Page 858 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 858
832 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 54: Hemolytic Anemia Resulting from Immune Injury 833
A B
C D
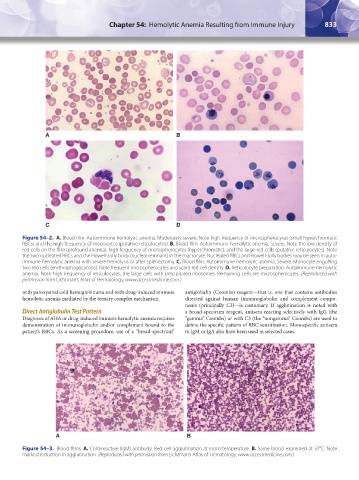
Figure 54–2. A. Blood film. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Moderately severe. Note high frequency of microspherocytes (small hyperchromatic
RBCs) and the high frequency of macrocytes (putative reticulocytes). B. Blood film. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Severe. Note the low density of
red cells on the film (profound anemia), high frequency of microspherocytes (hyperchromatic), and the large red cells (putative reticulocytes). Note
the two nucleated RBCs and the Howell-Jolly body (nuclear remnant) in the macrocyte. Nucleated RBCs and Howell-Jolly bodies may be seen in auto-
immune hemolytic anemia with severe hemolysis or after splenectomy. C. Blood film. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Severe. Monocyte engulfing
two red cells (erythrophagocytosis). Note frequent microspherocytes and scant red cell density. D. Reticulocyte preparation. Autoimmune hemolytic
anemia. Note high frequency of reticulocytes, the large cells with precipitated ribosomes. Remaining cells are microspherocytes. (Reproduced with
permission from Lichtman’s Atlas of Hematology, www.accessmedicine.com.)
with paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria and with drug-induced immune antiglobulin (Coombs) reagent—that is, one that contains antibodies
hemolytic anemia mediated by the ternary complex mechanism. directed against human immunoglobulin and complement compo-
nents (principally C3)—is customary. If agglutination is noted with
Direct Antiglobulin Test Pattern a broad-spectrum reagent, antisera reacting selectively with IgG (the
Diagnosis of AHA or drug-induced immune hemolytic anemia requires “gamma” Coombs) or with C3 (the “nongamma” Coombs) are used to
demonstration of immunoglobulin and/or complement bound to the define the specific pattern of RBC sensitization. Monospecific antisera
patient’s RBCs. As a screening procedure, use of a “broad-spectrum” to IgM or IgA also have been used in selected cases.
A B
Figure 54–3. Blood films. A. Cold-reactive (IgM) antibody. Red cell agglutination at room temperature. B. Same blood examined at 37°C. Note
marked reduction in agglutination. (Reproduced with permission from Lichtman’s Atlas of Hematology, www.accessmedicine.com.)
Kaushansky_chapter 54_p0823-0846.indd 833 9/19/15 12:27 AM