Page 27 - Focus SPM 2022 - Additional Mathematics
P. 27
Additional Mathematics SPM Chapter 1 Functions
Solution 33
2 – 3x
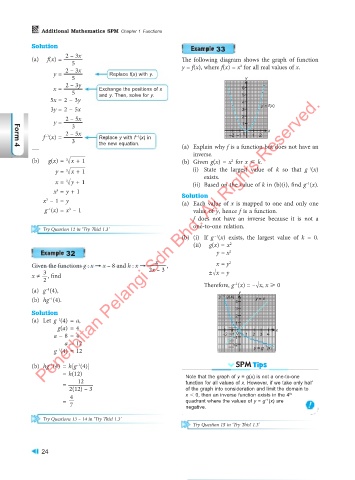
(a) f(x) = The following diagram shows the graph of function
5 2
2 – 3x y = f(x), where f(x) = x for all real values of x.
y = Replace f(x) with y.
5 y
x = 2 – 3y Exchange the positions of x 6
5 and y. Then, solve for y. 5
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
5x = 2 – 3y 4
3y = 2 – 5x 3 y = f(x)
y = 2 – 5x 2
3 1
2 – 5x 0 x
f (x) = Replace y with f (x) in –2 –1 1 2
–1
–1
3 the new equation.
(a) Explain why f is a function but does not have an
Form 4
inverse.
(b) g(x) = AB 1 (b) Given g(x) = x for x < k.
x +
3
2
–1
y = AB 1 (i) State the largest value of k so that g (x)
x +
3
exists.
x = AB 1 (ii) Based on the value of k in (b)(i), find g (x).
y +
3
–1
3
x = y + 1 Solution
x – 1 = y (a) Each value of x is mapped to one and only one
3
g (x) = x – 1 value of y, hence f is a function.
3
–1
f does not have an inverse because it is not a
one-to-one relation.
Try Question 12 in ‘Try This! 1.3’
(b) (i) If g (x) exists, the largest value of k = 0.
−1
(ii) g(x) = x
2
32 y = x
2
x 2
Given the functions g : x → x – 8 and h : x → , x = y
3 2x – 3 ±AB x = y
x ≠ —, find
2
–1
Therefore, g (x) = –AB x, x > 0
(a) g (4), y
−1
y = g(x)
(b) hg (4). 4 y = x
−1
3
Solution 2
−1
(a) Let g (4) = a, 1
g(a) = 4 x
a − 8 = 4 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4
–1
a = 12 –2
–1
–1
g (4) = 12 y = g (x)
–1
−1
(b) hg (4) = h[g (4)] SPM Tips
= h(12) Note that the graph of y = g(x) is not a one-to-one
12
= function for all values of x. However, if we take only half
2(12) – 3 of the graph into consideration and limit the domain to
x , 0, then an inverse function exists in the 4
th
4
= — quadrant where the values of y = g (x) are
−1
7
negative.
Try Questions 13 – 14 in ‘Try This! 1.3’
Try Question 15 in ‘Try This! 1.3’
24