Page 626 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 626
600 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 41: Folate, Cobalamin, and Megaloblastic Anemias 601
296
many have varying degrees of decreased cobalamin absorption. Ach-
lorhydria not present before surgery often develops some years after
gastrectomy. Postgastrectomy patients with low serum cobalamin levels
usually have low serum iron levels, in contrast to the high iron levels
297
otherwise typical of cobalamin deficiency.
Cobalamin deficiency after partial gastrectomy can be caused
by mucosal atrophy in the unresected remnant of the stomach or,
298
if a gastrojejunostomy was performed, by bacterial overgrowth in the
afferent loop (see “Competing Intestinal Flora and Fauna: ‘Blind Loop
Syndrome’” below). A surgical procedure that has gained popularity
for the treatment of morbid obesity is gastric reduction surgery. This
procedure results in multiple deficiencies of micronutrients including
cobalamin. 299
Of the various causes of cobalamin malabsorption described, those
that most often lead to megaloblastic anemia include PA, total or partial
gastrectomy, intestinal blind loop syndrome, fish tapeworm, ileal resec-
tion, regional enteritis (Crohn disease) and tropical sprue. In addition,
64
several of the inherited disorders affecting cobalamin absorption and
metabolism, such as congenital intrinsic factor deficiency, selective
cobalamin malabsorption and congenital TC deficiency can also result
in megaloblastic anemia.
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome In Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, a
gastrin-producing tumor, usually in the pancreas, stimulates the gastric
mucosa to secrete immense amounts of HCl. The major clinical problem
is a severe ulcer diathesis. Malabsorption of cobalamin occurs when the
vast quantities of HCl secreted by the overactive gastric mucosa cannot
be completely neutralized by the pancreatic secretions. The resulting
acidification of the duodenal contents prevents transfer of Cbl from HC
binder to intrinsic factor and also inactivates pancreatic proteases. 300
Intestinal Diseases Because the terminal ileum is the site for
physiologic cobalamin absorption, a number of intestinal disorders
can lead to cobalamin deficiency, including (1) extensive resection of
the ileum ; (2) inflammatory bowel disease or regional ileitis or other
301
302
disease affecting the ileum (e.g., lymphoma, radiation damage ); (3)
303
Normal Pernicious cobalamin malabsorption associated with hypothyroidism, or certain
305
304
anemia drugs ; (4) the effects of cobalamin deficiency itself ; and (5) sprue,
either tropical or, less often, nontropical. In each of these disorders,
198
administration of exogenous intrinsic factor, as was carried out in the
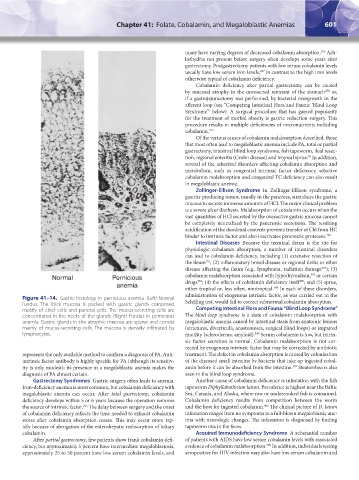
Figure 41–14. Gastric histology in pernicious anemia. (Left) Normal
fundus. The thick mucosa is packed with gastric glands composed Schilling test, would fail to correct subnormal cobalamin absorption.
mostly of chief cells and parietal cells. The mucus-secreting cells are Competing Intestinal Flora and Fauna: “Blind Loop Syndrome”
concentrated in the necks of the glands. (Right) Fundus in pernicious The blind loop syndrome is a state of cobalamin malabsorption with
anemia. Gastric glands in the atrophic mucosa are sparse and consist megaloblastic anemia caused by intestinal stasis from anatomic lesions
mainly of mucus-secreting cells. The mucosa is densely infiltrated by (strictures, diverticula, anastomoses, surgical blind loops) or impaired
lymphocytes. motility (scleroderma, amyloid). Serum cobalamin is low, but intrin-
306
sic factor secretion is normal. Cobalamin malabsorption is not cor-
rected by exogenous intrinsic factor but may be corrected by antibiotic
represents the only available method to confirm a diagnosis of PA. Anti- treatment. The defect in cobalamin absorption is caused by colonization
intrinsic factor antibody is highly specific for PA (although its sensitiv- of the diseased small intestine by bacteria that take up ingested cobal-
ity is only modest); its presence in a megaloblastic anemia makes the amin before it can be absorbed from the intestine. Steatorrhea is also
307
diagnosis of PA almost certain. seen in the blind loop syndrome.
Gastrectomy Syndromes Gastric surgery often leads to anemia. Another cause of cobalamin deficiency is infestation with the fish
Iron-deficiency anemia is most common, but cobalamin deficiency with tapeworm Diphyllobothrium latum. Prevalence is highest near the Baltic
megaloblastic anemia can occur. After total gastrectomy, cobalamin Sea, Canada, and Alaska, where raw or undercooked fish is consumed.
deficiency develops within 5 or 6 years because the operation removes Cobalamin deficiency results from competition between the worm
308
the source of intrinsic factor. The delay between surgery and the onset and the host for ingested cobalamin. The clinical picture of D. latum
295
of cobalamin deficiency reflects the time needed to exhaust cobalamin infestation ranges from no symptoms to a full-blown megaloblastic ane-
stores after cobalamin absorption ceases. This may occur more rap- mia with neurologic changes. The infestation is diagnosed by finding
idly because of abrogation of the enterohepatic reabsorption of biliary tapeworm ova in the feces.
cobalamin. Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome A substantial number
After partial gastrectomy, few patients show frank cobalamin defi- of patients with AIDS have low serum cobalamin levels with associated
309
ciency, but approximately 5 percent have intermediate megaloblastosis, evidence of cobalamin malabsorption. In addition, individuals testing
approximately 25 to 50 percent have low serum cobalamin levels, and seropositive for HIV infection may also have low serum cobalamin and
Kaushansky_chapter 41_p0583-0616.indd 601 9/17/15 6:24 PM