Page 460 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 460
ChaPTEr 31 Immune Responses to Helminth Infection 439
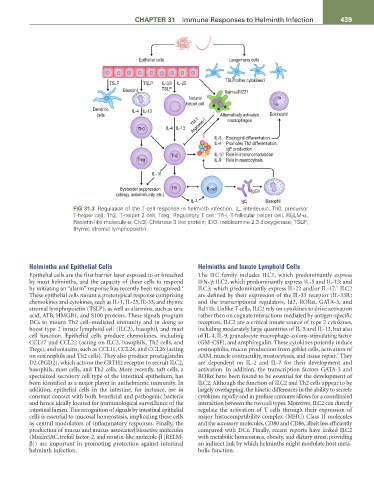
Epithelial cells Langerhans cells
TSLP/other cytokines?
TSLP TSLP IL-33/ IL-25
Basophil TSLP Relmα/FIZZ1
Natural
helper cell
Dendritic IL-4 IL-13
cells Alternatively activated Eosinophil
YM-1 macrophages
Th0 IL-4 IL-13 Arginase-1
IL-5 Eosinophil differentiation
IL-4 Promotes Th2 differentiation,
IgE production
Th2 IL-10 Role in immunomodulation
Treg IL-9 Role in mastocytosis
IL-10
Bystander suppression Tfh B cell IgG1
(allergy, autoimmunity, etc.)
IL-4 IgE Basophil
FIG 31.3 Regulation of the T-cell response in helminth infection. IL, interleukin; Th0, precursor
T-helper cell; Th2, T-helper 2 cell; Treg, Regulatory T cell; TfH, T-follicular helper cell, RELM-α,
Resistin-like molecule-α; Chi3l, Chitinase 3 like protein; IDO, indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase; TSLP,
thymic stromal lymphopoietin.
Helminths and Epithelial Cells Helminths and Innate Lymphoid Cells
Epithelial cells are the first barrier layer exposed to or breached The ILC family includes ILC1, which predominantly express
by most helminths, and the capacity of these cells to respond IFN-γ; ILC2, which predominantly express IL-5 and IL-13; and
4
5
by initiating an “alarm” response has recently been recognized. ILC3; which predominantly express IL-22 and/or IL-17. ILC2
These epithelial cells mount a prototypical response comprising are defined by their expression of the IL-33 receptor (IL-33R)
chemokines and cytokines, such as IL-1, IL-25, IL-33, and thymic and the transcriptional regulators, Id2, RORα, GATA-3, and
stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), as well as alarmins, such as uric Bcl11b. Unlike T cells, ILC2 rely on cytokines to drive activation
acid, ATB, HMGB1, and S100 proteins. These signals program rather than on cognate interactions mediated by antigen-specific
DCs to mount Th2 cell–mediated immunity and in doing so receptors. ILC2 are a critical innate source of type 2 cytokines,
boost type 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2), basophil, and mast including moderately large quantities of IL-5 and IL-13, but also
cell function. Epithelial cells produce chemokines, including of IL-4, IL-9, granulocyte macrophage–colony-stimulating factor
CCL17 and CCL22 (acting on ILC2, basophils, Th2 cells, and (GM-CSF), and amphiregulin. These cytokines potently induce
Tregs), and eotaxins, such as CCL11, CCL24, and CCL26 (acting eosinophilia, mucus production from goblet cells, activation of
5
on eosinophils and Th2 cells). They also produce prostaglandin AAM, muscle contractility, mastocytosis, and tissue repair. They
D2 (PGD2), which acts on the CRTH2 receptor to recruit ILC2, are dependent on IL-2 and IL-7 for their development and
basophils, mast cells, and Th2 cells. More recently, tuft cells, a activation. In addition, the transcription factors GATA-3 and
specialized secretory cell type of the intestinal epithelium, has RORα have been found to be essential for the development of
been identified as a major player in anthelmintic immunity. In ILC2. Although the function of ILC2 and Th2 cells appear to be
addition, epithelial cells in the intestine, for instance, are in largely overlapping, the kinetic differences in the ability to secrete
constant contact with both beneficial and pathogenic bacteria cytokines rapidly and in profuse amounts allows for a coordinated
and hence ideally located for immunological surveillance of the interaction between the two cell types. Moreover, ILC2 can directly
intestinal lumen. This recognition of signals by intestinal epithelial regulate the activation of T cells through their expression of
cells is essential to mucosal homeostasis, implicating these cells major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Class II molecules
as central modulators of inflammatory responses. Finally, the and the accessory molecules, CD80 and CD86, albeit less efficiently
production of mucus and mucus-associated bioactive molecules compared with DCs. Finally, recent reports have linked ILC2
(Mucin5AC, trefoil factor-2, and resistin-like molecule-β [RELM- with metabolic homeostasis, obesity, and dietary stress, providing
β]) are important in promoting protection against intestinal an indirect link by which helminths might modulate host meta-
helminth infection. bolic function.