Page 476 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 476
460 PART 6 ■ Neoplastic Disorders
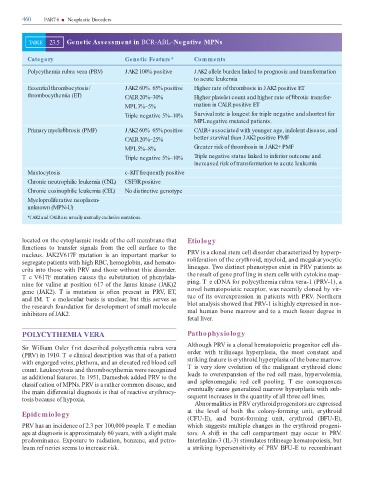
TABLE 23.5 Genetic Assessment in BCR-ABL–Negative MPNs
Category Genetic Feature* Comments
Polycythemia rubra vera (PRV) JAK2 100% positive JAK2 allele burden linked to prognosis and transformation
to acute leukemia
Essential thrombocytosis/ JAK2 60%–65% positive Higher rate of thrombosis in JAK2 positive ET
thrombocythemia (ET) CALR 20%–30% Higher platelet count and higher rate of brotic transfor-
MPL 3%–5% mation in CALR positive ET
Triple negative 5%–10% Survival rate is longest for triple negative and shortest for
MPL negative mutated patients.
Primary myelo brosis (PMF) JAK2 60%–65% positive CALR+ associated with younger age, indolent disease, and
CALR 20%–25% better survival than JAK2 positive PMF
MPL 5%–8% Greater risk of thrombosis in JAK2+ PMF
Triple negative 5%–10% Triple negative status linked to inferior outcome and
increased risk of transformation to acute leukemia
Mastocytosis c-KIT frequently positive
Chronic neutrophilic leukemia (CNL) CSF3R positive
Chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL) No distinctive genotype
Myeloproliferative neoplasm-
unknown (MPN-U)
*JAK2 and CALR are usually mutually exclusive mutations.
loc te on the cytopl s ic insi e o the cell e br ne th t Etiology
unctions to tr ns er sign ls ro the cell sur ce to the
nucleus. JAK2V617F ut tion is n i port nt rker to PRV is clon l ste cell isor er ch r cterize by hyperp-
segreg te p tients with high RBC, he oglobin, n he to- roli er tion o the erythroi , yeloi , n eg k ryocytic
crits into those with PRV n those without this isor er. line ges. wo istinct phenotypes exist in PRV p tients s
T e V617F ut tion c uses the substitution o phenyl l - the result o gene prof ling in ste cells with cytokine p-
nine or v line t position 617 o the J nus kin se (JAK)2 ping. T e cDNA or polycythe i rubr ver -1 (PRV-1),
gene (JAK2). T is ut tion is o en present in PRV, E , novel he topoietic receptor, w s recently clone by vir-
n IM. T e olecul r b sis is uncle r, but this serves s tue o its overexpression in p tients with PRV. Northern
the rese rch oun tion or evelop ent o s ll olecule blot n lysis showe th t PRV-1 is highly expresse in nor-
inhibitors o JAK2. l hu n bone rrow n to uch lesser egree in
et l liver.
POLYCYTHEMIA VERA Pathophysiology
Although PRV is clon l he topoietic progenitor cell is-
Sir Willi Osler f rst escribe polycythe i rubr ver
(PRV) in 1910. T e clinic l escription w s th t o p tient or er with triline ge hyperpl si , the ost const nt n
with engorge veins, plethor , n n elev te re bloo cell striking e ture is erythroi hyperpl si o the bone rrow.
count. Leukocytosis n thro bocythe i were recognize T is very slow evolution o the lign nt erythroi clone
s ition l e tures. In 1951, D eshek e PRV to the le s to overexp nsion o the re cell ss, hypervole i ,
cl ssif c tion o MPNs. PRV is r ther co on ise se, n n spleno eg lic re cell pooling. T ese consequences
the in i erenti l i gnosis is th t o re ctive erythrocy- eventu lly c use gener lize rrow hyperpl si with sub-
tosis bec use o hypoxi . sequent incre ses in the qu ntity o ll three cell lines.
Abnor lities in PRV erythroi progenitors re expresse
Epidemiology t the level o both the colony- or ing unit, erythroi
(CFU-E), n burst- or ing unit, erythroi (BFU-E),
PRV h s n inci ence o 2.3 per 100,000 people. T e e i n which suggests ultiple ch nges in the erythroi progeni-
ge t i gnosis is pproxi tely 60 ye rs, with slight le tors. A shi in the cell co p rt ent y occur in PRV.
pre o in nce. Exposure to r i tion, benzene, n petro- Interleukin-3 (IL-3) sti ul tes triline ge he topoiesis, but
leu ref neries see s to incre se risk. striking hypersensitivity o PRV BFU-E to reco bin nt