Page 429 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 429
404 Part V: Therapeutic Principles Chapter 25: Antithrombotic Therapy 405
lasted for several days. It was demonstrated that acetylation of COX
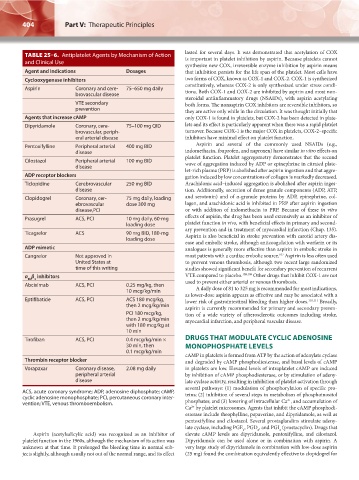
TABLE 25–6. Antiplatelet Agents by Mechanism of Action is important in platelet inhibition by aspirin. Because platelets cannot
and Clinical Use
synthesize new COX, irreversible enzyme inhibition by aspirin means
Agent and Indications Dosages that inhibition persists for the life span of the platelet. Most cells have
Cyclooxygenase inhibitors two forms of COX, known as COX-1 and COX-2. COX-1 is synthesized
Aspirin Coronary and cere- 75–650 mg daily constitutively, whereas COX-2 is only synthesized under stress condi-
tions. Both COX-1 and COX-2 are inhibited by aspirin and most non-
brovascular disease
steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), with aspirin acetylating
VTE secondary both forms. The nonaspirin COX inhibitors are reversible inhibitors, so
prevention they are active only while in the circulation. It was thought initially that
Agents that increase cAMP only COX-1 is found in platelets, but COX-2 has been detected in plate-
Dipyridamole Coronary, cere- 75–100 mg QID lets and its effect is particularly apparent when there was a rapid platelet
brovascular, periph- turnover. Because COX-1 is the major COX in platelets, COX-2–specific
eral arterial disease inhibitors have minimal effect on platelet function.
Pentoxifylline Peripheral arterial 400 mg BID Aspirin and several of the commonly used NSAIDs (e.g.,
disease indomethacin, ibuprofen, and naproxen) have similar in vitro effects on
platelet function. Platelet aggregometry demonstrates that the second
Cilostazol Peripheral arterial 100 mg BID wave of aggregation induced by ADP or epinephrine in citrated plate-
disease
let-rich plasma (PRP) is abolished after aspirin ingestion and that aggre-
ADP receptor blockers gation induced by low concentrations of collagen is markedly decreased.
Ticlopidine Cerebrovascular 250 mg BID Arachidonic acid–induced aggregation is abolished after aspirin inges-
disease tion. Additionally, secretion of dense granule components (ADP, ATP,
Clopidogrel Coronary, cer- 75 mg daily, loading and serotonin) and of α-granule proteins by ADP, epinephrine, col-
ebrovascular dose 300 mg lagen, and arachidonic acid is inhibited in PRP after aspirin ingestion
disease,PCI or with addition of indomethacin to PRP. Because of these in vitro
effects of aspirin, the drug has been used extensively as an inhibitor of
Prasugrel ACS, PCI 10 mg daily, 60-mg
loading dose platelet function in vivo, with beneficial effects in primary and second-
ary prevention and in treatment of myocardial infarction (Chap. 135).
Ticagrelor ACS 90 mg BID, 180-mg Aspirin is also beneficial in stroke prevention with carotid artery dis-
loading dose
ease and embolic stroke, although anticoagulation with warfarin or its
ADP mimetic analogues is generally more effective than aspirin in embolic stroke in
107
Cangrelor Not approved in most patients with a cardiac embolic source. Aspirin is less often used
United States at to prevent venous thrombosis, although two recent large randomized
time of this writing studies showed significant benefit for secondary prevention of recurrent
α β inhibitors VTE compared to placebo. 108,109 Other drugs that inhibit COX-1 are not
IIb 3 used to prevent either arterial or venous thrombosis.
Abciximab ACS, PCI 0.25 mg/kg, then A daily dose of 81 to 325 mg is recommended for most indications,
10 mcg/kg/min
as lower-dose aspirin appears as effective and may be associated with a
Eptifibatide ACS, PCI ACS 180 mcg/kg, lower risk of gastrointestinal bleeding than higher doses. 110,111 Broadly,
then 2 mcg/kg/min aspirin is currently recommended for primary and secondary preven-
PCI 180 mcg/kg, tion of a wide variety of atherosclerotic outcomes including stroke,
then 2 mcg/kg/min myocardial infarction, and peripheral vascular disease.
with 180 mcg/kg at
10 min
Tirofiban ACS, PCI 0.4 mcg/kg/min × DRUGS THAT MODULATE CYCLIC ADENOSINE
30 min, then MONOPHOSPHATE LEVELS
0.1 mcg/kg/min cAMP in platelets is formed from ATP by the action of adenylate cyclase
Thrombin receptor blocker and degraded by cAMP phosphodiesterase, and basal levels of cAMP
Vorapaxar Coronary disease, 2.08 mg daily in platelets are low. Elevated levels of intraplatelet cAMP are induced
peripheral arterial by inhibition of cAMP phosphodiesterase, or by stimulation of adeny-
disease late cyclase activity, resulting in inhibition of platelet activation through
several pathways: (1) modulation of phosphorylation of specific pro-
ACS, acute coronary syndrome; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; cAMP, teins; (2) inhibition of several steps in metabolism of phosphoinositol
cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PCI, percutaneous coronary inter- phosphates; and (3) lowering of intracellular Ca , and accumulation of
2+
vention; VTE, venous thromboembolism.
Ca by platelet microsomes. Agents that inhibit the cAMP phosphodi-
2+
esterase include theophylline, papaverine, and dipyridamole, as well as
pentoxifylline and cilostazol. Several prostaglandins stimulate adeny-
late cyclase, including PGE , PGD , and PGI (prostacyclin). Drugs that
1
2
2
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) was recognized as an inhibitor of elevate cAMP levels are dipyridamole, pentoxifylline, and cilostazol.
platelet function in the 1960s, although the mechanism of its action was Dipyridamole can be used alone or in combination with aspirin. A
unknown at that time. It prolonged the bleeding time in normal sub- very large study of dipyridamole in combination with low-dose aspirin
jects slightly, although usually not out of the normal range, and its effect (25 mg) found the combination equivalently effective to clopidogrel for
Kaushansky_chapter 25_p0393-0408.indd 404 9/19/15 12:20 AM