Page 593 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 593
CHAPTER 28 ■ Disorders of Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Blood Coagulation Factors, Hypercoagulable State, and Anticoagulant Therapy 577
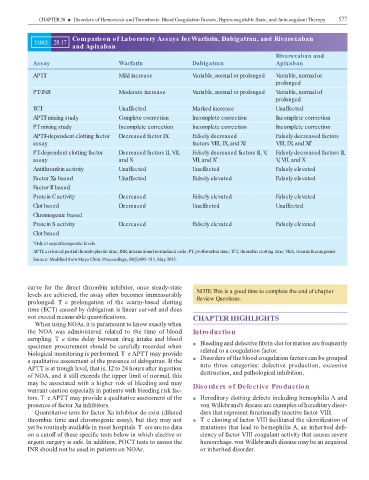
Comparison of Laboratory Assays for Warfarin, Dabigatran, and Rivaroxaban
TABLE 28.17
and Apixaban
Rivaroxaban and
Assay Warfarin Dabigatran Apixaban
APTT Mild increase Variable, normal or prolonged Variable, normal or
prolonged
PT/INR Moderate increase Variable, normal or prolonged Variable, normal of
prolonged
TCT Unaffected Marked increase Unaffected
APTT mixing study Complete correction Incomplete correction Incomplete correction
PT mixing study Incomplete correction Incomplete correction Incomplete correction
APTT-dependent clotting factor Decreased factor IX Falsely decreased Falsely decreased factors
assay factors VIII, IX, and XI VIII, IX, and XI *
PT-dependent clotting factor Decreased factors II, VII, Falsely decreased factors II, V Falsely decreased factors II,
,
,
assay and X VII, and X * V VII, and X
Antithrombin activity Unaffected Unaffected Falsely elevated
Factor Xa based Unaffected Falsely elevated Falsely elevated
Factor II based
Protein C activity Decreased Falsely elevated Falsely elevated
Clot based Decreased Unaffected Unaffected
Chromogenic based
Protein S activity Decreased Falsely elevated Falsely elevated
Clot based
* Only at supratherapeutic levels.
APTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; INR, international normalized ratio; PT, prothrombin time; TCT, thrombin clotting time; VKA, vitamin K antagonist.
Source: Modi ed from Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 88(5):495–511, May 2013.
curve or the irect thro bin inhibitor, once stea y-state NOTE: This is a good time to complete the end of chapter
eve s are achieve , the assay o en beco es i easurab y Review Questions.
ro onge . T e ro ongation o the ecarin-base c otting
ti e (EC ) cause by abigatran is inear curve an oes
not excee easurab e quanti cations. CHAP ER HIGHLIGH S
When using NOAs, it is ara ount to know exact y when
the NOA was a inistere re ate to the ti e o b oo Introduction
sa ing. T e ti e e ay between rug intake an b oo
s eci en rocure ent shou be care u y recor e when ■ B ee ing an e ective brin c ot or ation are requent y
bio ogica onitoring is er or e . T e AP ay rovi e re ate to a coagu ation actor.
a qua itative assess ent o the resence o abigatran. I the ■ Disor ers o the b oo coagu ation actors can be grou e
AP is at trough eve , that is, 12 to 24 hours a er ingestion into three categories: e ective ro uction, excessive
o NOA, an it sti excee s the u er i it o nor a , this estruction, an atho ogica inhibition.
ay be associate with a higher risk o b ee ing an ay Disorders of Defective Production
warrant caution es ecia y in atients with b ee ing risk ac-
tors. T e AP ay rovi e a qua itative assess ent o the ■ Here itary c otting e ects inc u ing he o hi ia A an
resence o actor Xa inhibitors. von Wi ebran ’s isease are exa es o here itary isor-
Quantitative tests or actor Xa inhibitor o exist ( i ute ers that re resent unctiona y inactive actor VIII.
thro bin ti e an chro ogenic assay), but they ay not ■ T e c oning o actor VIII aci itate the i enti cation o
yet be routine y avai ab e in ost hos ita s. T ere are no ata utations that ea to he o hi ia A, an inherite e -
on a cuto o these s eci c tests be ow in which e ective or ciency o actor VIII coagu ant activity that causes severe
urgent surgery is sa e. In a ition, POC tests to assess the he orrhage. von Wi ebran ’s isease ay be an acquire
INR shou not be use in atients on NOAs. or inherite isor er.