Page 32 - Ranger SPM 2022 - Additional Mathematics
P. 32
Additional Mathematics SPM Chapter 2 Differentiation
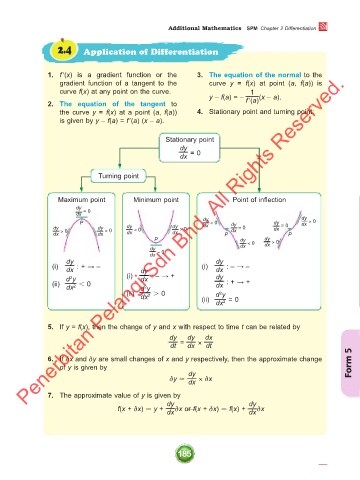
2.4 Application of Differentiation
Turning point
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
1. f ʹ(x) is a gradient function or the 3. The equation of the normal to the
gradient function of a tangent to the curve y = f(x) at point (a, f(a)) is
curve f(x) at any point on the curve. 1
y – f(a) = – f ʹ(a) (x – a).
2. The equation of the tangent to
the curve y = f(x) at a point (a, f(a)) 4. Stationary point and turning point:
is given by y – f(a) = f ʹ(a) (x – a).
Stationary point
dy
dx = 0
Turning point
Maximum point Minimum point Point of inflection
dy
dx = 0
dy dy
P dx < 0 dy dy = 0 dx > 0
dy > 0 dy < 0 dy < 0 dy > 0 dx = 0 dx
dx dx dx dx P P
P dy < 0 dy > 0
dy dx dx
dx = 0
dy dy
(i) dx : + → – dy (i) dx : – → –
d y (i) dx : – → + dy
2
(ii) 2 0 dx : + → +
dx d y
2
(ii) dx 2 0 (ii) d y 2 = 0
2
dx
5. If y = f(x), then the change of y and x with respect to time t can be related by
dy dy dx
dt = dx × dt
6. If δx and δy are small changes of x and y respectively, then the approximate change
of y is given by Form 5
dy
δy dx × δx
7. The approximate value of y is given by
dy dy
f(x + δx) y + dx δx or f(x + δx) f(x) + dx δx
185
02 Ranger Mate Tambahan Tg5.indd 185 25/02/2022 9:23 AM