
any rearrangement of the α-chain genes inactivates the genes encod-
REARRANGEMENT ing the δ chain. Second, there are fewer V gene segments in the γ and
Similar to immunoglobulin genes, each chain of the T-cell receptors δ gene complexes than at either the T-cell receptor α or β gene loci. The
is encoded by distinct genetic elements that rearrange during devel- γ-gene complex on band p15 on the short arm of chromosome 7, for
opment generating a diverse T-cell repertoire (Fig. 76–2). Located at example, has only approximately 12 Vγ gene segments, two virtually
4
band q35 on the long arm of chromosome 7, the β-chain complex has identical Jγ segments, and two constant region gene segments. More-
two closely linked genes, each capable of encoding the β-chain constant over, there are only approximately four Vδ gene segments, three Dδ
region. Each constant region gene is associated with a cluster of func- gene segments, three Jδ gene segments, and a single constant region
tional Jβ-gene segments and a single Dβ segment. The functional gene gene in the δ gene complex. Consequently, most of the variability in
encoding the variable region of the β chain is constructed from the rear- the γ and δ chains is found in the junctional region formed during
rangement of any of approximately 50 variable region gene segments to the process of γδ T-cell receptor gene rearrangement. The amino acids
either one of the two Dβ regions and one of 13 Jβ regions. encoded by this region form the center of the T-cell receptor-binding
The α-chain complex is located at band q11.2 on the long arm of site.
chromosome 14 and thus is linked to the immunoglobulin heavy-chain The identification of TCR gene rearrangements is also widely used
complex. The α-chain gene complex consists of one constant region for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes: In suspected lymphoprolifer-
gene and at least 50 different variable region gene segments. The func- ative disorders, PCR-based clonality testing has been standardized and
tional gene encoding the α-chain variable region is derived from the guidelines and consensus reporting systems have been established.
5
juxtaposition of any one of the variable region gene segments with one Moreover, the molecular analysis for clonal T-cell receptor gene rear-
of the many Jα segments through rearrangement that generally involves rangements can be used to detect minimal residual disease in patients
the deletion of the intervening DNA. treated for clonal T-cell disorders, such as T-cell acute lymphoblastic
V DJ C 1 Figure 76–2. Schematic of possible rear-
y
rangements of the T-cell receptor (TCR)-
β–chain genes. The TCR-β–chain genes in the
germline DNA configuration are depicted in
the middle. Possible recombination of either
the first constant region (C , above) or the
1
V 1 V 2 V n D 1 J 1 C 1 D 2 J 2 C 2 second constant region (C , below) with the
2
variable region (V), diversity (D), or joining (J)
segments are indicated by the lines.
V D J C 2
x
Kaushansky_chapter 76_p1175-1188.indd 1176 9/17/15 4:00 PM