Page 570 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 570
554 PART 7 ■ Principles and Disorders of Hemostasis and Thrombosis
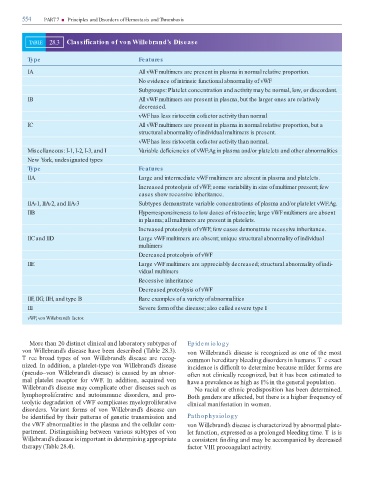
TABLE 28.3 Classi cation of von Willebrand’s Disease
Type Features
IA All vWF multimers are present in plasma in normal relative proportion.
No evidence of intrinsic functional abnormality of vWF
Subgroups: Platelet concentration and activity may be normal, low, or discordant.
IB All vWF multimers are present in plasma, but the larger ones are relatively
decreased.
vWF has less ristocetin cofactor activity than normal
IC All vWF multimers are present in plasma in normal relative proportion, but a
structural abnormality of individual multimers is present.
vWF has less ristocetin cofactor activity than normal.
Miscellaneous: I-1, I-2, I-3, and I Variable de ciencies of vWF:Ag in plasma and/or platelets and other abnormalities
New York, undesignated types
Type Features
IIA Large and intermediate vWF multimers are absent in plasma and platelets.
Increased proteolysis of vWF; some variability in size of multimer present; few
cases show recessive inheritance.
IIA-1, IIA-2, and IIA-3 Subtypes demonstrate variable concentrations of plasma and/or platelet vWF:Ag.
IIB Hyperresponsiveness to low doses of ristocetin; large vWF multimers are absent
in plasma; all multimers are present in platelets.
Increased proteolysis of vWF; few cases demonstrate recessive inheritance.
IIC and IID Large vWF multimers are absent; unique structural abnormality of individual
multimers
Decreased proteolysis of vWF
IIE Large vWF multimers are appreciably decreased; structural abnormality of indi-
vidual multimers
Recessive inheritance
Decreased proteolysis of vWF
IIF, IIG, IIH, and type B Rare examples of a variety of abnormalities
III Severe form of the disease; also called severe type I
vWF, von Willebrand’s factor.
More than 20 istinct c inica an aboratory subty es o Epidem iology
von Wi ebran ’s isease have been escribe ( ab e 28.3). von Wi ebran ’s isease is recognize as one o the ost
T ree broa ty es o von Wi ebran ’s isease are recog- co on here itary b ee ing isor ers in hu ans. T e exact
nize . In a ition, a ate et-ty e von Wi ebran ’s isease inci ence is i cu t to eter ine because i er or s are
( seu o–von Wi ebran ’s isease) is cause by an abnor- o en not c inica y recognize , but it has been esti ate to
a ate et rece tor or vWF. In a ition, acquire von have a reva ence as high as 1% in the genera o u ation.
Wi ebran ’s isease ay co icate other iseases such as No racia or ethnic re is osition has been eter ine .
y ho ro i erative an autoi une isor ers, an ro- Both gen ers are a ecte , but there is a higher requency o
teo ytic egra ation o vWF co icates ye o ro i erative c inica ani estation in wo en.
isor ers. Variant or s o von Wi ebran ’s isease can
be i enti e by their atterns o genetic trans ission an Pathophysiology
the vWF abnor a ities in the as a an the ce u ar co - von Wi ebran ’s isease is characterize by abnor a ate-
art ent. Distinguishing between various subty es o von et unction, ex resse as a ro onge b ee ing ti e. T is is
Wi ebran ’s isease is i ortant in eter ining a ro riate a consistent n ing an ay be acco anie by ecrease
thera y ( ab e 28.4). actor VIII rocoagu ant activity.