Page 8 - Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics Core and Extended
P. 8
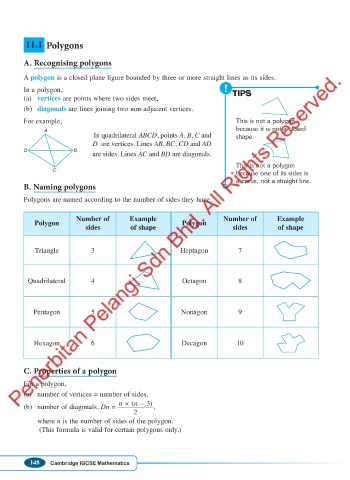
11.1 Polygons
A. Recognising polygons
A polygon is a closed plane figure bounded by three or more straight lines as its sides.
In a polygon, TIPS
(a) vertices are points where two sides meet,
(b) diagonals are lines joining two non- adjacent vertices.
For example, This is not a polygon
because it is not a closed
A
In quadrilateral ABCD, points A, B, C and shape.
D are vertices. Lines AB, BC, CD and AD
D B
are sides. Lines AC and BD are diagonals.
This is not a polygon
C
because one of its sides is
a curve, not a straight line.
B. Naming polygons
Polygons are named according to the number of sides they have.
Number of Example Number of Example
Polygon Polygon
sides of shape sides of shape
Triangle 3 Heptagon 7
Quadrilateral 4 Octagon 8
Pentagon 5 Nonagon 9
Hexagon 6 Decagon 10
C. Properties of a polygon
For a polygon,
(a) number of vertices = number of sides,
n × (n – 3)
(b) number of diagonals, Dn = ,
2
where n is the number of sides of the polygon.
(This formula is valid for certain polygons only.)
148 Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics
14/07/2022 10:14 AM
DA1501_pg 147 to 161.indd 148 14/07/2022 10:14 AM
DA1501_pg 147 to 161.indd 148