Page 410 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 410
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Habitat mebooksfree.com Portal of Entry CHAPTER 47 Basic Mycology 399 mebooksfree.com
countries mebooksfree.com
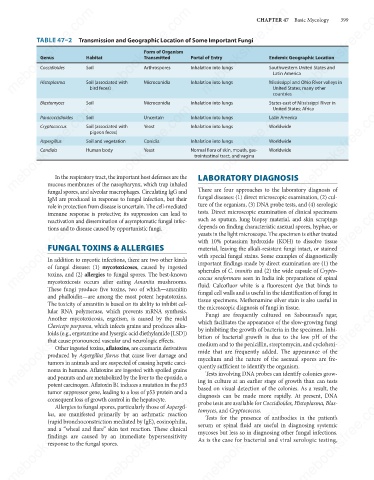
TABLE 47–2 Transmission and Geographic Location of Some Important Fungi
Form of Organism
Endemic Geographic Location
Transmitted
Genus
Coccidioides
Soil
Arthrospores
Southwestern United States and
Inhalation into lungs
Latin America
Histoplasma
United States; many other
bird feces)
Microconidia
Inhalation into lungs
Soil
Blastomyces Soil (associated with Microconidia Inhalation into lungs Mississippi and Ohio River valleys in
States east of Mississippi River in
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Soil (associated with Yeast Inhalation into lungs Worldwide mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
United States; Africa
Inhalation into lungs
Latin America
Uncertain
Paracoccidioides
Soil
Cryptococcus
pigeon feces)
Soil and vegetation
Conidia
Aspergillus
Worldwide
Inhalation into lungs
Candida
Yeast
Human body
Worldwide
Normal flora of skin, mouth, gas-
trointestinal tract, and vagina
In the respiratory tract, the important host defenses are the
mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, which trap inhaled
There are four approaches to the laboratory diagnosis of
fungal spores, and alveolar macrophages. Circulating IgG and
fungal diseases: (1) direct microscopic examination, (2) cul-
IgM are produced in response to fungal infection, but their LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com depends on finding characteristic asexual spores, hyphae, or mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
ture of the organism, (3) DNA probe tests, and (4) serologic
role in protection from disease is uncertain. The cell-mediated
tests. Direct microscopic examination of clinical specimens
immune response is protective; its suppression can lead to
such as sputum, lung biopsy material, and skin scrapings
reactivation and dissemination of asymptomatic fungal infec-
tions and to disease caused by opportunistic fungi.
yeasts in the light microscope. The specimen is either treated
with 10% potassium hydroxide (KOH) to dissolve tissue
FUNGAL TOXINS & ALLERGIES
material, leaving the alkali-resistant fungi intact, or stained
with special fungal stains. Some examples of diagnostically
In addition to mycotic infections, there are two other kinds
important findings made by direct examination are (1) the
of fungal disease: (1) mycotoxicoses, caused by ingested
spherules of C. immitis and (2) the wide capsule of Crypto-
toxins, and (2) allergies to fungal spores. The best-known
mycotoxicosis occurs after eating Amanita mushrooms.
fluid. Calcofluor white is a fluorescent dye that binds to
These fungi produce five toxins, two of which—amanitin
fungal cell walls and is useful in the identification of fungi in
and phalloidin—are among the most potent hepatotoxins. coccus neoformans seen in India ink preparations of spinal
tissue specimens. Methenamine silver stain is also useful in
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com which facilitates the appearance of the slow-growing fungi mebooksfree.com
The toxicity of amanitin is based on its ability to inhibit cel-
the microscopic diagnosis of fungi in tissue.
lular RNA polymerase, which prevents mRNA synthesis.
Fungi are frequently cultured on Sabouraud’s agar,
Another mycotoxicosis, ergotism, is caused by the mold
Claviceps purpurea, which infects grains and produces alka-
by inhibiting the growth of bacteria in the specimen. Inhi-
loids (e.g., ergotamine and lysergic acid diethylamide [LSD])
bition of bacterial growth is due to the low pH of the
that cause pronounced vascular and neurologic effects.
medium and to the penicillin, streptomycin, and cyclohexi-
Other ingested toxins, aflatoxins, are coumarin derivatives
mide that are frequently added. The appearance of the
produced by Aspergillus flavus that cause liver damage and
mycelium and the nature of the asexual spores are fre-
tumors in animals and are suspected of causing hepatic carci-
quently sufficient to identify the organism.
noma in humans. Aflatoxins are ingested with spoiled grains
Tests involving DNA probes can identify colonies grow-
and peanuts and are metabolized by the liver to the epoxide, a
potent carcinogen. Aflatoxin B1 induces a mutation in the p53
based on visual detection of the colonies. As a result, the
tumor suppressor gene, leading to a loss of p53 protein and a ing in culture at an earlier stage of growth than can tests
diagnosis can be made more rapidly. At present, DNA
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com serum or spinal fluid are useful in diagnosing systemic mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
consequent loss of growth control in the hepatocyte.
probe tests are available for Coccidioides, Histoplasma, Blas-
Allergies to fungal spores, particularly those of Aspergil-
tomyces, and Cryptococcus.
lus, are manifested primarily by an asthmatic reaction
Tests for the presence of antibodies in the patient’s
(rapid bronchoconstriction mediated by IgE), eosinophilia,
and a “wheal and flare” skin test reaction. These clinical
mycoses but less so in diagnosing other fungal infections.
findings are caused by an immediate hypersensitivity
As is the case for bacterial and viral serologic testing,
response to the fungal spores.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com