Page 8 - Top Class Additional Mathematics Tg 4
P. 8
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 1 Functions
1.2 Composite Functions Textbook
Fungsi Gubahan
pg. 12 – 19
SMART Notes
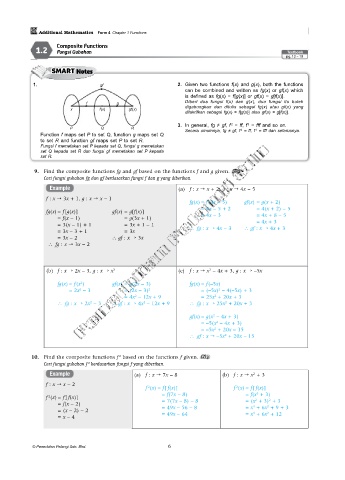
1. gf 2. Given two functions f(x) and g(x), both the functions
can be combined and written as fg(x) or gf(x) which
is defined as fg(x) = f[g(x)] or gf(x) = g[f(x)].
f g Diberi dua fungsi f(x) dan g(x), dua fungsi itu boleh
x f(x) gf(x) digabungkan dan ditulis sebagai fg(x) atau gf(x) yang
ditakrifkan sebagai fg(x) = f[g(x)] atau gf(x) = g[f(x)].
3. In general, fg ≠ gf, f = ff, f = fff and so on.
3
2
P Q R Secara umumnya, fg ≠ gf, f = ff, f = fff dan seterusnya.
3
2
Function f maps set P to set Q, function g maps set Q
to set R and function gf maps set P to set R.
Fungsi f memetakan set P kepada set Q, fungsi g memetakan
set Q kepada set R dan fungsi gf memetakan set P kepada
set R.
9. Find the composite functions fg and gf based on the functions f and g given. PL 3
Cari fungsi gubahan fg dan gf berdasarkan fungsi f dan g yang diberikan.
Example (a) f : x → x + 2, g : x → 4x – 5
f : x → 3x + 1, g : x → x – 1
fg(x) = f(4x – 5) gf(x) = g(x + 2)
= 4x – 5 + 2 = 4(x + 2) – 5
fg(x) = f[g(x)] gf(x) = g[f(x)] = 4x – 3 = 4x + 8 – 5
= f(x – 1) = g(3x + 1)
= 4x + 3
= 3(x – 1) + 1 = 3x + 1 – 1 ∴ fg : x → 4x – 3 ∴ gf : x → 4x + 3
= 3x – 3 + 1 = 3x
= 3x – 2 ∴ gf : x → 3x
∴ fg : x → 3x – 2
2
(b) f : x → 2x – 3, g : x → x 2 (c) f : x → x – 4x + 3, g : x → –5x
fg(x) = f(x ) gf(x) = g(2x – 3) fg(x) = f(–5x)
2
= 2x – 3 = (2x – 3) 2 = (–5x) – 4(–5x) + 3
2
2
= 4x – 12x + 9 = 25x + 20x + 3
2
2
∴ fg : x → 2x – 3 ∴ gf : x → 4x – 12x + 9 ∴ fg : x → 25x + 20x + 3
2
2
2
gf(x) = g(x – 4x + 3)
2
= –5(x – 4x + 3)
2
= –5x + 20x – 15
2
∴ gf : x → –5x + 20x – 15
2
2
10. Find the composite functions f based on the functions f given. PL 3
Cari fungsi gubahan f berdasarkan fungsi f yang diberikan.
2
Example (a) f : x → 7x – 8 (b) f : x → x + 3
2
f : x → x – 2
2
2
f (x) = f[ f(x)] f (x) = f[ f(x)]
2
= f(7x – 8) = f(x + 3)
f (x) = f[ f(x)] = 7(7x – 8) – 8 = (x + 3) + 3
2
2
2
= f(x – 2) 4 2
= (x – 2) – 2 = 49x – 56 – 8 = x + 6x + 9 + 3
2
= 49x – 64
= x + 6x + 12
4
= x – 4
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 6