Page 512 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 512
496 PART 7 ■ Principles and Disorders of Hemostasis and Thrombosis
pl telets re in the systemic circulation, where s the re in- n unction l ch nge is cco p nie by series o bio-
ing one thir exist s pool o pl telets in the spleen th t che ic l re ctions th t occur uring the process o pl te-
reely exch nge with the gener l circul tion. let ctiv tion. T e pl telet pl s e br ne is the ocus o
A nor l person h s n ver ge o 250 × 10 /L (r nge o inter ctions between extr cellul r n intr cellul r environ-
9
150 × 10 /L to 450 × 10 /L) pl telets in the syste ic circu- ents. Agonists th t le to pl telet ctiv tion re v rie
9
9
l tion. I the tot l pl telet count is less th n 150 × 10 /L, it n inclu e nucleoti e (ADP), lipi s (thro box ne A ,
9
2
is escribe s thrombocytopenia. I the tot l pl telet count is pl telet- ctiv ting ctor), structur l protein (coll gen),
gre ter th n 450 × 10 /L, it is re erre to s thrombocytosis. n proteolytic enzy e (thro bin).
9
Pl telet turnover or e ective thro bopoiesis ver ges 350 × One o the istinct ctivities ssoci te with pl telet ctiv-
10 /L ± 4.3 × 10 /L/ y. ity in response to v scul r ge is the continue inte-
9
9
T e li e sp n o ture pl telet is 9.0 ys ± 1 y. At n nce o v scul r integrity by the r pi herence o pl telets
the en o their li e sp n, pl telets re ph gocytize by the to expose en otheliu . In ition, pl telets spre , beco e
croph ges o the liver n spleen n other tissues o the ctiv te , n or l rge ggreg tes. For tion o pl telet
mononuclear phagocytic system. plug initi lly rrests blee ing.
T e herence n ggreg tion o pl telets t the sites o
CELL-BASED MECHANISM OF v scul r ge llow or the rele se o olecules involve
HEMOSTASIS: PLATELET FUNCTION in he ost sis n woun he ling n provi e e br ne
sur ce or the sse bly o co gul tion enzy es th t le to
Pl telets nor lly ove reely through the lu en o bloo f brin or tion. V scul r he ling is pro ote by sti ul t-
vessels s co ponents o the circul tory syste . M inten nce ing the igr tion n proli er tion o en otheli l cells n
o nor l v scul r integrity involves nourish ent o the e i l s ooth uscle cells through the rele se o the ito-
en otheliu by so e pl telet constituents or the ctu l gen, pl telet- erive growth ctor.
incorpor tion o pl telets into the vessel w ll. T is process
requires less th n 10% o the pl telets nor lly in the cir- Platelet Adhesion
cul ting bloo . For he ost sis to occur, pl telets not only
ust be present in nor l qu ntities but lso ust unction I v scul r injury exposes the en otheli l sur ce n un er-
properly. T is section iscusses the he ost tic unctions o lying coll gen (Fig. 25.7), pl telets here to the suben othe-
pl telets, inclu ing pl telet herence n ggreg tion. li l coll gen f bers, spre pseu opo s long the sur ce, n
clu p together (aggregate). Platelet adhesion to suben othe-
li l connective tissues, especi lly coll gen, occurs within 1 to
Overall Functions of Platelets
2 inutes er bre k in the en otheliu .
Following ge to the en otheliu o bloo vessel, Epinephrine n serotonin pro ote v soconstriction.
series o events occur, inclu ing hesion to the injure ves- ADP incre ses the hesiveness o pl telets. Consi er ble
sel, sh pe ch nge, ggreg tion, n secretion. E ch structur l evi ence in ic tes th t the hesion n ggreg tion o
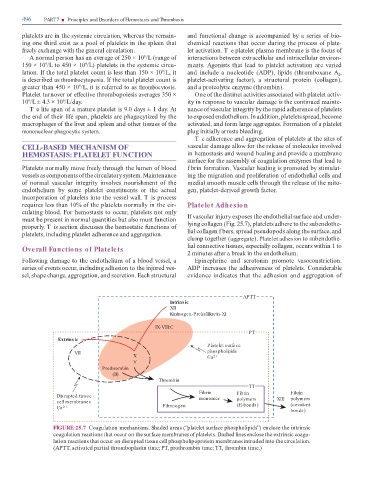
APTT
Intrins ic
XII
Kininogen-Prekallikrein-XI
IX-VIII:C
PT
Extrins ic
Platelet surface
VII phospholipids
X Ca 2+
V
Prothrombin
(II)
Thrombin
TT
Fibrin Fibrin Fibrin
Disrupted tissue monomer polymers
cell membranes polymers XIII (covalent
Ca 2+ Fibrinogen (H-bonds)
bonds)
FIGURE 25.7 Co gul tion ech nis s. Shaded areas (“pl telet sur ce phospholipi s”) enclose the intrinsic
co gul tion re ctions th t occur on the sur ce e br nes o pl telets. Dashed lines enclose the extrinsic co gu-
l tion re ctions th t occur on isrupte tissue cell phospholipoprotein e br nes intru e into the circul tion.
(AP , ctiv te p rti l thro bopl stin ti e; P , prothro bin ti e; , thro bin ti e.)