Page 1659 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1659
1634 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 98: Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Related Diseases 1635
LYMPHOMA DURING PREGNANCY
100
Lymphoma is the fourth most frequent malignancy diagnosed during
pregnancy, occurring in approximately 1 in 6000 deliveries. Reports
110
of therapeutic interventions in pregnant patients with lymphoma are
limited, and management recommendations are largely based on small
75 retrospective studies and case reports. Both radiation therapy and che-
Germinal center motherapy during pregnancy are potentially teratogenic. Fetal exposure
B cell to antineoplastic agents may result in impaired growth, diminished
Survival, percent 50 ductive function, mutagenesis of germline tissue, and carcinogenesis.
neurologic and/or intellectual function, decreased gonadal and repro-
111
The risks of treatment to the fetus are greatest during the first trimester
and therapeutic abortion is a consideration under these circumstances.
CHOP during the second and third trimesters may be administered rel-
atively safely with little risk of significant adverse fetal outcomes. 112,113
The prognosis of patients who receive optimal chemotherapy is similar
Activated 114
25 B cell to that of nonpregnant patients.
Only a few cases of rituximab administration during pregnancy
have been reported, most of them for the treatment of nonmalignant
disorders such as autoimmune diseases. Patients with supradiaphrag-
P = 0.01 matic stage I disease may be considered for localized radiotherapy as
0 a temporary measure until the second trimester, when chemotherapy
115
0 4 8 12 holds less risk for the fetus. Patients in the second or third trimester
Years should be treated with full-dose chemotherapy.
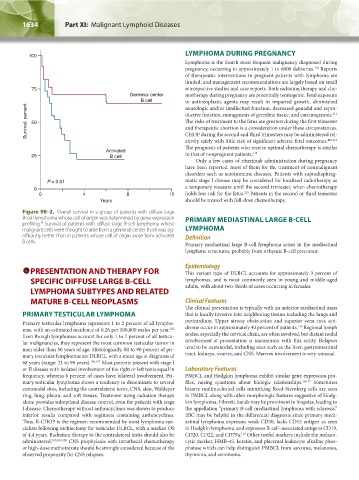
Figure 98–2. Overall survival in a group of patients with diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma whose cell of origin was determined by gene-expression PRIMARY MEDIASTINAL LARGE B-CELL
14
profiling. Survival of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma whose
malignant cells were thought to arise from a germinal center B cell was sig- LYMPHOMA
nificantly better than in patients whose cell of origin arose from activated Definition
B cells. Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma arises in the mediastinal
lymphatic structures, probably from a thymic B-cell precursor.
PRESENTATION AND THERAPY FOR Epidemiology
This variant type of DLBCL accounts for approximately 3 percent of
SPECIFIC DIFFUSE LARGE B-CELL lymphomas, and is most commonly seen in young and middle-aged
LYMPHOMA SUBTYPES AND RELATED adults, with about two-thirds of cases occurring in females.
MATURE B-CELL NEOPLASMS Clinical Features
The clinical presentation is typically with an anterior mediastinal mass
PRIMARY TESTICULAR LYMPHOMA that is locally invasive into neighboring tissues including the lungs and
Primary testicular lymphoma represents 1 to 2 percent of all lympho- pericardium. Upper airway obstruction and superior vena cava syn-
116
105
mas, with an estimated incidence of 0.26 per 100,000 males per year. drome occur in approximately 40 percent of patients. Regional lymph
Even though lymphomas account for only 1 to 7 percent of all testicu- nodes, especially the cervical chain, are often involved, but distant nodal
lar malignancies, they represent the most common testicular tumor in involvement at presentation is uncommon with this entity. Relapses
men older than 50 years of age. Histologically, 80 to 90 percent of pri- tend to be extranodal, including sites such as the liver, gastrointestinal
mary testicular lymphomas are DLBCL, with a mean age at diagnosis of tract, kidneys, ovaries, and CNS. Marrow involvement is very unusual.
68 years (range: 21 to 98 years). 106,107 Most patients present with stage I
or II disease with isolated involvement of the right or left testis equal in Laboratory Features
frequency, whereas 6 percent of cases have bilateral involvement. Pri- PMBCL and Hodgkin lymphoma exhibit similar gene-expression pro-
mary testicular lymphoma shows a tendency to disseminate to several files, raising questions about biologic relationships. 16,117 Sometimes
extranodal sites, including the contralateral testis, CNS, skin, Waldeyer bizarre multinucleated cells mimicking Reed-Sternberg cells are seen
ring, lung, pleura, and soft tissues. Treatment using radiation therapy in PMBCL along with other morphologic features suggestive of Hodg-
alone provides suboptimal disease control, even for patients with stage kin lymphoma. Fibrotic bands may be prominent in biopsies, leading to
I disease. Chemotherapy without anthracyclines was shown to produce the appellation “primary B-cell mediastinal lymphoma with sclerosis.”
inferior results compared with regimens containing anthracyclines. IHC may be helpful in the differential diagnosis since primary medi-
Thus, R-CHOP is the regimen recommended by most lymphoma spe- astinal lymphoma expresses weak CD30, lacks CD15 antigen as seen
cialists following orchiectomy for testicular DLBCL, with a median OS in Hodgkin lymphoma, and expresses B-cell–associated antigens CD19,
118
of 4.4 years. Radiation therapy to the contralateral testis should also be CD20, CD22, and CD79a. Other useful markers include the melano-
administered. 105,108,109 CNS prophylaxis with intrathecal chemotherapy cytic marker, HMB-45, keratin, and placental leukocyte alkaline phos-
or high-dose methotrexate should be strongly considered because of the phatase which can help distinguish PMBCL from sarcoma, melanoma,
observed propensity for CNS relapses. thymoma, and seminoma.
Kaushansky_chapter 98_p1625-1640.indd 1634 9/18/15 11:42 PM