Page 26 - Focus SPM 2022 - Additional Mathematics
P. 26
Additional Mathematics SPM Chapter 1 Functions
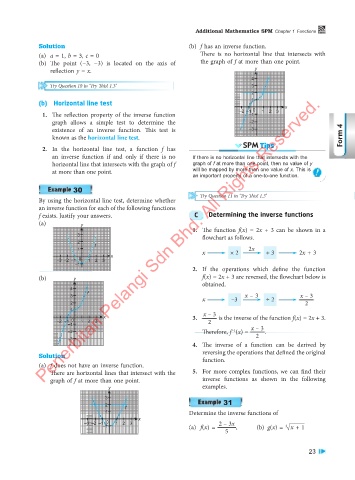
Solution Solution (b) f has an inverse function.
(a) y (a) a = 1, b = 3, c = 0 There is no horizontal line that intersects with
y = f(x) the graph of f at more than one point.
5 y = x (b) The point (−3, −3) is located on the axis of
4 reflection y = x. y
3 4
2 y = g(x) Try Question 10 in ‘Try This! 1.3’ 3
1 2
x 1
–6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 (b) Horizontal line test
–1 0 x
–2 1. The reflection property of the inverse function –2 –1 –1 1 2 3
–3 graph allows a simple test to determine the –2
–4 existence of an inverse function. This test is –3
–5 known as the horizontal line test. Form 4
–6 SPM Tips
2. In the horizontal line test, a function f has
(b) y an inverse function if and only if there is no If there is no horizontal line that intersects with the
y = x
5 y = g(x) horizontal line that intersects with the graph of f graph of f at more than one point, then no value of y
4 at more than one point. will be mapped by more than one value of x. This is
an important property of a one-to-one function.
3 y = f(x)
2 30
1 Try Question 11 in ‘Try This! 1.3’
x By using the horizontal line test, determine whether
–4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 x Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
–1 an inverse function for each of the following functions
–2 f exists. Justify your answers. C Determining the inverse functions
–3 (a) y
–4 1. The function f(x) = 2x + 3 can be shown in a
3 flowchart as follows.
2
Try Question 9 in ‘Try This! 1.3’ 1 f x × 2 2 x + 3 2x + 3
x
–3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3
–1
(V) If a point (a, b) lies on the graph y = f(x), then 2. If the operations which define the function
the point (b, a) lies on the graph y = g(x) where (b) y f(x) = 2x + 3 are reversed, the flowchart below is
f and g are inverse functions of each other. obtained.
4
f
3 x – 3 x – 3
29 2 x –3 ÷ 2 2
The following table shows the points on the graph of 1 x – 3
y = f(x) and the corresponding points on the graph of –2 –1 0 1 2 3 3. 2 is the inverse of the function f(x) = 2x + 3.
y = g(x). –1 Therefore, f (x) = x – 3 .
–1
–2
2
Point on the graph of Point on the graph of –3 4. The inverse of a function can be derived by
y = f(x) y = g(x) Penerbitan
Solution reversing the operations that defined the original
(−3, −3) (−3, −3) function.
(a) f does not have an inverse function.
(−1, 1) (a, −1) There are horizontal lines that intersect with the 5. For more complex functions, we can find their
inverse functions as shown in the following
(0, b) (3, c) graph of f at more than one point. examples.
y
Given f and g are inverse functions of each other. 3 31
(a) Determine the values of a, b and c. 2 f
(b) Why does the point (−3, −3) on the graph 1 Determine the inverse functions of
of y = f(x) remain unchanged on the graph of –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 x 2 – 3x
x +
3
y = g(x)? –1 (a) f(x) = 5 , (b) g(x) = AB 1
23