Page 509 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 509
CHAPTER 25 ■ Principles of Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Vasculature and Platelets 493
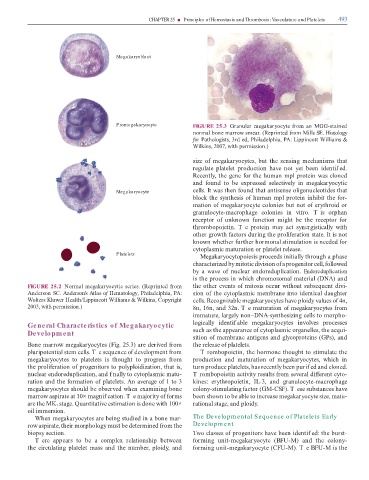
Megakaryoblast
Promegakaryocyte FIGURE 25.3 Gr nul r eg k ryocyte ro n MGG-st ine
nor l bone rrow s e r. (Reprinte ro Mills SE. Histology
or Pathologists, 3r e , Phil elphi , PA: Lippincott Willi s &
Wilkins, 2007, with per ission.)
size o eg k ryocytes, but the sensing ech nis s th t
regul te pl telet pro uction h ve not yet been i entif e .
Recently, the gene or the hu n pl protein w s clone
n oun to be expresse selectively in eg k ryocytic
Megakaryocyte cells. It w s then oun th t ntisense oligonucleoti es th t
block the synthesis o hu n pl protein inhibit the or-
tion o eg k ryocyte colonies but not o erythroi or
gr nulocyte- croph ge colonies in vitro. T is orph n
receptor o unknown unction ight be the receptor or
thro bopoietin. T e protein y ct synergistic lly with
other growth ctors uring the proli er tion st te. It is not
known whether urther hor on l sti ul tion is nee e or
cytopl s ic tur tion or pl telet rele se.
Platelets
Meg k ryocytopoiesis procee s initi lly through ph se
ch r cterize by itotic ivision o progenitor cell, ollowe
by w ve o nucle r en ore uplic tion. Endoreduplication
is the process in which chro oso l teri l (DNA) n
FIGURE 25.2 Nor l eg k ryocytic series. (Reprinte ro the other events o itosis occur without subsequent ivi-
An erson SC. Anderson’s Atlas o Hematology, Phil elphi , PA: sion o the cytopl s ic e br ne into i entic l ughter
Wolters Kluwer He lth/Lippincott Willi s & Wilkins, Copyright cells. Recogniz ble eg k ryocytes h ve ploi y v lues o 4n,
2003, with per ission.) 8n, 16n, n 32n. T e tur tion o eg k ryocytes ro
i ture, l rgely non–DNA-synthesizing cells to orpho-
General Characteristics of Megakaryocytic logic lly i entif ble eg k ryocytes involves processes
Development such s the ppe r nce o cytopl s ic org nelles, the cqui-
sition o e br ne ntigens n glycoproteins (GPs), n
Bone rrow eg k ryocytes (Fig. 25.3) re erive ro the rele se o pl telets.
pluripotenti l ste cells. T e sequence o evelop ent ro T ro bopoietin, the hor one thought to sti ul te the
eg k ryocytes to pl telets is thought to progress ro pro uction n tur tion o eg k ryocytes, which in
the proli er tion o progenitors to polyploi iz tion, th t is, turn pro uce pl telets, h s recently been purif e n clone .
nucle r en ore uplic tion, n f n lly to cytopl s ic tu- T ro bopoietin ctivity results ro sever l i erent cyto-
r tion n the or tion o pl telets. An ver ge o 1 to 3 kines: erythropoietin, IL-3, n gr nulocyte- croph ge
eg k ryocytes shoul be observe when ex ining bone colony-sti ul ting ctor (GM-CSF). T ese subst nces h ve
rrow spir te t 10× gnif c tion. T e jority o or s been shown to be ble to incre se eg k ryocyte size, tu-
re the MK st ge. Qu ntit tive esti tion is one with 100× r tion l st ge, n ploi y.
1
oil i ersion.
When eg k ryocytes re being stu ie in bone r- The Developm ental Sequence of Platelets Early
row spir te, their orphology ust be eter ine ro the Developm ent
biopsy section. wo cl sses o progenitors h ve been i entif e : the burst-
T ere ppe rs to be co plex rel tionship between or ing unit- eg k ryocyte (BFU-M) n the colony-
the circul ting pl telet ss n the nu ber, ploi y, n or ing unit- eg k ryocyte (CFU-M). T e BFU-M is the