Page 1544 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1544
1518 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 91: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia 1519
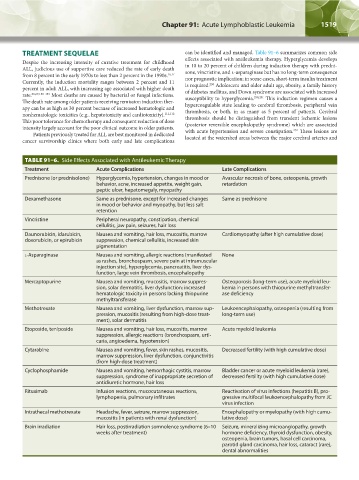
TREATMENT SEQUELAE can be identified and managed. Table 91–6 summarizes common side
Despite the increasing intensity of curative treatment for childhood effects associated with antileukemia therapy. Hyperglycemia develops
ALL, judicious use of supportive care reduced the rate of early death in 10 to 20 percent of children during induction therapy with predni-
from 8 percent in the early 1970s to less than 2 percent in the 1990s. 16,17 sone, vincristine, and l-asparaginase but has no long-term consequence
Currently, the induction mortality ranges between 2 percent and 11 nor prognostic implication; in some cases, short-term insulin treatment
250
percent in adult ALL, with increasing age associated with higher death is required. Adolescent and older adult age, obesity, a family history
rate. 66,67,150–153 Most deaths are caused by bacterial or fungal infections. of diabetes mellitus, and Down syndrome are associated with increased
250,251
The death rate among older patients receiving remission induction ther- susceptibility to hyperglycemia. This induction regimen causes a
apy can be as high as 30 percent because of increased hematologic and hypercoagulable state leading to cerebral thrombosis, peripheral vein
nonhematologic toxicities (e.g., hepatotoxicity and cardiotoxicity). 111,112 thrombosis, or both, in as many as 5 percent of patients. Cerebral
This poor tolerance for chemotherapy and consequent reduction of dose thrombosis should be distinguished from transient ischemic lesions
intensity largely account for the poor clinical outcome in older patients. (posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome) which are associated
252
Patients previously treated for ALL are best monitored in dedicated with acute hypertension and severe constipation. These lesions are
cancer survivorship clinics where both early and late complications located at the watershed areas between the major cerebral arteries and
TABLE 91–6. Side Effects Associated with Antileukemic Therapy
Treatment Acute Complications Late Complications
Prednisone (or prednisolone) Hyperglycemia, hypertension, changes in mood or Avascular necrosis of bone, osteopenia, growth
behavior, acne, increased appetite, weight gain, retardation
peptic ulcer, hepatomegaly, myopathy
Dexamethasone Same as prednisone, except for increased changes Same as prednisone
in mood or behavior and myopathy, but less salt
retention
Vincristine Peripheral neuropathy, constipation, chemical
cellulitis, jaw pain, seizures, hair loss
Daunorubicin, idarubicin, Nausea and vomiting, hair loss, mucositis, marrow Cardiomyopathy (after high cumulative dose)
doxorubicin, or epirubicin suppression, chemical cellulitis, increased skin
pigmentation
l-Asparaginase Nausea and vomiting, allergic reactions (manifested None
as rashes, bronchospasm, severe pain at intramuscular
injection site), hyperglycemia, pancreatitis, liver dys-
function, large vein thrombosis, encephalopathy
Mercaptopurine Nausea and vomiting, mucositis, marrow suppres- Osteoporosis (long-term use), acute myeloid leu-
sion, solar dermatitis, liver dysfunction: increased kemia in persons with thiopurine methyltransfer-
hematologic toxicity in persons lacking thiopurine ase deficiency
methyltransferase
Methotrexate Nausea and vomiting, liver dysfunction, marrow sup- Leukoencephalopathy, osteopenia (resulting from
pression, mucositis (resulting from high-dose treat- long-term use)
ment), solar dermatitis
Etoposide, teniposide Nausea and vomiting, hair loss, mucositis, marrow Acute myeloid leukemia
suppression, allergic reactions (bronchospasm, urti-
caria, angioedema, hypotension)
Cytarabine Nausea and vomiting, fever, skin rashes, mucositis, Decreased fertility (with high cumulative dose)
marrow suppression, liver dysfunction, conjunctivitis
(from high-dose treatment)
Cyclophosphamide Nausea and vomiting, hemorrhagic cystitis, marrow Bladder cancer or acute myeloid leukemia (rare),
suppression, syndrome of inappropriate secretion of decreased fertility (with high cumulative dose)
antidiuretic hormone, hair loss
Rituximab Infusion reactions, mucocutaneous reactions, Reactivation of virus infections (hepatitis B), pro-
lymphopenia, pulmonary infiltrates gressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy from JC
virus infection
Intrathecal methotrexate Headache, fever, seizure, marrow suppression, Encephalopathy or myelopathy (with high cumu-
mucositis (in patients with renal dysfunction) lative dose)
Brain irradiation Hair loss, postirradiation somnolence syndrome (6–10 Seizure, mineralizing microangiopathy, growth
weeks after treatment) hormone deficiency, thyroid dysfunction, obesity,
osteopenia, brain tumors, basal cell carcinoma,
parotid gland carcinoma, hair loss, cataract (rare),
dental abnormalities
Kaushansky_chapter 91_p1505-1526.indd 1519 9/21/15 12:20 PM