Page 932 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 932
906 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 58: The Porphyrias 907
Iron and HFE Mutations Mild to moderate iron overload is found in cases with the C282Y/C282Y HFE genotype. Fluid-filled vesicles
286
in most patients with PCT, and iron deficiency is protective. The impor- develop most commonly on the backs of the hands (Fig. 58–7A). Skin
tance of iron has been confirmed in animal models, such as rodents friability is increased and blisters often follow minor trauma. These also
treated with hexachlorobenzene and other halogenated polyaromatic occur on the forearms, face, ears, neck, legs, and feet. The blisters often
hydrocarbons. Mice with disruption of one UROD allele (UROD[+/– rupture, crust over, and are prone to infection before healing slowly.
266
]) and two disrupted HFE alleles (HFE[–/–]) develop uroporphyria Milia may precede or follow vesicle formation. Facial hypertrichosis
without administration of exogenous chemicals. Prevalence of the and hyperpigmentation are particularly noticed by female patients (Fig.
261
C282Y mutation of the HFE gene, which is the major cause of hemo- 58–7B). Severe thickening of affected areas of skin is termed pseudoscle-
chromatosis in whites, is increased in both sporadic and familial PCT, roderma and resembles systemic scleroderma.
and 10 to 20 percent of patients may be C282Y homozygotes (Chap. Blistering skin lesions in VP and HCP are identical to those in
43). In southern Europe, where the C282Y is less prevalent, the H63D PCT. Those in CEP and HEP resemble PCT but are usually much more
282
mutation is more commonly associated with PCT. Excess iron may severe and mutilating. Mild or moderate erythrocytosis is common in
283
contribute to UROD inhibition by providing an oxidative environment PCT, and is not well explained. Chronic lung disease from smoking may
that is apparently needed for generation of a UROD inhibitor. Hepatic contribute.
hepcidin expression is reduced in hemochromatosis, and is also reduced Drugs that exacerbate the acute porphyrias are only occasionally
287
in PCT patients without hemochromatosis genotypes when compared reported to play a role in PCT. PCT may occur with other conditions
to patients without PCT and comparable iron overload, suggesting predisposing to iron overload such as myelofibrosis 288,289 and end-stage
270
that reduced expression of this peptide is important in causing hepatic renal disease, and with diabetes mellitus and cutaneous and sys-
290
siderosis in PCT. 274 temic lupus erythematosus. PCT associated with end-stage renal dis-
Antioxidants Substantial reductions in plasma levels of ascorbate ease is usually more severe, sometimes with severe mutilation. Lack
and carotenoids have been noted in some patients with PCT. Ascor- of urinary porphyrin excretion in these patients leads to much higher
263
bate deficiency in rodents enhances susceptibility to development or concentrations of porphyrins in plasma, and the excess porphyrins are
uroporphyria, and ascorbate decreases uroporphyrin accumulation poorly dialyzable. The disease occasionally develops during preg-
290
except in animals treated with large amounts of iron. 262 nancy, perhaps related to effects of estrogen.
A large outbreak of PCT occurred during a period of food short- The clinical manifestations of HEP usually resemble CEP, with
age in a population in eastern Turkey in the 1950s from consumption onset of blistering skin lesions, hypertrichosis, scarring, and red urine
of seed wheat treated with the fungicide hexachlorobenzene. Smaller in infancy or childhood. Sclerodermoid skin changes are sometimes
11
outbreaks and individual cases have occurred after exposures to prominent. Excess porphyrins originate mostly from the liver in this
other chemicals such as 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD, condition. Unusually mild cases have been described. 291
dioxin). These chemicals were subsequently shown to cause hepatic
284
UROD deficiency and biochemical features resembling PCT in labo- Diagnosis
ratory animals, and many studies that followed have greatly increased A diagnosis of PCT is established by finding a substantial elevation of
our understanding of this acquired enzyme deficiency. 266,285 But such porphyrins in urine or plasma, with a predominance of highly carboxylated
exposures are rarely identified in PCT patients in current clinical porphyrins (uroporphyrin and hepta-, hexa-, and pentacarboxyl-
practice. porphyrins); coproporphyrins are also increased. Levels of PBG are
normal, and urinary ALA is normal or slightly increased. The pattern of
Clinical Features porphyrins in feces is complex, and includes heptacarboxylporphyrins
Disease onset is usually in the fourth or fifth decade of life, and is more and isocoproporphyrins. The latter are overproduced in the presence of
common in men. Onset may occur earlier in familial (type 2) disease or UROD deficiency because pentacarboxylporphyrinogen is a substrate
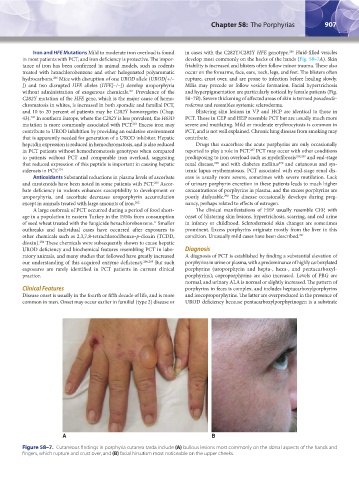
A B
Figure 58–7. Cutaneous findings in porphyria cutanea tarda include (A) bullous lesions most commonly on the dorsal aspects of the hands and
fingers, which rupture and crust over, and (B) facial hirsutism most noticeable on the upper cheeks.
Kaushansky_chapter 58_p0889-0914.indd 907 9/18/15 5:58 PM