Page 13 - Pra U STPM 2022 Penggal 2 - Mathematics
P. 13
Mathematics Semester 2 STPM Chapter 1 Limits and Continuity
10. The function f is defined as follows:
x, 0 < x < 2,
f(x) = C, 2 , x < 4, 1
x – 4x + 2, 4 , x < 5.
2
(a) Determine the value of C which makes f continuous on the interval 0 < x < 5.
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
(b) Sketch the graph of f.
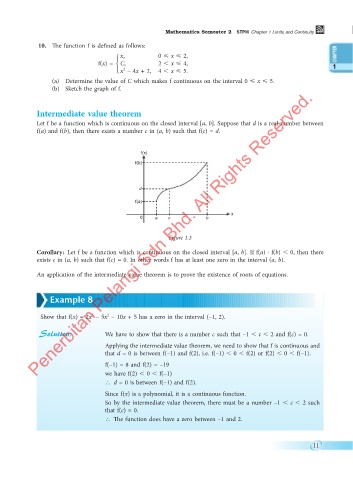
Intermediate value theorem
Let f be a function which is continuous on the closed interval [a, b]. Suppose that d is a real number between
f(a) and f(b), then there exists a number c in (a, b) such that f(c) = d.
f(x)
f(b)
d
f(a)
x
0 a c b
Figure 1.3
Corollary: Let f be a function which is continuous on the closed interval [a, b]. If f(a) · f(b) , 0, then there
exists c in (a, b) such that f(c) = 0. In other words f has at least one zero in the interval (a, b).
An application of the intermediate value theorem is to prove the existence of roots of equations.
Example 8
2
3
Show that f(x) = 2x – 5x – 10x + 5 has a zero in the interval (–1, 2).
Solution: We have to show that there is a number c such that –1 , c , 2 and f(c) = 0.
Applying the intermediate value theorem, we need to show that f is continuous and
that d = 0 is between f(–1) and f(2), i.e. f(–1) , 0 , f(2) or f(2) , 0 , f(–1).
f(–1) = 8 and f(2) = –19
we have f(2) , 0 , f(–1)
\ d = 0 is between f(–1) and f(2).
Since f(x) is a polynomial, it is a continuous function.
So by the intermediate value theorem, there must be a number –1 , c , 2 such
that f(c) = 0.
\ The function does have a zero between –1 and 2.
11
01 STPM Math(T) T2.indd 11 28/01/2022 5:30 PM