Page 1905 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1905
1880 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 112: Platelet Morphology, Biochemistry, and Function 1881
Pro-
MMP-1 MMP-1 PAR-1
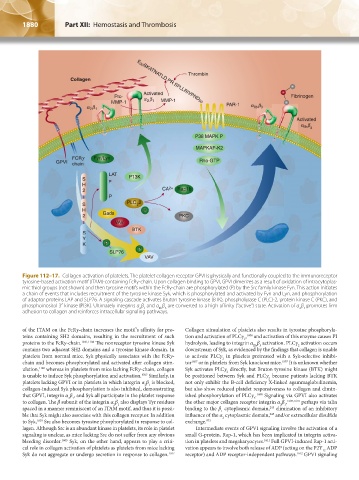
Figure 112–17. Collagen activation of platelets. The platelet collagen receptor GPVI is physically and functionally coupled to the immunoreceptor
tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)-containing FcRγ-chain. Upon collagen binding to GPVI, GPVI dimerizes as a result of oxidation of intracytoplas-
mic thiol groups (not shown) and then tyrosine motifs within the FcRγ-chain are phosphorylated (P) by the Src family kinase Fyn. This action initiates
a chain of events that includes recruitment of the tyrosine kinase Syk, which is phosphorylated and activated by Fyn and Lyn, and phosphorylation
of adaptor proteins LAP and SLP76. A signaling cascade activates Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK), phospholipase C (PLC)-2, protein kinase C (PKC), and
phosphoinositol 3′-kinase (PI3K). Ultimately integrins α β and α β are converted to a high-affinity (“active”) state. Activation of α β promotes firm
2 1
2 1
IIb 3
adhesion to collagen and reinforces intracellular signaling pathways.
of the ITAM on the FcRγ-chain increases the motif’s affinity for pro- Collagen stimulation of platelets also results in tyrosine phosphoryla-
teins containing SH2 domains, resulting in the recruitment of such tion and activation of PLCγ , 2 1606 and activation of this enzyme causes PI
proteins to the FcRγ-chain. 1041,1104 The nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Syk hydrolysis, leading to integrin α β activation. PLCγ activation occurs
IIb 3
2
contains two adjacent SH2 domains and a tyrosine kinase domain. In downstream of Syk, as evidenced by the findings that collagen is unable
platelets from normal mice, Syk physically associates with the FcRγ- to activate PLCγ in platelets pretreated with a Syk-selective inhibi-
2
chain and becomes phosphorylated and activated after collagen stim- tor 1607 or in platelets from Syk knockout mice. 1597 It is unknown whether
ulation, 1180 whereas in platelets from mice lacking FcRγ-chain, collagen Syk activates PLCγ directly, but Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) might
2
is unable to induce Syk phosphorylation and activation. 1597 Similarly, in be positioned between Syk and PLCγ because patients lacking BTK
2
platelets lacking GPVI or in platelets in which integrin α β is blocked, not only exhibit the B-cell deficiency X-linked agammaglobulinemia,
2 1
collagen-induced Syk phosphorylation is also inhibited, demonstrating but also show reduced platelet responsiveness to collagen and dimin-
that GPVI, integrin α β , and Syk all participate in the platelet response ished phosphorylation of PLCγ . 1608 Signaling via GPVI also activates
2
2 1
to collagen. The β subunit of the integrin α β also displays Tyr residues the other major collagen receptor integrin α β , 1609,1610 perhaps via talin
2 1
2 1
spaced in a manner reminiscent of an ITAM motif, and thus it is possi- binding to the β cytoplasmic domain, elimination of an inhibitory
245
1
245
ble that Syk might also associate with this collagen receptor. In addition influence of the α cytoplasmic domain, and/or extracellular disulfide
2
to Syk, 1603 Src also becomes tyrosine phosphorylated in response to col- exchange. 973
lagen. Although Src is an abundant kinase in platelets, its role in platelet Intermediate events of GPVI signaling involve the activation of a
signaling is unclear, as mice lacking Src do not suffer from any obvious small G-protein, Rap-1, which has been implicated in integrin activa-
bleeding disorder. 1605 Syk, on the other hand, appears to play a criti- tion in platelets and megakaryocytes. 1611 Full GPVI-induced Rap-1 acti-
cal role in collagen activation of platelets as platelets from mice lacking vation appears to involve both release of ADP (acting on the P2Y ADP
12
Syk do not aggregate or undergo secretion in response to collagen. 1597 receptor) and ADP receptor-independent pathways. 1612 GPVI signaling
Kaushansky_chapter 112_p1829-1914.indd 1880 17/09/15 3:30 pm