Page 474 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 474
458 PART 6 ■ Neoplastic Disorders
n hu n cells c n kill resh CML cells in n HLA- In usion o onor cells t ti e o ini l resi u l
restricte pepti e-specif c nner. T is kes it possible ise se y be require within the f rst ye r o tr nspl nt.
to esign CML-specif c oligopepti es th t re presente in Newer un erst n ing o the lloi une e ect h s le to
conjunction with HLA cl ss I or cl ss II olecules th t y the evelop ent o re uce intensity con itioning or tr ns-
be i unogenic in hu ns. V ccin tion o s ll nu - pl nt tion th t ocuses on i unosuppression o the host
ber o p tients with junction-specif c pepti es h s pro uce r ther th n yelo bl tion. Engr ent o onor he to-
p rti l or co plete he tologic l response in p tients poietic cells c n t ke pl ce without necess rily er ic ting
with CML. T e v ccin te p tients evelope el ye -type ll the host popul tion o cells. Despite the benef ts, llo-SC
hypersensitivity re ctions n CD4+ ly phocyte proli er - is proce ure with consi er ble proce ur l-rel te or-
tive response. T is ppro ch to tre t ent y be v lu ble in t lity n chronic orbi ity (e.g., chronic gr -versus-host
suppressing proli er tion o leuke i cells in p tients with ise se or so e long-ter survivors).
ini l resi u l ise se.
When CML p tients h rbor ini l resi u l ise se, n Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia and Atypical
ppro ch is to try to in uce i unity to ntigens known Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
to be overexpresse in leuke i cells. Hu n cytotoxic
cells (C Ls) c n kill Ph-positive CD34+ progenitor cells. CNL n typic l chronic yeloi leuke i ( CML) re r re
Te use o C Ls irecte g inst the Pr-1 co ponent o yeloi leuke i s with poor prognosis. Recently, ut -
protein se 3 is lso pro ising. Protein se 3 is serine pro- tions in colony-sti ul ting ctor 3 receptor (CSF3R) h ve
te se th t is in uce uring cell i erenti tion n store been iscovere t high requency in CNL n t lower
in zurophilic gr nules. It is overexpresse in yeloi requency in CML.
leuke i s. T e evelop ent o CML coul be c use by Initi lly, bloo s e rs o p tients with CML n CML
selective eletion o Pr-specif c C L clone; this supports y look in istinguish ble bec use both ispl y pro i-
the theory th t bre king specif c toler nce coul be v lu- nent i ture gr nulocytosis-pro yelocytes, yelocytes,
ble tre t ent ppro ch or p tients with ini l resi u l n et yelocytes. However, there re istinct i erences
ise se. between the chronic ph se o CML, CML, n CNL (see
ble 23.4).
Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation In co p rison to CML, CML n CNL h ve no istinct
ph ses o ise se, but they requently e onstr te n ccel-
A long-st n ing n univers lly ccepte ther py or CML er te ph se ssoci te with n incre se tot l leukocyte
is llogeneic ste cell tr nspl nt tion ( llo-SC ). Allo-SC count n incre se nu ber o yelobl sts.
chieves its cur tive potenti l vi t le st two ech nis s:
CML p tients h ve e i n surviv l o 25 onths.
1. Myelo bl tion in uce by high- ose che or iother py Shorter surviv l ti e is ssoci te with ge gre ter th n
2. Alloi une gr -versus-leuke i (GvL) e ect e i te 65 ye rs o ge, e le gen er, n tot l WBC count gre ter
by onor ly phocytes th n 50 × 10 /L with the presence o i ture gr nulocytes.
9
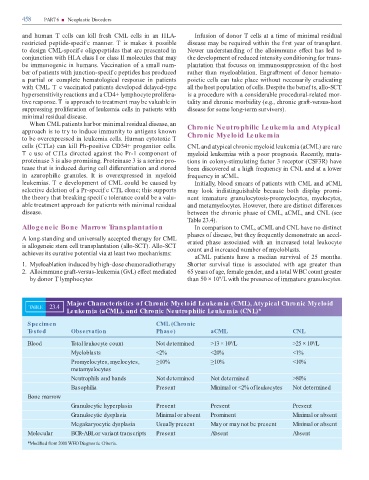
Major Characteristics of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML), Atypical Chronic Myeloid
TABLE 23.4
Leukemia (aCML), and Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia (CNL)*
Specimen CML (Chronic
Tested Observation Phase) aCML CNL
Blood Total leukocyte count Not determined >13 × 10 /L >25 × 10 /L
9
9
Myeloblasts <2% <20% <1%
Promyelocytes, myelocytes, ≥10% ≥10% <10%
metamyelocytes
Neutrophils and bands Not determined Not determined >80%
Basophilia Present Minimal or <2% of leukocytes Not determined
Bone marrow
Granulocytic hyperplasia Present Present Present
Granulocytic dysplasia Minimal or absent Prominent Minimal or absent
Megakaryocytic dysplasia Usually present May or may not be present Minimal or absent
Molecular BCR-ABL or variant transcripts Present Absent Absent
*Modi ed from 2008 WHO Diagnostic Criteria.