Page 588 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 588
572 PART 7 ■ Principles and Disorders of Hemostasis and Thrombosis
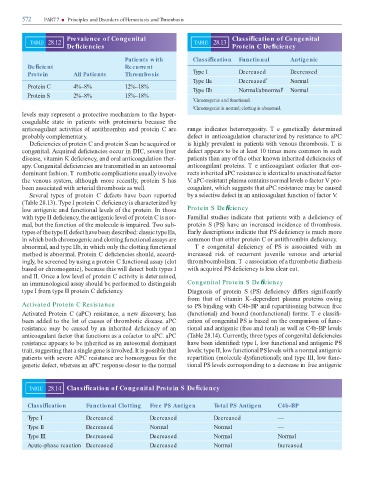
Prevalence of Congenital Classi cation of Congenital
TABLE 28.12 TABLE 28.13
De ciencies Protein C De ciency
Patients w ith Classi cation Functional Antigenic
De cient Recurrent
Protein All Patients Thrombosis Type I Decreased Decreased
Type IIa Decreased * Normal
Protein C 4%–8% 12%–18%
Type IIb Normal/abnormal † Normal
Protein S 2%–8% 15%–18%
* Chromogenic and functional.
† Chromogenic is normal; clotting is abnormal.
eve s ay re resent a rotective echanis to the hy er-
coagu ab e state in atients with roteinuria because the
anticoagu ant activities o antithro bin an rotein C are range in icates heterozygosity. T e genetica y eter ine
robab y co e entary. e ect in anticoagu ation characterize by resistance to aPC
De ciencies o rotein C an rotein S can be acquire or is high y reva ent in atients with venous thro bosis. T is
congenita . Acquire e ciencies occur in DIC, severe iver e ect a ears to be at east 10 ti es ore co on in such
isease, vita in K e ciency, an ora anticoagu ation ther- atients than any o the other known inherite e ciencies o
a y. Congenita e ciencies are trans itte in an autoso a anticoagu ant roteins. T e anticoagu ant co actor that cor-
o inant ashion. T ro botic co ications usua y invo ve rects inherite aPC resistance is i entica to unactivate actor
the venous syste , a though ore recent y, rotein S has V. aPC-resistant as a contains nor a eve s o actor V ro-
been associate with arteria thro bosis as we . coagu ant, which suggests that aPC resistance ay be cause
Severa ty es o rotein C e ects have been re orte by a se ective e ect in an anticoagu ant unction o actor V.
( ab e 28.13). y e I rotein C e ciency is characterize by
ow antigenic an unctiona eve s o the rotein. In those Protein S De ciency
with ty e II e ciency, the antigenic eve o rotein C is nor- Fa i ia stu ies in icate that atients with a e ciency o
a , but the unction o the o ecu e is i aire . wo sub- rotein S (PS) have an increase inci ence o thro bosis.
ty es o the ty e II e ect have been escribe : c assic ty e IIa, Ear y escri tions in icate that PS e ciency is uch ore
in which both chro ogenic an c otting unctiona assays are co on than either rotein C or antithro bin e ciency.
abnor a , an ty e IIb, in which on y the c otting unctiona Te congenita e ciency o PS is associate with an
etho is abnor a . Protein C e ciencies shou , accor - increase risk o recurrent juveni e venous an arteria
ing y, be screene by using a rotein C unctiona assay (c ot thro boe bo is . T e association o a thro botic iathesis
base or chro ogenic), because this wi etect both ty es I with acquire PS e ciency is ess c ear cut.
an II. Once a ow eve o rotein C activity is eter ine ,
an i uno ogica assay shou be er or e to istinguish Congenital Protein S De ciency
ty e I ro ty e II rotein C e ciency. Diagnosis o rotein S (PS) e ciency i ers signi cant y
ro that o vita in K– e en ent as a roteins owing
Activated Protein C Resistance to PS bin ing with C4b-BP an re artitioning between ree
Activate Protein C (aPC) resistance, a new iscovery, has ( unctiona ) an boun (non unctiona ) or s. T e c assi -
been a e to the ist o causes o thro botic isease. aPC cation o congenita PS is base on the co arison o unc-
resistance ay be cause by an inherite e ciency o an tiona an antigenic ( ree an tota ) as we as C4b-BP eve s
anticoagu ant actor that unctions as a co actor to aPC. aPC ( ab e 28.14). Current y, three ty es o congenita e ciencies
resistance a ears to be inherite as an autoso a o inant have been i enti e : ty e I, ow unctiona an antigenic PS
trait, suggesting that a sing e gene is invo ve . It is ossib e that eve s; ty e II, ow unctiona PS eve s with a nor a antigenic
atients with severe APC resistance are ho ozygous or the re artition ( o ecu e ys unctiona ); an ty e III, ow unc-
genetic e ect, whereas an aPC res onse c oser to the nor a tiona PS eve s corres on ing to a ecrease in ree antigenic
TABLE 28.14 Classi cation of Congenital Protein S De ciency
Classi cation Functional Clotting Free PS Antigen Total PS Antigen C4b-BP
Type I Decreased Decreased Decreased —
Type II Decreased Normal Normal —
Type III Decreased Decreased Normal Normal
Acute-phase reaction Decreased Decreased Normal Increased