Page 518 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 518
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Class II CD4 protein TCR Helper Cytotoxic TCR CD8 protein MG infected 507 mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER 58 Cellular Basis of the Immune Response
Class I
MHC
Antigen
2
Antigen-
MHC
presenting
Virus-
cell
cell
T cell
T cell
CD28
B7
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com protein protein IL-2R IL-2 mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
IL-2R
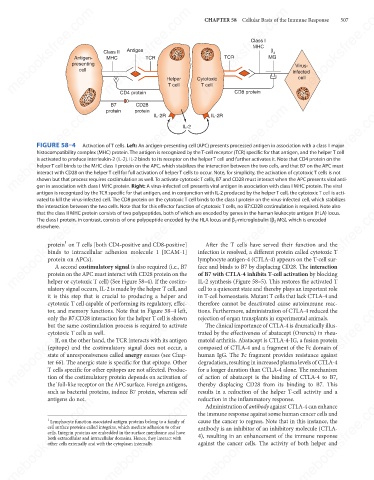
FIGURE 58–4
Activation of T cells. Left: An antigen-presenting cell (APC) presents processed antigen in association with a class II major
histocompatibility complex (MHC) protein. The antigen is recognized by the T-cell receptor (TCR) specific for that antigen, and the helper T cell
is activated to produce interleukin-2 (IL-2). IL-2 binds to its receptor on the helper T cell and further activates it. Note that CD4 protein on the
helper T cell binds to the MHC class II protein on the APC, which stabilizes the interaction between the two cells, and that B7 on the APC must
interact with CD28 on the helper T cell for full activation of helper T cells to occur. Note, for simplicity, the activation of cytotoxic T cells is not
shown but that process requires costimulation as well. To activate cytotoxic T cells, B7 and CD28 must interact when the APC presents viral anti-
gen in association with class I MHC protein. Right: A virus-infected cell presents viral antigen in association with class I MHC protein. The viral
antigen is recognized by the TCR specific for that antigen, and in conjunction with IL-2 produced by the helper T cell, the cytotoxic T cell is acti-
vated to kill the virus-infected cell. The CD8 protein on the cytotoxic T cell binds to the class I protein on the virus-infected cell, which stabilizes
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com infection is resolved, a different protein called cytotoxic T mebooksfree.com
the interaction between the two cells. Note that for this effector function of cytotoxic T cells, no B7:CD28 costimulation is required. Note also
that the class II MHC protein consists of two polypeptides, both of which are encoded by genes in the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) locus.
The class I protein, in contrast, consists of one polypeptide encoded by the HLA locus and β 2 -microglobulin (β 2 MG), which is encoded
elsewhere.
1
protein on T cells [both CD4-positive and CD8-positive]
After the T cells have served their function and the
binds to intracellular adhesion molecule 1 [ICAM-1]
lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) appears on the T-cell sur-
protein on APCs).
face and binds to B7 by displacing CD28. The interaction
A second costimulatory signal is also required (i.e., B7
protein on the APC must interact with CD28 protein on the
IL-2 synthesis (Figure 58–5). This restores the activated T
helper or cytotoxic T cell) (See Figure 58–4). If the costim-
ulatory signal occurs, IL-2 is made by the helper T cell, and
cell to a quiescent state and thereby plays an important role
it is this step that is crucial to producing a helper and of B7 with CTLA-4 inhibits T-cell activation by blocking
in T-cell homeostasis. Mutant T cells that lack CTLA-4 and
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com trated by the effectiveness of abatacept (Orencia) in rheu- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
cytotoxic T cell capable of performing its regulatory, effec-
therefore cannot be deactivated cause autoimmune reac-
tions. Furthermore, administration of CTLA-4 reduced the
tor, and memory functions. Note that in Figure 58–4 left,
rejection of organ transplants in experimental animals.
only the B7:CD28 interaction for the helper T cell is shown
The clinical importance of CTLA-4 is dramatically illus-
but the same costimulation process is required to activate
cytotoxic T cells as well.
If, on the other hand, the TCR interacts with its antigen
matoid arthritis. Abatacept is CTLA-4-IG, a fusion protein
composed of CTLA-4 and a fragment of the Fc domain of
(epitope) and the costimulatory signal does not occur, a
human IgG. The Fc fragment provides resistance against
state of unresponsiveness called anergy ensues (see Chap-
degradation, resulting in increased plasma levels of CTLA-4
ter 66). The anergic state is specific for that epitope. Other
T cells specific for other epitopes are not affected. Produc-
tion of the costimulatory protein depends on activation of
of action of abatacept is the binding of CTLA-4 to B7,
thereby displacing CD28 from its binding to B7. This
the Toll-like receptor on the APC surface. Foreign antigens,
such as bacterial proteins, induce B7 protein, whereas self for a longer duration than CTLA-4 alone. The mechanism
results in a reduction of the helper T-cell activity and a
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com cause the cancer to regress. Note that in this instance, the mebooksfree.com
antigens do not.
reduction in the inflammatory response.
Administration of antibody against CTLA-4 can enhance
the immune response against some human cancer cells and
1
Lymphocyte function-associated antigen proteins belong to a family of
cell surface proteins called integrins, which mediate adhesion to other
antibody is an inhibitor of an inhibitory molecule (CTLA-
cells. Integrin proteins are embedded in the surface membrane and have
4), resulting in an enhancement of the immune response
both extracellular and intracellular domains. Hence, they interact with
against the cancer cells. The activity of both helper and
other cells externally and with the cytoplasm internally.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com