Page 473 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 473
448 Part V: Therapeutic Principles Chapter 30: Regenerative Medicine: Multipotential Cell Therapy for Tissue Repair 449
Genome Systems
• Gene correction biology
• Gene addition
• Epigenetic modification
Cell
Genome
Regenerative Cell
Synthetic medicine • Quality of cells for specific task
biology • Quantity of cells for specific task
• Cell–cell interactions (3D tissues)
• Cells engineered to:
– Migrate to specific tissue
– Destroy cells (cancer)
Patient – Deliver therapeutics
• Transplant biology Patient • Cell banks
– Autologous
– Allogeneic
• Mode of delivery Personal
• Conditioning genomics
– Host
– Graft
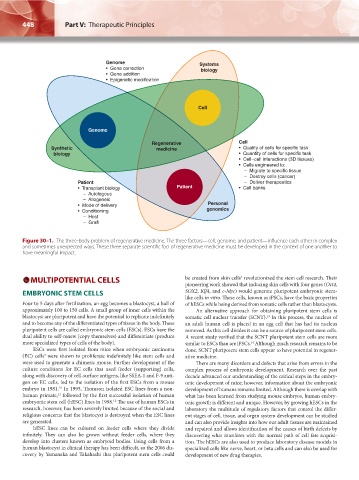
Figure 30–1. The three-body problem of regenerative medicine. The three factors—cell, genome, and patient—influence each other in complex
and sometimes unexpected ways. These three separate scientific foci of regenerative medicine must be developed in the context of one another to
have meaningful impact.
MULTIPOTENTIAL CELLS be created from skin cells revolutionized the stem cell research. Their
6
pioneering work showed that inducing skin cells with four genes (Oct4,
EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS SOX2, Klf4, and c-Myc) would generate pluripotent embryonic stem-
like cells in vitro. These cells, known as iPSCs, have the basic properties
Four to 5 days after fertilization, an egg becomes a blastocyst, a ball of of hESCs while being derived from somatic cells rather than blastocysts.
approximately 100 to 150 cells. A small group of inner cells within the An alternative approach for obtaining pluripotent stem cells is
blastocyst are pluripotent and have the potential to replicate indefinitely somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT). In this process, the nucleus of
13
and to become any of the differentiated types of tissue in the body. These an adult human cell is placed in an egg cell that has had its nucleus
pluripotent cells are called embryonic stem cells (ESCs). ESCs have the removed. As this cell divides it can be a source of pluripotent stem cells.
dual ability to self-renew (copy themselves) and differentiate (produce A recent study verified that the SCNT pluripotent stem cells are more
more specialized types of cells of the body). similar to ESCs than are iPSCs. Although much research remains to be
14
ESCs were first isolated from mice when embryonic carcinoma done, SCNT pluripotent stem cells appear to have potential in regener-
(EC) cells were shown to proliferate indefinitely like stem cells and ative medicine.
9
were used to generate a chimeric mouse. Further development of the There are many disorders and defects that arise from errors in the
culture conditions for EC cells that used feeder (supporting) cells, complex process of embryonic development. Research over the past
along with discovery of cell-surface antigens, like SSEA-1 and F-9 anti- decade advanced our understanding of the critical steps in the embry-
gen on EC cells, led to the isolation of the first ESCs from a mouse onic development of mice; however, information about the embryonic
embryo in 1981. In 1995, Thomson isolated ESC lines from a non- development of humans remains limited. Although there is overlap with
10
human primate, followed by the first successful isolation of human what has been learned from studying mouse embryos, human embry-
11
embryonic stem cell (hESC) lines in 1998. The use of human ESCs in onic growth is different and unique. However, by growing hESCs in the
12
research, however, has been severely limited because of the social and laboratory the multitude of regulatory factors that control the differ-
religious concerns that the blastocyst is destroyed when the ESC lines ent stages of cell, tissue, and organ system development can be studied
are generated. and can also provide insights into how our adult tissues are maintained
hESC lines can be cultured on feeder cells where they divide and repaired and allows identification of the causes of birth defects by
infinitely. They can also be grown without feeder cells, where they discovering what interferes with the normal path of cell fate acquisi-
develop into clusters known as embryoid bodies. Using cells from a tion. The hESCs are also used to produce laboratory disease models in
human blastocyst in clinical therapy has been difficult, so the 2006 dis- specialized cells like nerve, heart, or beta cells and can also be used for
covery by Yamanaka and Takahashi that pluripotent stem cells could development of new drug therapies.
Kaushansky_chapter 30_p0447-0458.indd 448 9/17/15 6:07 PM