Page 415 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 415
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Important Clinical Findings Laboratory Diagnosis mebooksfree.com
404
PART V Mycology
TABLE 48–2 Important Features of Skin and Subcutaneous Fungal Diseases
Forms in Tissue Seen
Mode of Transmission
Genus
by Microscopy
Hyphae
Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
Tinea capitis, tinea pedis, etc.,
Human to human
Trichophyton,
“ringworm” Ring of inflammatory,
prep shows septate
Epidermophyton
pruritic vesicles with a healing
hyphae culture on Sab-
center
ouraud’s agar
Microsporum
Animal to human as well as
Hyphae
human to human Tinea capitis, tinea pedis, etc., KOH prep shows septate
“ringworm” Ring of inflammatory,
hyphae culture on Sab-
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com contain hyphae. Patients with tinea infections show positive mebooksfree.com
ouraud’s agar
pruritic vesicles with a healing center
Human to human
Scaly plaques on trunk; often
Hyphae and yeasts
KOH prep shows mixture of
Malassezia
hypopigmented; often nonpruritic
hyphae and yeasts
Yeasts
KOH prep shows cigar-
Penetrating lesion in gar-
Pustule or ulcer on hands often with
Sporothrix
den implants fungal
shaped yeasts culture at
nodules on arms
20°C shows hyphae with
spores, e.g., rose thorn
daisy-like conidia
CUTANEOUS MYCOSES
Dermatophytoses
Scrapings of skin or nail placed in 10% potassium
hydroxide (KOH) on a glass slide show septate hyphae
Dermatophytoses are caused by fungi (dermatophytes)
under microscopy. Cultures on Sabouraud’s agar at room
that infect only superficial keratinized structures (skin, skin tests with fungal extracts (e.g., trichophytin).
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com exposed to ultraviolet light from a Wood’s lamp. mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
temperature develop typical hyphae and conidia. Tinea
hair, and nails), not deeper tissues. The most important
capitis lesions caused by Microsporum species can be
dermatophytes are classified in three genera: Trichophyton,
detected by seeing fluorescence when the lesions are
Epidermophyton, and Microsporum. They are spread from
infected persons by direct contact. Microsporum is also
Treatment involves local antifungal creams, such as (ter-
spread from animals such as dogs and cats. This indicates
binafine (Lamisil), undecylenic acid (Desenex), micon-
that to prevent reinfection, the animal must be treated also.
azole (Micatin), or tolnaftate (Tinactin). Oral griseofulvin
Dermatophytoses (tinea, ringworm) are chronic infec-
(Fulvicin) or oral itraconazole (Sporanox) can also be used.
tions often located in the warm, humid areas of the body
Tinea unguium can be treated with efinaconazole solution
1
(e.g., athlete’s foot and jock itch). Typical ringworm lesions
have an inflamed circular border containing papules and
skin dry and cool.
vesicles surrounding a clear area of relatively normal skin.
The lesions are typically pruritic. Broken hairs and dam-
aged nails are often seen. The disease is typically named for applied topically to the nails. Prevention centers on keeping
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
the affected body part (i.e., tinea capitis [head], tinea cor-
poris [body], tinea cruris [groin], and tinea pedis [foot])
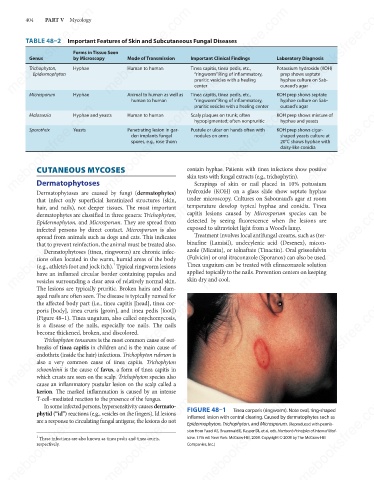
(Figure 48–1). Tinea unguium, also called onychomycosis,
is a disease of the nails, especially toe nails. The nails
become thickened, broken, and discolored.
Trichophyton tonsurans is the most common cause of out-
breaks of tinea capitis in children and is the main cause of
endothrix (inside the hair) infections. Trichophyton rubrum is
also a very common cause of tinea capitis. Trichophyton
schoenleinii is the cause of favus, a form of tinea capitis in
which crusts are seen on the scalp. Trichophyton species also
cause an inflammatory pustular lesion on the scalp called a
kerion. The marked inflammation is caused by an intense FIGURE 48–1 Tinea corporis (ringworm). Note oval, ring-shaped
mebooksfree.com
T-cell–mediated reaction to the presence of the fungus.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com inflamed lesion with central clearing. Caused by dermatophytes such as mebooksfree.com
In some infected persons, hypersensitivity causes dermato-
phytid (“id”) reactions (e.g., vesicles on the fingers). Id lesions
are a response to circulating fungal antigens; the lesions do not
Epidermophyton, Trichophyton, and Microsporum. (Reproduced with permis-
sion from Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Kasper DL et al, eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Med-
1
icine. 17th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2008. Copyright © 2008 by The McGraw-Hill
These infections are also known as tinea pedis and tinea cruris,
respectively.
Companies, Inc.)
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com