Page 2161 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 2161
2136 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 124: Inherited Deficiencies of Coagulation Factors II, V, V+VIII, VII, X, XI, and XIII 2137
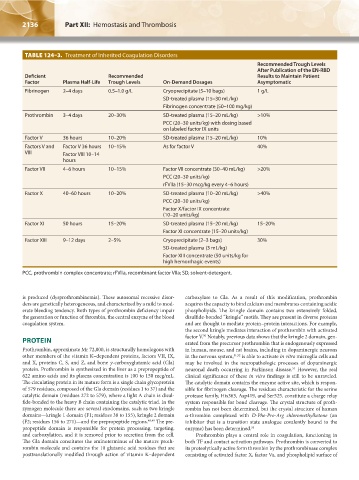
TABLE 124–3. Treatment of Inherited Coagulation Disorders
Recommended Trough Levels
After Publication of the EN-RBD
Deficient Recommended Results to Maintain Patient
Factor Plasma Half-Life Trough Levels On-Demand Dosages Asymptomatic
Fibrinogen 2–4 days 0.5–1.0 g/L Cryoprecipitate (5–10 bags) 1 g/L
SD-treated plasma (15–30 mL/kg)
Fibrinogen concentrate (50–100 mg/kg)
Prothrombin 3–4 days 20–30% SD-treated plasma (15–20 mL/kg) >10%
PCC (20–30 units/kg) with dosing based
on labeled factor IX units
Factor V 36 hours 10–20% SD-treated plasma (15–20 mL/kg) 10%
Factors V and Factor V 36 hours 10–15% As for factor V 40%
VIII Factor VIII 10–14
hours
Factor VII 4–6 hours 10–15% Factor VII concentrate (30–40 mL/kg) >20%
PCC (20–30 units/kg)
rFVIIa (15–30 mcg/kg every 4–6 hours)
Factor X 40–60 hours 10–20% SD-treated plasma (10–20 mL/kg) >40%
PCC (20–30 units/kg)
Factor X/factor IX concentrate
(10–20 units/kg)
Factor XI 50 hours 15–20% SD-treated plasma (15–20 mL/kg) 15–20%
Factor XI concentrate (15–20 units/kg)
Factor XIII 9–12 days 2–5% Cryoprecipitate (2–3 bags) 30%
SD-treated plasma (3 mL/kg)
Factor XIII concentrate (50 units/kg for
high hemorrhagic events)
PCC, prothrombin complex concentrate; rFVIIa, recombinant factor VIIa; SD, solvent-detergent.
is produced (dysprothrombinemia). These autosomal recessive disor- carboxylase to Gla. As a result of this modification, prothrombin
ders are genetically heterogeneous, and characterized by a mild to mod- acquires the capacity to bind calcium and membranes containing acidic
erate bleeding tendency. Both types of prothrombin deficiency impair phospholipids. The kringle domain contains two extensively folded,
the generation or function of thrombin, the central enzyme of the blood disulfide-bonded “kringle” motifs. They are present in diverse proteins
coagulation system. and are thought to mediate protein–protein interactions. For example,
the second kringle mediates interaction of prothrombin with activated
factor V. Notably, previous data shows that the kringle 2 domain, gen-
50
PROTEIN erated from the precursor prothrombin that is endogenously expressed
Prothrombin, approximate Mr 72,000, is structurally homologous with in human, mouse, and rat brains, including in dopaminergic neurons
other members of the vitamin K–dependent proteins, factors VII, IX, in the nervous system, 51,52 is able to activate in vitro microglia cells and
and X, proteins C, S, and Z, and bone γ-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) may be involved in the neuropathologic processes of dopaminergic
protein. Prothrombin is synthesized in the liver as a prepropeptide of neuronal death occurring in Parkinson disease. However, the real
52
622 amino acids and its plasma concentration is 100 to 150 mcg/mL. clinical significance of these in vitro findings is still to be unraveled.
The circulating protein in its mature form is a single chain glycoprotein The catalytic domain contains the enzyme active site, which is respon-
of 579 residues, composed of the Gla domain (residues 1 to 37) and the sible for fibrinogen cleavage. The residues characteristic for the serine
catalytic domain (residues 272 to 579), where a light A chain is disul- protease family, His363, Asp419, and Ser525, constitute a charge relay
fide-bonded to the heavy B chain containing the catalytic triad. In the system responsible for bond cleavage. The crystal structure of proth-
zymogen molecule there are several exodomains, such as two kringle rombin has not been determined, but the crystal structure of human
domains—kringle 1 domain (F1; residues 38 to 155), kringle 2 domain α-thrombin complexed with D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone (an
(F2; residues 156 to 271)—and the prepropeptide regions. 48,49 The pre- inhibitor that is a transition state analogue covalently bound to the
propeptide domain is responsible for protein processing, targeting, enzyme) has been determined. 53
and carboxylation, and it is removed prior to secretion from the cell. Prothrombin plays a central role in coagulation, functioning in
The Gla domain constitutes the aminoterminus of the mature proth- both TF and contact activation pathways. Prothrombin is converted to
rombin molecule and contains the 10 glutamic acid residues that are its proteolytically active form thrombin by the prothrombinase complex
posttranslationally modified through action of vitamin K–dependent consisting of activated factor X, factor Va, and phospholipid surface of
Kaushansky_chapter 124_p2133-2150.indd 2136 17/09/15 3:40 pm