Page 569 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 569
CHAPTER 28 ■ Disorders of Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Blood Coagulation Factors, Hypercoagulable State, and Anticoagulant Therapy 553
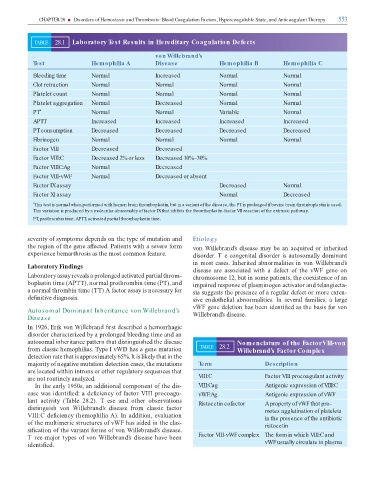
TABLE 28.1 Laboratory Test Results in Hereditary Coagulation Defects
von Willebrand’s
Test Hemophilia A Disease Hemophilia B Hemophilia C
Bleeding time Normal Increased Normal Normal
Clot retraction Normal Normal Normal Normal
Platelet count Normal Normal Normal Normal
Platelet aggregation Normal Decreased Normal Normal
PT * Normal Normal Variable Normal
APTT Increased Increased Increased Increased
PT consumption Decreased Decreased Decreased Decreased
Fibrinogen Normal Normal Normal Normal
Factor VIII Decreased Decreased
Factor VIII:C Decreased 2% or less Decreased 10%–30%
Factor VIIIC:Ag Normal Decreased
Factor VIII-vWF Normal Decreased or absent
Factor IX assay Decreased Normal
Factor XI assay Normal Decreased
* This test is normal when performed with human brain thromboplastin, but in a variant of the disease, the PT is prolonged if bovine brain thromboplastin is used.
This variation is produced by a molecular abnormality of factor IX that inhibits the thromboplastin-factor VII reaction of the extrinsic pathway.
PT, prothrombin time; APTT, activated partial thromboplastin time.
severity o sy to s e en s on the ty e o utation an Etiology
the region o the gene a ecte . Patients with a severe or von Wi ebran ’s isease ay be an acquire or inherite
ex erience he arthrosis as the ost co on eature. isor er. T e congenita isor er is autoso a y o inant
in ost cases. Inherite abnor a ities in von Wi ebran ’s
Laboratory Findings
isease are associate with a e ect o the vWF gene on
Laboratory assay revea s a ro onge activate artia thro - chro oso e 12, but in so e atients, the coexistence o an
bo astin ti e (AP ), nor a rothro bin ti e (P ), an i aire res onse o as inogen activator an te angiecta-
a nor a thro bin ti e ( ) A actor assay is necessary or sia suggests the resence o a regu ar e ect or ore exten-
e nitive iagnosis. sive en othe ia abnor a ities. In severa a i ies, a arge
vWF gene e etion has been i enti e as the basis or von
Autosom al Dom inant Inheritance von Willebrand’s
Disease Wi ebran ’s isease.
In 1926, Erik von Wi ebran rst escribe a he orrhagic
isor er characterize by a ro onge b ee ing ti e an an
autoso a inheritance attern that istinguishe the isease Nomenclature of the Factor VIII-von
ro c assic he o hi ias. y e I vWD has a gene utation TABLE 28.2 Willebrand’s Factor Complex
etection rate that is a roxi ate y 65%. It is ike y that in the
ajority o negative utation etection cases, the utations Term Description
are ocate within introns or other regu atory sequences that
are not routine y ana yze . VIII:C Factor VIII procoagulant activity
In the ear y 1950s, an a itiona co onent o the is- VIII:Cag Antigenic expression of VIII:C
ease was i enti e : a e ciency o actor VIII rocoagu- vWF:Ag Antigenic expression of vWF
ant activity ( ab e 28.2). T ese an other observations Ristocetin cofactor A property of vWF that pro-
istinguish von Wi ebran ’s isease ro c assic actor motes agglutination of platelets
VIII:C e ciency (he o hi ia A). In a ition, eva uation in the presence of the antibiotic
o the u ti eric structures o vWF has ai e in the c as- ristocetin
si cation o the variant or s o von Wi ebran ’s isease.
Tree ajor ty es o von Wi ebran ’s isease have been Factor VIII-vWF complex The form in which VIII:C and
i enti e . vWF usually circulate in plasma