Page 379 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 379
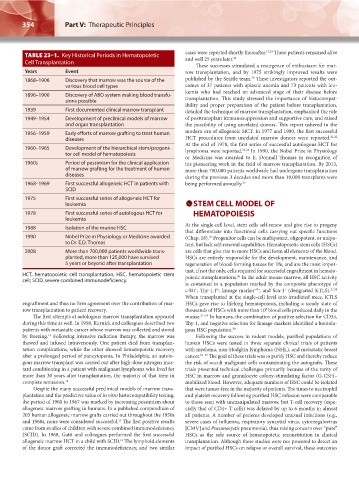
354 Part V: Therapeutic Principles Chapter 23: Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation 355
TABLE 23–1. Key Historical Periods in Hematopoietic cases were reported shortly thereafter. 17,18 These patients remained alive
and well 25 years later.
19
Cell Transplantation
These successes stimulated a resurgence of enthusiasm for mar-
Years Event row transplantation, and by 1975 strikingly improved results were
20
1868–1906 Discovery that marrow was the source of the published by the Seattle team. These investigators reported the out-
various blood cell types comes of 37 patients with aplastic anemia and 73 patients with leu-
kemia who had reached an advanced stage of their disease before
1896–1900 Discovery of ABO system making blood transfu-
sions possible transplantation. This study stressed the importance of histocompat-
ibility and proper preparation of the patient before transplantation,
1939 First documented clinical marrow transplant detailed the technique of marrow transplantation, emphasized the role
1949–1954 Development of preclinical models of marrow of posttransplant immunosuppression and supportive care, and raised
and organ transplantation the possibility of using unrelated donors. This report ushered in the
1956–1959 Early efforts of marrow grafting to treat human modern era of allogeneic HCT. In 1977 and 1980, the first successful
diseases HCT procedures from unrelated marrow donors were reported. 21,22
At the end of 1978, the first series of successful autologous HCT for
1960–1965 Development of the hierarchical stem/progeni- lymphoma were reported. 23,24 In 1990, the Nobel Prize in Physiology
tor cell model of hematopoiesis
or Medicine was awarded to E. Donnall Thomas in recognition of
1960s Period of pessimism for the clinical application his pioneering work in the field of marrow transplantation. By 2013,
of marrow grafting for the treatment of human more than 700,000 patients worldwide had undergone transplantation
diseases during the previous 3 decades and more than 19,000 transplants were
1968–1969 First successful allogeneic HCT in patients with being performed annually. 25
SCID
1975 First successful series of allogeneic HCT for
leukemia STEM CELL MODEL OF
1978 First successful series of autologous HCT for HEMATOPOIESIS
leukemia
At the single-cell level, stem cells self-renew and give rise to progeny
1988 Isolation of the murine HSC
that differentiate into functional cells carrying out specific functions
1990 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine awarded (Chap. 18). Progenitor cells can be multipotent, oligopotent, or unipo-
26
to Dr. E.D. Thomas tent, but lack self-renewal capabilities. Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs)
2008 More than 700,000 patients worldwide trans- are cells that give rise to more HSCs and form all elements of the blood.
planted, more than 125,000 have survived HSCs are entirely responsible for the development, maintenance, and
5 years or beyond after transplantation regeneration of blood-forming tissues for life, and are the most impor-
tant, if not the only, cells required for successful engraftment in hemato-
HCT, hematopoietic cell transplantation; HSC, hematopoietic stem poietic transplantations. In the adult mouse marrow, all HSC activity
26
cell; SCID, severe combined immunodeficiency.
is contained in a population marked by the composite phenotype of
lo
–/lo
+
+
c-kit , Thy-1.1 , lineage marker , and Sca-1 (designated KTLS). 27,28
When transplanted at the single-cell level into irradiated mice, KTLS
engraftment and thus no firm agreement over the contribution of mar- HSCs gave rise to lifelong hematopoiesis, including a steady state of
row transplantation to patient recovery. thousands of HSCs with more than 10 blood cells produced daily in the
9
The first attempts at autologous marrow transplantation appeared mouse. 27–29 In humans, the combination of positive selection for CD34,
during this time as well. In 1958, Kurnick and colleagues described two Thy-1, and negative selection for lineage markers identified a homolo-
patients with metastatic cancer whose marrow was collected and stored gous HSC population. 30
by freezing. Following intensive radiation therapy, the marrow was Following the success in rodent models, purified populations of
13
thawed and infused intravenously. One patient died from transplan- human HSCs were tested in three separate clinical trials of patients
tation complications, while the other showed hematopoietic recovery with myeloma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), and metastatic breast
after a prolonged period of pancytopenia. In Philadelphia, an autolo- cancer. 31–33 The goal of these trials was to purify HSC and thereby reduce
gous marrow transplant was carried out after high-dose nitrogen mus- the risk of occult malignant cells contaminating the autografts. These
tard conditioning in a patient with malignant lymphoma who lived for trials presented technical challenges primarily because of the rarity of
more than 30 years after transplantation, the majority of that time in HSC in marrow and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)–
complete remission. 14 mobilized blood. However, adequate numbers of HSC could be isolated
Despite the many successful preclinical models of marrow trans- that were tumor-free in the majority of patients. The times to neutrophil
plantation and the predictive value of in vitro histocompatibility testing, and platelet recovery following purified HSC infusion were comparable
the period of 1960 to 1967 was marked by increasing pessimism about to those seen with unmanipulated marrow, but T-cell recovery (espe-
allogeneic marrow grafting in humans. In a published compendium of cially that of CD4+ T cells) was delayed by up to 6 months in almost
203 human allogeneic marrow grafts carried out throughout the 1950s all patients. A number of patients developed unusual infections (e.g.,
and 1960s, none were considered successful. The first positive results severe cases of influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, cytomegalovirus
15
came from studies of children with severe combined immunodeficiency [CMV] and Pneumocystis pneumonia), thus raising concern over “pure”
(SCID). In 1968, Gatti and colleagues performed the first successful HSCs as the sole source of hematopoietic reconstitution in clinical
allogeneic marrow HCT in a child with SCID. The lymphoid elements transplantation. Although these studies were not powered to detect an
16
of the donor graft corrected the immunodeficiency, and two similar impact of purified HSCs on relapse or overall survival, these outcomes
Kaushansky_chapter 23_p0353-0382.indd 354 9/19/15 12:45 AM