Page 510 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 510
494 PART 7 ■ Principles and Disorders of Hemostasis and Thrombosis
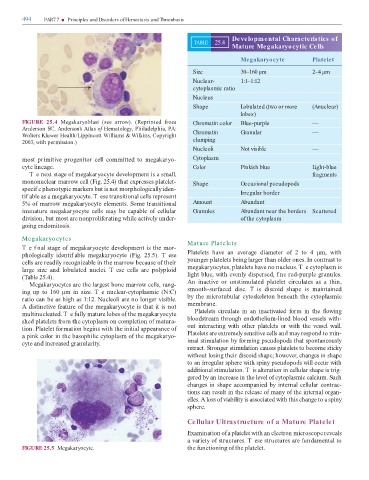
Developmental Characteristics of
TABLE 25.4
Mature Megakaryocytic Cells
Megakaryocyte Platelet
Size 30–160 µm 2–4 µm
Nuclear- 1:1–1:12
cytoplasmic ratio
Nucleus
Shape Lobulated (two or more (Anuclear)
lobes)
FIGURE 25.4 Meg k ryobl st (see arrow). (Reprinte ro Chromatin color Blue-purple —
An erson SC. Anderson’s Atlas o Hematology, Phil elphi , PA:
Wolters Kluwer He lth/Lippincott Willi s & Wilkins, Copyright Chromatin Granular —
2003, with per ission.) clumping
Nucleoli Not visible —
ost pri itive progenitor cell co itte to eg k ryo- Cytoplasm
cyte line ge. Color Pinkish blue Light-blue
T e next st ge o eg k ryocyte evelop ent is s ll, fragments
ononucle r rrow cell (Fig. 25.4) th t expresses pl telet- Shape Occasional pseudopods
specif c phenotypic rkers but is not orphologic lly i en-
tif ble s eg k ryocyte. T ese tr nsition l cells represent Irregular border
5% o rrow eg k ryocyte ele ents. So e tr nsition l Amount Abundant
i ture eg k ryocyte cells y be c p ble o cellul r Granules Abundant near the borders Scattered
ivision, but ost re nonproli er ting while ctively un er- of the cytoplasm
going en o itosis.
Megakaryocytes
Mature Platelets
T e f n l st ge o eg k ryocyte evelop ent is the or-
phologic lly i entif ble eg k ryocyte (Fig. 25.5). T ese Pl telets h ve n ver ge i eter o 2 to 4 µ , with
cells re re ily recogniz ble in the rrow bec use o their younger pl telets being l rger th n ol er ones. In contr st to
l rge size n lobul te nuclei. T ese cells re polyploi eg k ryocytes, pl telets h ve no nucleus. T e cytopl s is
( ble 25.4). light blue, with evenly isperse , f ne re -purple gr nules.
Meg k ryocytes re the l rgest bone rrow cells, r ng- An in ctive or unsti ul te pl telet circul tes s thin,
ing up to 160 µ in size. T e nucle r-cytopl s ic (N:C) s ooth-sur ce isc. T is iscoi sh pe is int ine
r tio c n be s high s 1:12. Nucleoli re no longer visible. by the icrotubul r cytoskeleton bene th the cytopl s ic
A istinctive e ture o the eg k ryocyte is th t it is not e br ne.
ultinucle te . T e ully ture lobes o the eg k ryocyte Pl telets circul te in n in ctiv te or in the owing
she pl telets ro the cytopl s on co pletion o tur - bloo stre through en otheliu -line bloo vessels with-
tion. Pl telet or tion begins with the initi l ppe r nce o out inter cting with other pl telets or with the vessel w ll.
pink color in the b sophilic cytopl s o the eg k ryo- Pl telets re extre ely sensitive cells n y respon to in-
cyte n incre se gr nul rity. i l sti ul tion by or ing pseu opo s th t spont neously
retr ct. Stronger sti ul tion c uses pl telets to beco e sticky
without losing their iscoi sh pe; however, ch nges in sh pe
to n irregul r sphere with spiny pseu opo s will occur with
ition l sti ul tion. T is lter tion in cellul r sh pe is trig-
gere by n incre se in the level o cytopl s ic c lciu . Such
ch nges in sh pe cco p nie by intern l cellul r contr c-
tions c n result in the rele se o ny o the intern l org n-
elles. A loss o vi bility is ssoci te with this ch nge to spiny
sphere.
Cellular Ultrastructure of a Mature Platelet
Ex in tion o pl telet with n electron icroscope reve ls
v riety o structures. T ese structures re un ent l to
FIGURE 25.5 Meg k ryocyte. the unctioning o the pl telet.