Page 12 - Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics Core and Extended
P. 12
11.3 Triangles
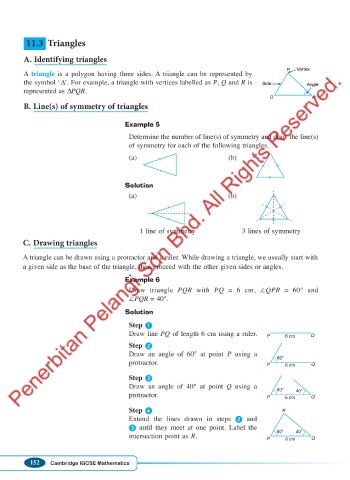
A. Identifying triangles
P Ve rtex
Vertex
A triangle is a polygon having three sides. A triangle can be represented by
the symbol ‘∆’. For example, a triangle with vertices labelled as P, Q and R is Side Angle
Side
Angle
represented as ∆PQR.
Q R
B. Line(s) of symmetry of triangles
Example 5
Determine the number of line(s) of symmetry and draw the line(s)
of symmetry for each of the following triangles.
(a) (b)
Solution
(a) (b)
1 line of symmetry 3 lines of symmetry
C. Drawing triangles
A triangle can be drawn using a protractor and a ruler. While drawing a triangle, we usually start with
a given side as the base of the triangle, then proceed with the other given sides or angles.
Example 6
Draw triangle PQR with PQ = 6 cm, ∠QPR = 60° and
∠PQR = 40°.
Solution
Step
Draw line PQ of length 6 cm using a ruler. P 6 cm Q
Step 2
Draw an angle of 60° at point P using a
60°
protractor. P 6 cm Q
Step 3
Draw an angle of 40° at point Q using a
60° 40°
protractor. P 6 cm Q
Step 4 R
Extend the lines drawn in steps 2 and
3 until they meet at one point. Label the
60° 40°
intersection point as R.
P 6 cm Q
152 Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics
14/07/2022 10:14 AM
DA1501_pg 147 to 161.indd 152 14/07/2022 10:14 AM
DA1501_pg 147 to 161.indd 152