Page 1414 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1414
1388 Part X: Malignant Myeloid Diseases Chapter 88: Acute Myelogenous Leukemia 1389
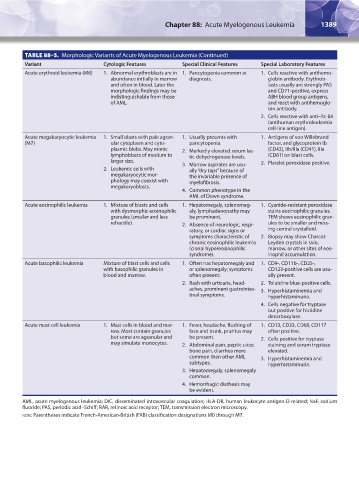
TABLE 88–5. Morphologic Variants of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (Continued)
Variant Cytologic Features Special Clinical Features Special Laboratory Features
Acute erythroid leukemia (M6) 1. Abnormal erythroblasts are in 1. Pancytopenia common at 1. Cells reactive with antihemo-
abundance initially in marrow diagnosis. globin antibody. Erythrob-
and often in blood. Later the lasts usually are strongly PAS
morphologic findings may be and CD71-positive, express
indistinguishable from those ABH blood group antigens,
of AML. and react with antihemoglo-
bin antibody.
2. Cells reactive with anti–Rc-84
(antihuman erythroleukemia
cell-line antigen).
Acute megakaryocytic leukemia 1. Small blasts with pale agran- 1. Usually presents with 1. Antigens of von Willebrand
(M7) ular cytoplasm and cyto- pancytopenia. factor, and glycoprotein Ib
plasmic blebs. May mimic 2. Markedly elevated serum lac- (CD42), IIb/IIIa (CD41), IIIa
lymphoblasts of medium to tic dehydrogenase levels. (CD61) on blast cells.
larger size. 3. Marrow aspirates are usu- 2. Platelet peroxidase positive.
2. Leukemic cells with ally “dry taps” because of
megakaryocytic mor- the invariable presence of
phology may coexist with myelofibrosis.
megakaryoblasts.
4. Common phenotype in the
AML of Down syndrome.
Acute eosinophilic leukemia 1. Mixture of blasts and cells 1. Hepatomegaly, splenomeg- 1. Cyanide-resistant peroxidase
with dysmorphic eosinophilic aly, lymphadenopathy may stains eosinophilic granules.
granules (smaller and less be prominent. TEM shows eosinophilic gran-
refractile). 2. Absence of neurologic, respi- ules to be smaller and miss-
ratory, or cardiac signs or ing central crystalloid.
symptoms characteristic of 2. Biopsy may show Charcot-
chronic eosinophilic leukemia Leyden crystals in skin,
(clonal hypereosinophilic marrow, or other sites of eos-
syndrome). inophil accumulation.
Acute basophilic leukemia Mixture of blast cells and cells 1. Often has hepatomegaly and 1. CD9-, CD11b-, CD25-,
with basophilic granules in or splenomegaly; symptoms CD123-positive cells are usu-
blood and marrow. often present. ally present.
2. Rash with urticaria, head- 2. Toluidine blue-positive cells.
aches, prominent gastrointes- 3. Hyperhistaminemia and
tinal symptoms. hyperhistaminuria.
4. Cells negative for tryptase
but positive for histidine
decarboxylase.
Acute mast cell leukemia 1. Mast cells in blood and mar- 1. Fever, headache, flushing of 1. CD13, CD33, CD68, CD117
row. Most contain granules face and trunk, pruritus may often positive.
but some are agranular and be present. 2. Cells positive for tryptase
may simulate monocytes. 2. Abdominal pain, peptic ulcer, staining and serum tryptase
bone pain, diarrhea more elevated.
common than other AML 3. Hyperhistaminemia and
subtypes. hyperhistaminuria.
3. Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly
common.
4. Hemorrhagic diathesis may
be evident.
AML, acute myelogenous leukemia; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; HLA-DR, human leukocyte antigen-D related; NaF, sodium
fluoride; PAS, periodic acid–Schiff; RAR, retinoic acid receptor; TEM, transmission electron microscopy.
note: Parentheses indicate French-American-British (FAB) classification designations M0 through M7.
Kaushansky_chapter 88_p1373-1436.indd 1389 9/21/15 11:01 AM