Page 896 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 896
CHaPtEr 63 Bullous Diseases of the Skin and Mucous Membranes 867
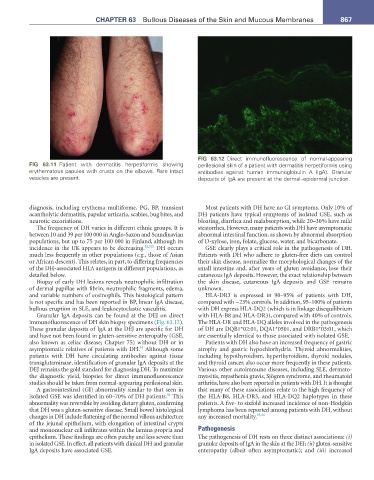
FIG 63.12 Direct immunofluorescence of normal-appearing
FIG 63.11 Patient with dermatitis herpetiformis showing perilesional skin of a patient with dermatitis herpetiformis using
erythematous papules with crusts on the elbows. Rare intact antibodies against human immunoglobulin A (IgA). Granular
vesicles are present. deposits of IgA are present at the dermal–epidermal junction.
diagnosis, including erythema multiforme, PG, BP, transient Most patients with DH have no GI symptoms. Only 10% of
acantholytic dermatitis, papular urticaria, scabies, bug bites, and DH patients have typical symptoms of isolated GSE, such as
neurotic excoriations. bloating, diarrhea and malabsorption, while 20–30% have mild
The frequency of DH varies in different ethnic groups. It is steatorrhea. However, many patients with DH have asymptomatic
between 10 and 39 per 100 000 in Anglo-Saxon and Scandinavian abnormal intestinal function, as shown by abnormal absorption
populations, but up to 75 per 100 000 in Finland, although its of D-xylose, iron, folate, glucose, water, and bicarbonate.
incidence in the UK appears to be decreasing. 52,52a DH occurs GSE clearly plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of DH.
much less frequently in other populations (e.g., those of Asian Patients with DH who adhere to gluten-free diets can control
or African descent). This relates, in part, to differing frequencies their skin disease, normalize the morphological changes of the
of the DH-associated HLA antigens in different populations, as small intestine and, after years of gluten avoidance, lose their
detailed below. cutaneous IgA deposits. However, the exact relationship between
Biopsy of early DH lesions reveals neutrophilic infiltration the skin disease, cutaneous IgA deposits and GSE remains
of dermal papillae with fibrin, neutrophilic fragments, edema, unknown.
and variable numbers of eosinophils. This histological pattern HLA-DR3 is expressed in 90–95% of patients with DH,
is not specific and has been reported in BP, linear IgA disease, compared with ~23% controls. In addition, 95–100% of patients
bullous eruption in SLE, and leukocytoclastic vasculitis. with DH express HLA-DQ2 (which is in linkage disequilibrium
Granular IgA deposits can be found at the DEJ on direct with HLA-B8 and HLA-DR3), compared with 40% of controls.
immunofluorescence of DH skin biopsy specimens (Fig. 63.12). The HLA-DR and HLA-DQ alleles involved in the pathogenesis
These granular deposits of IgA at the DEJ are specific for DH of DH are DQB1*02:01, DQA1*0501, and DRB1*03:01, which
and have not been found in gluten-sensitive enteropathy (GSE, are essentially identical to those associated with isolated GSE.
also known as celiac disease; Chapter 75) without DH or in Patients with DH also have an increased frequency of gastric
53
asymptomatic relatives of patients with DH. Although some atrophy and gastric hypochlorhydria. Thyroid abnormalities,
patients with DH have circulating antibodies against tissue including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroid nodules,
transglutaminase, identification of granular IgA deposits at the and thyroid cancer, also occur more frequently in these patients.
DEJ remains the gold standard for diagnosing DH. To maximize Various other autoimmune diseases, including SLE, dermato-
the diagnostic yield, biopsies for direct immunofluorescence myositis, myasthenia gravis, Sjögren syndrome, and rheumatoid
studies should be taken from normal-appearing perilesional skin. arthritis, have also been reported in patients with DH. It is thought
A gastrointestinal (GI) abnormality similar to that seen in that many of these associations relate to the high frequency of
54
isolated GSE was identified in 60–70% of DH patients. This the HLA-B8, HLA-DR3, and HLA-DQ2 haplotypes in these
abnormality was reversible by avoiding dietary gluten, confirming patients. A five- to sixfold increased incidence of non-Hodgkin
that DH was a gluten-sensitive disease. Small bowel histological lymphoma has been reported among patients with DH, without
changes in DH include flattening of the normal villous architecture any increased mortality. 55,56
of the jejunal epithelium, with elongation of intestinal crypts
and mononuclear cell infiltrates within the lamina propria and Pathogenesis
epithelium. These findings are often patchy and less severe than The pathogenesis of DH rests on three distinct associations: (i)
in isolated GSE. In effect, all patients with clinical DH and granular granular deposits of IgA in the skin at the DEJ; (ii) gluten-sensitive
IgA deposits have associated GSE. enteropathy (albeit often asymptomatic); and (iii) increased