Page 2390 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 2390
2360 Part XIII: Transfusion Medicine Chapter 137: Human Leukocyte and Platelet Antigens 2361
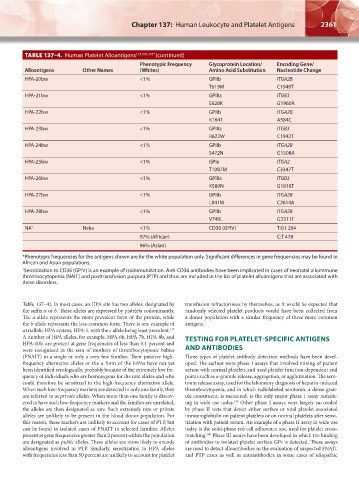
TABLE 137–4. Human Platelet Alloantigens 127,136,163* (continued)
Phenotypic Frequency Glycoprotein Location/ Encoding Gene/
Alloantigens Other Names (Whites) Amino Acid Substitution Nucleotide Change
HPA-20bw <1% GPIIb ITGA2B
T619M C1949T
HPA-21bw <1% GPIIIa ITGB3
E628K G1960A
HPA-22bw <1% GPIIb ITGA2B
K164T A584C
HPA-23bw <1% GPIIIa ITGB3
R622W C1942T
HPA-24bw <1% GPIIb ITGA2B
S472N G1508A
HPA-25bw <1% GPIa ITGA2
T1087M C3347T
HPA-26bw <1% GPIIIa ITGB3
K580N G1818T
HPA-27bw <1% GPIIb ITGA2B
L841M C2614A
HPA-28bw <1% GPIIb ITGA2B
V740L G2311T
NA † Naka <1% CD36 (GPIV) T:G1 264
97% (African) C:T 478
96% (Asian)
*Phenotypic frequencies for the antigens shown are for the white population only. Significant differences in gene frequencies may be found in
African and Asian populations.
† Sensitization to CD36 (GPIV) is an example of isoimmunization. Anti-CD36 antibodies have been implicated in cases of neonatal alloimmune
thrombocytopenia (NAIT) and posttransfusion purpura (PTP) and thus are included in the list of platelet alloantigens that are associated with
these disorders.
Table 137–4). In most cases, an HPA site has two alleles, designated by transfusion refractoriness by themselves, as it would be expected that
the suffix a or b. These alleles are expressed by platelets codominantly. randomly selected platelet products would have been collected from
The a allele represents the more prevalent form of the protein, while a donor population with a similar frequency of these more common
the b allele represents the less-common form. There is one example of antigens.
a triallelic HPA system, HPA-1, with the c allele being least prevalent.
137
A number of HPA alleles, for example, HPA-6b, HPA-7b, HPA-8b, and TESTING FOR PLATELET-SPECIFIC ANTIGENS
HPA-10b, are present at gene frequencies of less than 0.1 percent and
were recognized in the sera of mothers of thrombocytopenic babies AND ANTIBODIES
(FNAIT) in a single or only a very few families. Their putative high- Three types of platelet antibody detection methods have been devel-
frequency alternative alleles or the a form of the HPAs have not yet oped. The earliest were phase I assays that involved mixing of patient
been identified serologically, probably because of the extremely low fre- serum with normal platelets and used platelet function-dependent end
quency of individuals who are homozygous for the rare alleles and who points such as α-granule release, aggregation, or agglutination. The sero-
could therefore be sensitized to the high-frequency alternative allele. tonin release assay, used for the laboratory diagnosis of heparin-induced
When such low-frequency markers are detected in only one family, they thrombocytopenia, and in which radiolabeled serotonin, a dense-gran-
are referred to as private alleles. When more than one family is discov- ule constituent, is measured, is the only major phase I assay remain-
ered to have such low-frequency markers and the families are unrelated, ing in wide use today. Other phase I assays were largely succeeded
139
the alleles are then designated as rare. Such extremely rare or private by phase II tests that detect either surface or total platelet-associated
alleles are unlikely to be present in the blood donor population. For immunoglobulin on patient platelets or on normal platelets after sensi-
this reason, these markers are unlikely to account for cases of PTP, but tization with patient serum. An example of a phase II assay in wide use
can be found in isolated cases of FNAIT in selected families. Alleles today is the solid-phase red cell adherence test, used for platelet cross-
present at gene frequencies greater than 2 percent within the population matching. Phase III assays have been developed in which the binding
140
are designated as public alleles. These alleles are more likely to encode of antibodies to isolated platelet surface GPs is detected. These assays
alloantigens involved in PTP. Similarly, sensitization to HPA alleles are used to detect alloantibodies in the evaluation of suspected FNAIT
with frequencies less than 50 percent are unlikely to account for platelet and PTP cases as well as autoantibodies in some cases of idiopathic
Kaushansky_chapter 137_p2353-2364.indd 2361 9/21/15 3:50 PM