Page 1325 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1325
1286 Part ElEvEn Diagnostic Immunology
1000 12
10
IgE anti-Dpt (ng/ml) 100 Puncture skin test (wheal. mm) 8
10 6
4
1 2
0.1 1 10 100 1000 10 000 0.1 1 10 100 1000 10 000
Intradermal skin test titration Intradermal skin test titration
(ng/ml Dpt at midpoint of 8-mm wheal) (ng/ml Dpt at midpoint of 8-mm wheal)
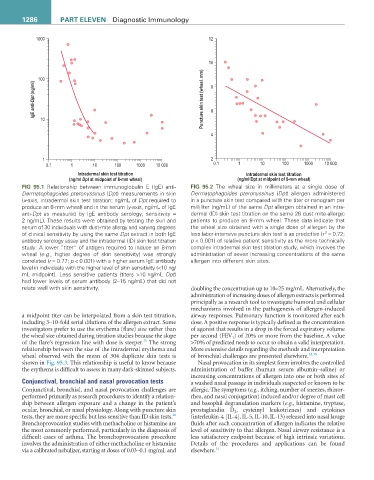
FIG 95.1 Relationship between immunoglobulin E (IgE) anti- FIG 95.2 The wheal size in millimeters at a single dose of
Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Dpt) measurements in skin Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Dpt) allergen administered
(x-axis, intradermal skin test titration; ng/mL of Dpt required to in a puncture skin test compared with the titer or nanogram per
produce an 8-mm wheal) and in the serum (y-axis, ng/mL of IgE milliliter (ng/mL) of the same Dpt allergen obtained in an intra-
anti-Dpt as measured by IgE antibody serology; sensitivity = dermal (ID) skin test titration on the same 26 dust mite-allergic
2 ng/mL). These results were obtained by testing the skin and patients to produce an 8-mm wheal. These data indicate that
serum of 30 individuals with dust-mite allergy and varying degrees the wheal size obtained with a single dose of allergen by the
of clinical sensitivity by using the same Dpt extract in both IgE less labor-intensive puncture skin test is as predictive (r = 0.72;
2
antibody serology assay and the intradermal (ID) skin test titration p < 0.001) of relative patient sensitivity as the more technically
study. A lower “titer” of antigen required to induce an 8-mm complex intradermal skin test titration study, which involves the
wheal (e.g., higher degree of skin sensitivity) was strongly administration of seven increasing concentrations of the same
correlated (r = 0.77; p < 0.001) with a higher serum IgE antibody allergen into different skin sites.
level in individuals with the higher level of skin sensitivity (<10 ng/
mL midpoint). Less sensitive patients (titers >10 ng/mL Dpt)
had lower levels of serum antibody (2–15 ng/mL) that did not
relate well with skin sensitivity. doubling the concentration up to 10–25 mg/mL. Alternatively, the
administration of increasing doses of allergen extracts is performed
principally as a research tool to investigate humoral and cellular
mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of allergen-induced
a midpoint titer can be interpolated from a skin test titration, airway responses. Pulmonary function is monitored after each
including 3–10-fold serial dilutions of the allergen extract. Some dose. A positive response is typically defined as the concentration
investigators prefer to use the erythema (flare) size rather than of agonist that results in a drop in the forced expiratory volume
the wheal size obtained during titration studies because the slope per second (FEV 1 ) of 20% or more from the baseline. A value
25
of the flare’s regression line with dose is steeper. The strong >70% of predicted needs to occur to obtain a valid interpretation.
relationship between the size of the intradermal erythema and More extensive details regarding the methods and interpretation
wheal observed with the mean of 304 duplicate skin tests is of bronchial challenges are presented elsewhere. 29,30
shown in Fig. 95.3. This relationship is useful to know because Nasal provocation in its simplest form involves the controlled
the erythema is difficult to assess in many dark-skinned subjects. administration of buffer (human serum albumin–saline) or
increasing concentrations of allergen into one or both sites of
Conjunctival, bronchial and nasal provocation tests a washed nasal passage in individuals suspected or known to be
Conjunctival, bronchial, and nasal provocation challenges are allergic. The symptoms (e.g., itching, number of sneezes, rhinor-
performed primarily as research procedures to identify a relation- rhea, and nasal conjugation) induced and/or degree of mast cell
ship between allergen exposure and a change in the patient’s and basophil degranulation markers (e.g., histamine, tryptase,
ocular, bronchial, or nasal physiology. Along with puncture skin prostaglandin D 2 , cysteinyl leukotrienes) and cytokines
28
tests, they are more specific but less sensitive than ID skin tests. (interleukin-4 [IL-4], IL-5, IL-10, IL-13) released into nasal lavage
Bronchoprovocation studies with methacholine or histamine are fluids after each concentration of allergen indicates the relative
the most commonly performed, particularly in the diagnosis of level of sensitivity to that allergen. Nasal airway resistance is a
difficult cases of asthma. The bronchoprovocation procedure less satisfactory endpoint because of high intrinsic variations.
involves the administration of either methacholine or histamine Details of the procedures and applications can be found
via a calibrated nebulizer, starting at doses of 0.03–0.1 mg/mL and elsewhere. 31