Page 559 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 559
CHAPTER 27 ■ Principles of Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Blood Coagulation Factors and Natural Coagulant Systems 543
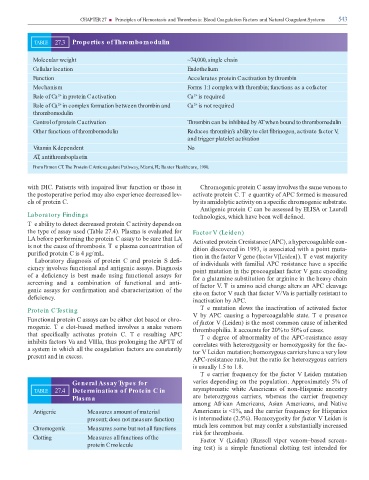
TABLE 27.3 Properties of Thrombomodulin
Molecular weight ~74,000, single chain
Cellular location Endothelium
Function Accelerates protein C activation by thrombin
Mechanism Forms 1:1 complex with thrombin; functions as a cofactor
Role of Ca in protein C activation Ca is required
2+
2+
Role of Ca in complex formation between thrombin and Ca is not required
2+
2+
thrombomodulin
Control of protein C activation Thrombin can be inhibited by AT when bound to thrombomodulin
Other functions of thrombomodulin Reduces thrombin’s ability to clot brinogen, activate factor V
,
and trigger platelet activation
Vitamin K dependent No
AT, antithromboplastin
From Esmon CT. The Protein C Anticoagulant Pathway, Miami, FL: Baxter Healthcare, 1990.
with DIC. Patients with i aire iver unction or those in Chro ogenic rotein C assay invo ves the sa e veno to
the osto erative erio ay a so ex erience ecrease ev- activate rotein C. T e quantity o APC or e is easure
e s o rotein C. by its a i o ytic activity on a s eci c chro ogenic substrate.
Antigenic rotein C can be assesse by ELISA or Laure
Laboratory Findings techno ogies, which have been we e ne .
T e abi ity to etect ecrease rotein C activity e en s on
the ty e o assay use ( ab e 27.4). P as a is eva uate or Factor V (Leiden)
LA be ore er or ing the rotein C assay to be sure that LA Activate rotein Cresistance (APC), a hy ercoagu ab e con-
is not the cause o thro bosis. T e as a concentration o ition iscovere in 1993, is associate with a oint uta-
uri e rotein C is 4 µg/ L. tion in the actor V gene (factor V [Leiden] ). T e vast ajority
Laboratory iagnosis o rotein C an rotein S e - o in ivi ua s with a i ia APC resistance have a s eci c
ciency invo ves unctiona an antigenic assays. Diagnosis oint utation in the rocoagu ant actor V gene enco ing
o a e ciency is best a e using unctiona assays or or a g uta ine substitution or arginine in the heavy chain
screening an a co bination o unctiona an anti- o actor V. T is a ino aci change a ters an APC c eavage
genic assays or con r ation an characterization o the site on actor V such that actor V/Va is artia y resistant to
e ciency.
inactivation by APC.
Protein C Testing T e utation s ows the inactivation o activate actor
V by APC causing a hy ercoagu ab e state. T e resence
Functiona rotein C assays can be either c ot base or chro- o actor V (Leiden) is the ost co on cause o inherite
ogenic. T e c ot-base etho invo ves a snake veno thro bo hi ia. It accounts or 20% to 50% o cases.
that s eci ca y activates rotein C. T e resu ting APC T e egree o abnor a ity o the APC-resistance assay
inhibits actors Va an VIIIa, thus ro onging the AP o corre ates with heterozygosity or ho ozygosity or the ac-
a syste in which a the coagu ation actors are constant y tor V Lei en utation; ho ozygous carriers have a very ow
resent an in excess.
APC-resistance ratio, but the ratio or heterozygous carriers
is usua y 1.5 to 1.8.
T e carrier requency or the actor V Leiden utation
General Assay Types for varies e en ing on the o u ation. A roxi ate y 5% o
TABLE 27.4 Determination of Protein C in asy to atic white A ericans o non-His anic ancestry
Plasma are heterozygous carriers, whereas the carrier requency
a ong A rican A ericans, Asian A ericans, an Native
Antigenic Measures amount of material A ericans is <1%, an the carrier requency or His anics
present; does not measure function is inter e iate (2.5%). Ho ozygosity or actor V Leiden is
Chromogenic Measures some but not all functions uch ess co on but ay con er a substantia y increase
risk or thro bosis.
Clotting Measures all functions of the Factor V (Leiden) (Russe vi er veno –base screen-
protein C molecule ing test) is a si e unctiona c otting test inten e or