Page 558 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 558
542 PART 7 ■ Principles and Disorders of Hemostasis and Thrombosis
IXa
TF
X
VIIa VIIA
Platelet
Protein S
C4b-BP
C4b-BP Inhibits
EPCR Xa Antithrombin
Protein S
Activated
Protein C Va Heparin
Protein C Inactivates Inhibits
Sulfate
TM Platelet
Thrombin Prothrombin Thrombin
Xa
Va
Platelet
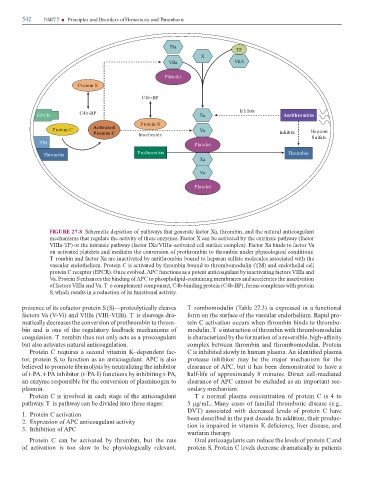
FIGURE 27.8 Sche atic e iction o athways that generate actor Xa, thro bin, an the natura anticoagu ant
echanis s that regu ate the activity o these enzy es. Factor X can be activate by the extrinsic athway ( actor
VIIIa- F) or the intrinsic athway ( actor IXa/VIIIa–activate ce sur ace co ex). Factor Xa bin s to actor Va
on activate ate ets an e iates the conversion o rothro bin to thro bin un er hysio ogica con itions.
T ro bin an actor Xa are inactivate by antithro bin boun to he aran su ate o ecu es associate with the
vascu ar en othe iu . Protein C is activate by thro bin boun to thro bo o u in ( M) an en othe ia ce
rotein C rece tor (EPCR). Once evo ve , APC unctions as a otent anticoagu ant by inactivating actors VIIIa an
Va. Protein S enhances the bin ing o APC to hos ho i i -containing e branes an acce erates the inactivation
o actors VIIIa an Va. T e co e ent co onent, C4b-bin ing rotein (C4b-BP), or s co exes with rotein
S, which resu ts in a re uction o its unctiona activity.
resence o its co actor rotein S (S)— roteo ytica y c eaves T ro bo o u in ( ab e 27.3) is ex resse in a unctiona
actors Va (V-Vi) an VIIIa (VIII-VIIIi). T is c eavage ra- or on the sur ace o the vascu ar en othe iu . Ra i ro-
atica y ecreases the conversion o rothro bin to thro - tein C activation occurs when thro bin bin s to thro bo-
bin an is one o the regu atory ee back echanis s o o u in. T e interaction o thro bin with thro bo o u in
coagu ation. T ro bin thus not on y acts as a rocoagu ant is characterize by the or ation o a reversib e, high-a nity
but a so activates natura anticoagu ation. co ex between thro bin an thro bo o u in. Protein
Protein C requires a secon vita in K– e en ent ac- C is inhibite s ow y in hu an as a. An i enti e as a
tor, rotein S, to unction as an anticoagu ant. APC is a so rotease inhibitor ay be the ajor echanis or the
be ieve to ro ote brino ysis by neutra izing the inhibitor c earance o APC, but it has been e onstrate to have a
o t-PA. t-PA inhibitor (t-PA-I) unctions by inhibiting t-PA, ha - i e o a roxi ate y 8 inutes. Direct ce - e iate
an enzy e res onsib e or the conversion o as inogen to c earance o APC cannot be exc u e as an i ortant sec-
as in. on ary echanis .
Protein C is invo ve in each stage o the anticoagu ant T e nor a as a concentration o rotein C is 4 to
athway. T is athway can be ivi e into three stages: 5 µg/ L. Many cases o a i ia thro botic isease (e.g.,
DV ) associate with ecrease eve s o rotein C have
1. Protein C activation been escribe in the ast eca e. In a ition, their ro uc-
2. Ex ression o APC anticoagu ant activity tion is i aire in vita in K e ciency, iver isease, an
3. Inhibition o APC
war arin thera y.
Protein C can be activate by thro bin, but the rate Ora anticoagu ants can re uce the eve s o rotein C an
o activation is too s ow to be hysio ogica y re evant. rotein S. Protein C eve s ecrease ra atica y in atients