Page 74 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 74
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER 9 Laboratory Diagnosis
63
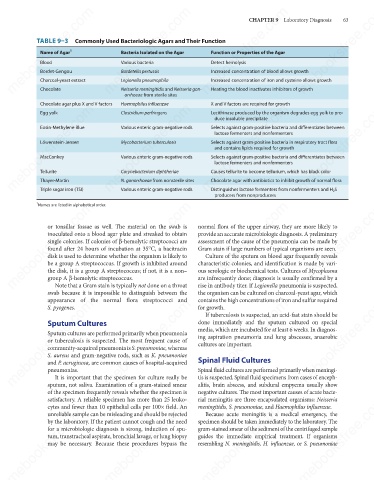
TABLE 9–3 Commonly Used Bacteriologic Agars and Their Function
1
Function or Properties of the Agar
Name of Agar
Bacteria Isolated on the Agar
Detect hemolysis
Blood
Various bacteria
Bordet-Gengou
Bordetella pertussis
Increased concentration of blood allows growth
Legionella pneumophila
Charcoal-yeast extract
Increased concentration of iron and cysteine allows growth
Heating the blood inactivates inhibitors of growth
Chocolate
Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gon-
orrhoeae from sterile sites
X and V factors are required for growth
Haemophilus influenzae
Chocolate agar plus X and V factors
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Lecithinase produced by the organism degrades egg yolk to pro-
Clostridium perfringens
Egg yolk
duce insoluble precipitate
Selects against gram-positive bacteria and differentiates between
Eosin-Methylene Blue
Various enteric gram-negative rods
lactose fermenters and nonfermenters
Löwenstein-Jensen
Selects against gram-positive bacteria in respiratory tract flora
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
and contains lipids required for growth
Selects against gram-positive bacteria and differentiates between
Various enteric gram-negative rods
MacConkey
lactose fermenters and nonfermenters
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Causes tellurite to become tellurium, which has black color
Tellurite
N. gonorrhoeae from nonsterile sites
Chocolate agar with antibiotics to inhibit growth of normal flora
Thayer-Martin
Distinguishes lactose fermenters from nonfermenters and H 2 S
Triple sugar iron (TSI)
Various enteric gram-negative rods
producers from nonproducers
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com normal flora of the upper airway, they are more likely to mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
1
Names are listed in alphabetical order.
or tonsillar fossae as well. The material on the swab is
provide an accurate microbiologic diagnosis. A preliminary
inoculated onto a blood agar plate and streaked to obtain
assessment of the cause of the pneumonia can be made by
single colonies. If colonies of β-hemolytic streptococci are
Gram stain if large numbers of typical organisms are seen.
found after 24 hours of incubation at 35°C, a bacitracin
Culture of the sputum on blood agar frequently reveals
disk is used to determine whether the organism is likely to
characteristic colonies, and identification is made by vari-
be a group A streptococcus. If growth is inhibited around
the disk, it is a group A streptococcus; if not, it is a non–
group A β-hemolytic streptococcus.
are infrequently done; diagnosis is usually confirmed by a
Note that a Gram stain is typically not done on a throat
rise in antibody titer. If Legionella pneumonia is suspected,
swab because it is impossible to distinguish between the ous serologic or biochemical tests. Cultures of Mycoplasma
the organism can be cultured on charcoal-yeast agar, which
appearance of the normal flora streptococci and
contains the high concentrations of iron and sulfur required
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com done immediately and the sputum cultured on special mebooksfree.com
for growth.
S. pyogenes.
If tuberculosis is suspected, an acid-fast stain should be
Sputum Cultures
media, which are incubated for at least 6 weeks. In diagnos-
Sputum cultures are performed primarily when pneumonia
ing aspiration pneumonia and lung abscesses, anaerobic
or tuberculosis is suspected. The most frequent cause of
cultures are important.
community-acquired pneumonia is S. pneumoniae, whereas
S. aureus and gram-negative rods, such as K. pneumoniae
Spinal Fluid Cultures
and P. aeruginosa, are common causes of hospital-acquired
pneumonias.
It is important that the specimen for culture really be
tis is suspected. Spinal fluid specimens from cases of enceph-
sputum, not saliva. Examination of a gram-stained smear
alitis, brain abscess, and subdural empyema usually show
of the specimen frequently reveals whether the specimen is Spinal fluid cultures are performed primarily when meningi-
negative cultures. The most important causes of acute bacte-
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com specimen should be taken immediately to the laboratory. The mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
rial meningitis are three encapsulated organisms: Neisseria
satisfactory. A reliable specimen has more than 25 leuko-
meningitidis, S. pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae.
cytes and fewer than 10 epithelial cells per 100× field. An
Because acute meningitis is a medical emergency, the
unreliable sample can be misleading and should be rejected
by the laboratory. If the patient cannot cough and the need
gram-stained smear of the sediment of the centrifuged sample
for a microbiologic diagnosis is strong, induction of spu-
tum, transtracheal aspirate, bronchial lavage, or lung biopsy
guides the immediate empirical treatment. If organisms
resembling N. meningitidis, H. influenzae, or S. pneumoniae
may be necessary. Because these procedures bypass the
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com