Page 1144 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1144
1110 Part NiNe Transplantation
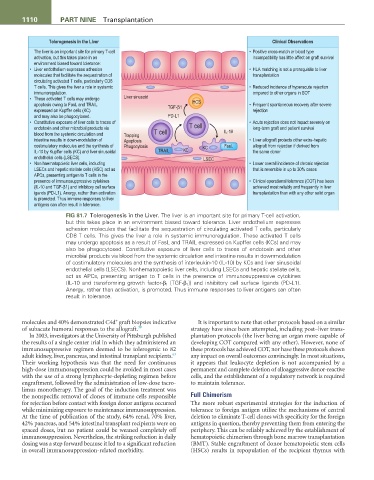
Tolerogenesis in the Liver Clinical Observations
The liver is an important site for primary T-cell • Positive cross-match or blood type
activation, but this takes place in an incompatibility has little affect on graft survival
environment biased toward tolerance:
• Liver endothelium expresses adhesion • HLA matching is not a prerequisite to liver
molecules that facilitate the sequestration of transplantation
circulating activated T cells, particularly CD8
T cells. This gives the liver a role in systemic • Reduced incidence of hyperacute rejection
immunoregulation. ompared to other organs in SOT
• These activated T cells may undergo Liver sinusoid
apoptosis owing to FasL and TRAIL TGF-β1 HCS • Frequent spontaneous recovery after severe
expressed on Kupffer cells (KC) rejection
and may also be phagocytosed. PD-L1
• Constitutive exposure of liver cells to traces of • Acute rejection does not impact severely on
endotoxin and other microbial products via T cell long-term graft and patient survival
blood from the systemic circulation and Trapping T cell IL-10
intestine results in down-modulation of Apoptosis • Liver allograft protects other extra-hepatic
costimulatory molecules and the synthesis of Phagocytosis KC FasL allograft from rejection if derived from
IL-10 by Kupffer cells (KC) and liver sinusoidal TRAIL KC the same donor
endothelial cells (LSECS). LSEC
• Non haematopoietic liver cells, including • Lower overall incidence of chronic rejection
LSECs and hepatic stellate cells (HSC) act as that is reversible in up to 30% cases
APCs, presenting antigen to T cells in the
presence of immunosuppressive cytokines • Clinical operational tolerance (COT) has been
(IL-10 and TGF-β1) and inhibitory cell surface achieved most reliably and frequently in liver
igands (PD-L1). Anergy, rather than activation transplantation than with any other solid organ
is promoted. Thus immune responses to liver
antigens can often result in tolerance.
FiG 81.7 Tolerogenesis in the Liver. The liver is an important site for primary T-cell activation,
but this takes place in an environment biased toward tolerance. Liver endothelium expresses
adhesion molecules that facilitate the sequestration of circulating activated T cells, particularly
CD8 T cells. This gives the liver a role in systemic immunoregulation. These activated T cells
may undergo apoptosis as a result of FasL and TRAIL expressed on Kupffer cells (KCs) and may
also be phagocytosed. Constitutive exposure of liver cells to traces of endotoxin and other
microbial products via blood from the systemic circulation and intestine results in downmodulation
of costimulatory molecules and the synthesis of interleukin-10 (IL-10) by KCs and liver sinusoidal
endothelial cells (LSECS). Nonhematopoietic liver cells, including LSECs and hepatic stellate cells,
act as APCs, presenting antigen to T cells in the presence of immunosuppressive cytokines
(IL-10 and transforming growth factor-β 1 [TGF-β 1 ]) and inhibitory cell surface ligands (PD-L1).
Anergy, rather than activation, is promoted. Thus immune responses to liver antigens can often
result in tolerance.
+
molecules and 40% demonstrated C4d graft biopsies indicative It is important to note that other protocols based on a similar
of subacute humoral responses to the allograft. 39 strategy have since been attempted, including post–liver trans-
In 2003, investigators at the University of Pittsburgh published plantation protocols (the liver being an organ more capable of
the results of a single center trial in which they administered an developing COT compared with any other). However, none of
immunosuppressive regimen deemed to be tolerogenic to 82 these protocols has achieved COT, nor have these protocols shown
63
adult kidney, liver, pancreas, and intestinal transplant recipients. any impact on overall outcomes convincingly. In most situations,
Their working hypothesis was that the need for continuous it appears that leukocyte depletion is not accompanied by a
high-dose immunosuppression could be avoided in most cases permanent and complete deletion of alloaggressive donor-reactive
with the use of a strong lymphocyte-depleting regimen before cells, and the establishment of a regulatory network is required
engraftment, followed by the administration of low-dose tacro- to maintain tolerance.
limus monotherapy. The goal of the induction treatment was
the nonspecific removal of clones of immune cells responsible Full Chimerism
for rejection before contact with foreign donor antigens occurred The more robust experimental strategies for the induction of
while minimizing exposure to maintenance immunosuppression. tolerance to foreign antigen utilize the mechanisms of central
At the time of publication of the study, 64% renal, 70% liver, deletion to eliminate T-cell clones with specificity for the foreign
42% pancreas, and 54% intestinal transplant recipients were on antigens in question, thereby preventing them from entering the
spaced doses, but no patient could be weaned completely off periphery. This can be reliably achieved by the establishment of
immunosuppression. Nevertheless, the striking reduction in daily hematopoietic chimerism through bone marrow transplantation
dosing was a step forward because it led to a significant reduction (BMT). Stable engraftment of donor hematopoietic stem cells
in overall immunosuppression-related morbidity. (HSCs) results in repopulation of the recipient thymus with