Page 1413 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1413
1388 Part X: Malignant Myeloid Diseases Chapter 88: Acute Myelogenous Leukemia 1389
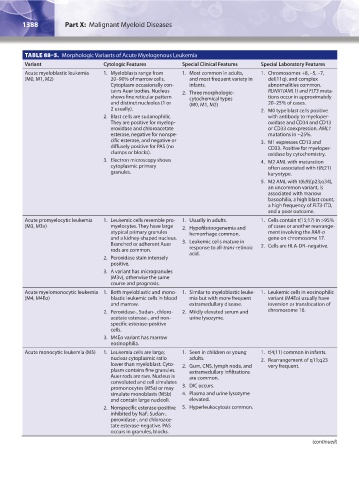
TABLE 88–5. Morphologic Variants of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
Variant Cytologic Features Special Clinical Features Special Laboratory Features
Acute myeloblastic leukemia 1. Myeloblasts range from 1. Most common in adults, 1. Chromosomes +8, –5, –7,
(M0, M1, M2) 20–90% of marrow cells. and most frequent variety in del(11q), and complex
Cytoplasm occasionally con- infants. abnormalities common.
tains Auer bodies. Nucleus 2. Three morphologic- RUNX1(AML1) and FLT3 muta-
shows fine reticular pattern cytochemical types tions occur in approximately
and distinct nucleolus (1 or (M0, M1, M2) 20–25% of cases.
2 usually). 2. M0 type blast cells positive
2. Blast cells are sudanophilic. with antibody to myeloper-
They are positive for myelop- oxidase and CD34 and CD13
eroxidase and chloroacetate or CD33 coexpression. AML1
esterase, negative for nonspe- mutations in ~25%.
cific esterase, and negative or 3. M1 expresses CD13 and
diffusely positive for PAS (no CD33. Positive for myeloper-
clumps or blocks). oxidase by cytochemistry.
3. Electron microscopy shows 4. M2 AML with maturation
cytoplasmic primary often associated with t(8;21)
granules. karyotype.
5. M2 AML with t(6;9)(p23;q34),
an uncommon variant, is
associated with marrow
basophilia, a high blast count,
a high frequency of FLT3-ITD,
and a poor outcome.
Acute promyelocytic leukemia 1. Leukemic cells resemble pro- 1. Usually in adults. 1. Cells contain t(15;17) in >95%
(M3, M3v) myelocytes. They have large 2. Hypofibrinogenemia and of cases or another rearrange-
atypical primary granules hemorrhage common. ment involving the RAR-α
and a kidney-shaped nucleus. gene on chromosome 17.
Branched or adherent Auer 3. Leukemic cells mature in 2. Cells are HLA-DR–negative.
rods are common. response to all-trans-retinoic
acid.
2. Peroxidase stain intensely
positive.
3. A variant has microgranules
(M3v), otherwise the same
course and prognosis.
Acute myelomonocytic leukemia 1. Both myeloblastic and mono- 1. Similar to myeloblastic leuke- 1. Leukemic cells in eosinophilic
(M4, M4Eo) blastic leukemic cells in blood mia but with more frequent variant (M4Eo) usually have
and marrow. extramedullary disease. inversion or translocation of
2. Peroxidase-, Sudan-, chloro- 2. Mildly elevated serum and chromosome 16.
acetate esterase-, and non- urine lysozyme.
specific esterase-positive
cells.
3. M4Eo variant has marrow
eosinophilia.
Acute monocytic leukemia (M5) 1. Leukemia cells are large; 1. Seen in children or young 1. t(4;11) common in infants.
nuclear cytoplasmic ratio adults. 2. Rearrangement of q11;q23
lower than myeloblast. Cyto- 2. Gum, CNS, lymph node, and very frequent.
plasm contains fine granules. extramedullary infiltrations
Auer rods are rare. Nucleus is are common.
convoluted and cell simulates
promonocytes (M5a) or may 3. DIC occurs.
simulate monoblasts (M5b) 4. Plasma and urine lysozyme
and contain large nucleoli. elevated.
2. Nonspecific esterase-positive 5. Hyperleukocytosis common.
inhibited by NaF; Sudan-,
peroxidase-, and chloroace-
tate esterase-negative. PAS
occurs in granules, blocks.
(continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 88_p1373-1436.indd 1388 9/21/15 11:01 AM