Page 1328 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1328
CHaPtEr 95 Assessment of Human Allergic Diseases 1289
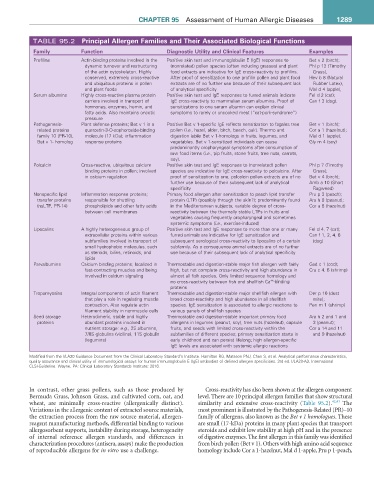
TABLE 95.2 Principal allergen Families and their associated Biological Functions
Family Function Diagnostic Utility and Clinical Features Examples
Profilins Actin-binding proteins involved in the Positive skin test and immunoglobulin E (IgE) responses to Bet v 2 (birch);
dynamic turnover and restructuring (nonrelated) pollen species (often including grasses) and plant Phl p 12 (Timothy
of the actin cytoskeleton. Highly food extracts are indicative for IgE cross-reactivity to profilins. Grass),
conserved, extremely cross-reactive After proof of sensitization to one profilin pollen and plant food Hev b 8 (Natural
and ubiquitous proteins in pollen extracts are of no further use because of their subsequent lack Rubber Latex),
and plant foods of analytical specificity Mal d 4 (apple),
Serum albumins Highly cross-reactive plasma protein Positive skin test and IgE responses to furred animals indicate Fel d 2 (cat);
carriers involved in transport of IgE cross-reactivity to mammalian serum albumins. Proof of Can f 3 (dog),
hormones, enzymes, hemin, and sensitizations to one serum albumin can explain clinical
fatty acids. Also maintains oncotic symptoms to rarely or uncooked meat (“cat-pork-syndrome”)
pressure
Pathogenesis- Plant defense proteins; Bet v 1 is a Positive Bet v 1-specific IgE reflects sensitization to fagales tree Bet v 1 (birch);
related proteins quercetin-3-O-sophoroside-binding pollen (i.e., hazel, alder, birch, beech, oak). Thermo and Cor a 1 (hazelnut);
family 10 (PR-10), molecule (17 kDa); inflammation digestion labile Bet v 1-homologs in fruits, legumes, and Mal d 1 (apple);
Bet v 1- homolog response proteins vegetables. Bet v 1-sensitized individuals can cause Gly m 4 (soy)
predominantly oropharyngeal symptoms after consumption of
raw food items (i.e., pip fruits, stone fruits, tree nuts, carrots,
soy).
Polcalcin Cross-reactive, ubiquitous calcium Positive skin test and IgE responses to (nonrelated) pollen Phl p 7 (Timothy
binding proteins in pollen; involved species are indicative for IgE cross-reactivity to polcalcins. After Grass);
in calcium regulation proof of sensitization to one, polcalcin pollen extracts are of no Bet v 4 (birch);
further use because of their subsequent lack of analytical Amb a 10 (Short
specificity Ragweed)
Nonspecific lipid Inflammation response proteins; Primary food allergen after sensitization to peach lipid transfer Pru p 3 (peach);
transfer proteins responsible for shuttling protein (LTP) (possibly through the skin?); predominantly found Ara h 9 (peanut);
(nsLTP, PR-14) phospholipids and other fatty acids in the Mediterranean subjects; variable degree of cross- Cor a 8 (hazelnut)
between cell membranes reactivity between the thermally stable LTPs in fruits and
vegetables causing frequently oropharyngeal and sometimes
systemic symptoms (i.e., exercise-induced)
Lipocalins A highly heterogeneous group of Positive skin test and IgE responses to more than one or many Fel d 4, 7 (cat);
extracellular proteins within various furred animals are indicative for IgE sensitization and Can f 1, 2, 4, 6
subfamilies involved in transport of subsequent serological cross-reactivity to lipocalins of a certain (dog)
small hydrophobic molecules, such subfamily. As a consequence animal extracts are of no further
as steroids, bilins, retinoids, and use because of their subsequent lack of analytical specificity
lipids
Parvalbumins Calcium binding proteins; localized in Thermostable and digestion-stable major fish allergen with fairly Gad c 1 (cod);
fast-contracting muscles and being high, but not complete cross-reactivity and high abundance in Cra c 4, 6 (shrimp)
involved in calcium signaling almost all fish species. Only limited sequence homology and
++
no cross-reactivity between fish and shellfish Ca -binding
proteins
Tropomyosins Integral components of actin filament Thermostable and digestion-stable major shellfish allergen with Der p 10 (dust
that play a role in regulating muscle broad cross-reactivity and high abundance in all shellfish mite);
contraction. Also regulate actin species. IgE sensitization is associated to allergic reactions to Pen m 1 (shrimp)
filament stability in nonmuscle cells various panels of shellfish species
Seed storage Heterodimeric, stable and highly Thermostable and digestion-stable important primary food Ara h 2 and 1 and
proteins abundant proteins involved in allergens in legumes (peanut, soy), tree nuts (hazelnut), capsule 3 (peanut);
nutrient storage: e.g., 2S albumins, fruits, and seeds with limited cross-reactivity within the Cor a 14 and 11
7/8S globulins (vicilins), 11S globulin subfamilies of different species; primary sensitization starts in and 9 (hazelnut)
(legumins) early childhood and can persist lifelong; high allergen-specific
IgE levels are associated with systemic allergic reactions
Modified from the I/LA20 Guidance Document from the Clinical Laboratory Standard’s Institute. Hamilton RG, Matsson PNJ, Chan S, et al. Analytical performance characteristics,
quality assurance and clinical utility of immunological assays for human immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies of defined allergen specificities. 3rd ed. I/LA20-A3, International
CLSI-Guideline. Wayne, PA: Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute; 2016.
In contrast, other grass pollens, such as those produced by Cross-reactivity has also been shown at the allergen component
Bermuda Grass, Johnson Grass, and cultivated corn, oat, and level. There are 10 principal allergen families that show structural
wheat, are minimally cross-reactive (allergenically distinct). similarity and extensive cross-reactivity (Table 95.2). 42,43 The
Variations in the allergenic content of extracted source materials, most prominent is illustrated by the Pathogenesis-Related (PR)–10
the extraction process from the raw source material, allergen- family of allergens, also known as the Bet v 1 homologues. These
reagent manufacturing methods, differential binding to various are small (17-kDa) proteins in many plant species that transport
allergosorbent supports, instability during storage, heterogeneity steroids and exhibit low stability at high pH and in the presence
of internal reference allergen standards, and differences in of digestive enzymes. The first allergen in this family was identified
characterization procedures (antisera, assays) make the production from birch pollen (Bet v 1). Others with high amino acid sequence
of reproducible allergens for in vitro use a challenge. homology include Cor a 1-hazelnut, Mal d 1-apple, Pru p 1-peach,