Page 1236 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1236
1198 ParT TEN Prevention and Therapy of Immunological Diseases
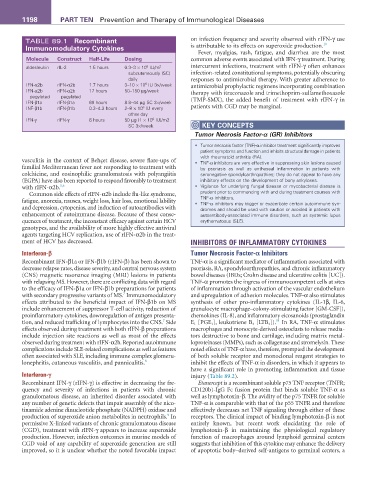
TABLE 89.1 recombinant on infection frequency and severity observed with rIFN-γ use
10
Immunomodulatory Cytokines is attributable to its effects on superoxide production.
Fever, myalgias, rash, fatigue, and diarrhea are the most
Molecule Construct Half-Life Dosing common adverse events associated with IFN-γ treatment. During
6
aldesleukin rIL-2 1.5 hours 0.3–3 × 10 IU/m intercurrent infections, treatment with rIFN-γ often enhances
2
subcutaneously (SC) infection-related constitutional symptoms, potentially obscuring
daily responses to antimicrobial therapy. With greater adherence to
IFN-α2b rIFN-α2b 1.7 hours 3–10 × 10 IU 3×/week antimicrobial prophylactic regimens incorporating combination
6
IFN-α2b rIFN-α2b 17 hours 50–150 µg/week therapy with itraconazole and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
pegylated pegylated
IFN-β1a rIFN-β1a 69 hours 8.8–44 µg SC 3×/week (TMP-SMX), the added benefit of treatment with rIFN-γ in
6
INF-β1b rIFN-β1b 0.2–4.3 hours 2–8 × 10 IU every patients with CGD may be marginal.
other day
6
IFN-γ rIFN-γ 6 hours 50 µg (1 × 10 IU)/m2
SC 3×/week KEY CONCEPTS
Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (GR) Inhibitors
• Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α inhibitor treatment significantly improves
patient symptoms and function and inhibits structural damage in patients
with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
vasculitis in the context of Behçet disease, severe flare-ups of • TNF-α inhibitors are very effective in suppressing skin lesions caused
familial Mediterranean fever not responding to treatment with by psoriasis as well as entheseal inflammation in patients with
colchicine, and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis seronegative spondyloarthropathies; they do not appear to have any
(EGPA) have also been reported to respond favorably to treatment inhibitory effects on the development of bony ankyloses.
with rIFN-α2b. 5,6 • Vigilance for underlying fungal disease or mycobacterial disease is
Common side effects of rIFN-α2b include flu-like syndrome, prudent prior to commencing with and during treatment courses with
TNF-α inhibitors.
fatigue, anorexia, nausea, weight loss, hair loss, emotional lability • TNF-α inhibitors may trigger or exacerbate certain autoimmune syn-
and depression, cytopenias, and induction of autoantibodies with dromes and should be used with caution or avoided in patients with
enhancement of autoimmune disease. Because of these conse- autoantibody-associated immune disorders, such as systemic lupus
quences of treatment, the inconstant efficacy against certain HCV erythematosus (SLE).
genotypes, and the availability of more highly effective antiviral
agents targeting HCV replication, use of rIFN-α2b in the treat-
ment of HCV has decreased. INHIBITORS OF INFLAMMATORY CYTOKINES
Interferon-β Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibitors
Recombinant IFN-β1a or IFN-β1b (rIFN-β) has been shown to TNF-α is a significant mediator of inflammation associated with
decrease relapse rates, disease severity, and central nervous system psoriasis, RA, spondyloarthropathies, and chronic inflammatory
(CNS) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) lesions in patients bowel diseases (IBDs; Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis [UC]).
with relapsing MS. However, there are conflicting data with regard TNF-α promotes the ingress of immunocompetent cells at sites
to the efficacy of IFN-β1a or IFN-β1b preparations for patients of inflammation through activation of the vascular endothelium
7
with secondary progressive variants of MS. Immunomodulatory and upregulation of adhesion molecules. TNF-α also stimulates
effects attributed to the beneficial impact of IFN-β1b on MS synthesis of other pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6,
include enhancement of suppressor T-cell activity, reduction of granulocyte macrophage–colony-stimulating factor [GM-CSF]),
proinflammatory cytokines, downregulation of antigen presenta- chemokines (IL-8), and inflammatory eicosanoids (prostaglandin
7
11
tion, and reduced trafficking of lymphocytes into the CNS. Side E 1 [PGE 1], leukotriene B 4 [LTB 4 ]). In RA, TNF-α stimulates
effects observed during treatment with both rIFN-β preparations macrophages and monocyte-derived osteoclasts to release media-
include injection site reactions as well as most of the effects tors destructive to bone and cartilage, including matrix metal-
observed during treatment with rIFN-α2b. Reported autoimmune loproteinases (MMPs), such as collagenase and stromelysin. These
complications include SLE-related complications as well as features noted effects of TNF-α have, therefore, prompted the development
often associated with SLE, including immune complex glomeru- of both soluble receptor and monoclonal reagent strategies to
lonephritis, cutaneous vasculitis, and panniculitis. 8 inhibit the effects of TNF-α in disorders, in which it appears to
have a significant role in promoting inflammation and tissue
Interferon-γ injury (Table 89.2).
Recombinant IFN-γ (rIFN-γ) is effective in decreasing the fre- Etanercept is a recombinant soluble p75 TNF receptor (TNFR;
quency and severity of infections in patients with chronic CD120b)-IgG Fc fusion protein that binds soluble TNF-α as
granulomatous disease, an inherited disorder associated with well as lymphotoxin-β. The avidity of the p75 TNFR for soluble
any number of genetic defects that impair assembly of the nico- TNF-α is comparable with that of the p55 TNFR and therefore
tinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase and effectively decreases net TNF signaling through either of these
9
production of superoxide anion metabolites in neutrophils. In receptors. The clinical impact of binding lymphotoxin-β is not
permissive X-linked variants of chronic granulomatous disease entirely known, but recent work elucidating the role of
(CGD), treatment with rIFN-γ appears to increase superoxide lymphotoxin-β in maintaining the physiological regulatory
production. However, infection outcomes in murine models of function of macrophages around lymphoid germinal centers
CGD void of any capability of superoxide generation are still suggests that inhibition of this cytokine may enhance the delivery
improved, so it is unclear whether the noted favorable impact of apoptotic body–derived self-antigens to germinal centers, a