Page 182 - The Effect of Hydrogen and Hydrides - ebook first test
P. 182
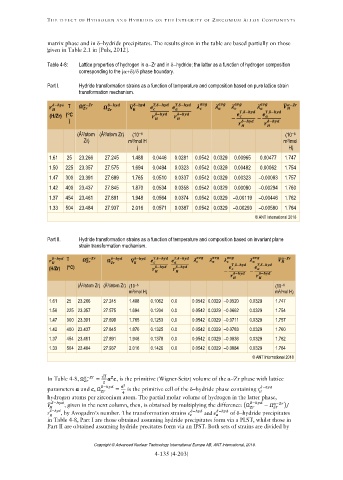
Table 4-8: Lattice properties of hydrogen in αZr and in hydride; the latter as a function of hydrogen composition
corresponding to the ( phase boundary.
Part I. Hydride transformation strains as a function of temperature and composition based on pure lattice strain
transformation mechanism.
̅
− T − − − , − , − ̅ −
(H/Zr) (C − − − , − − , −
) − −
(Å /atom (Å /atom Zr) (10 (10
3
3
6
6
Zr) m /mol H m /mol
3
3
) H)
1.61 25 23.266 27.245 1.488 0.0446 0.0281 0.0542 0.0329 0.00965 0.00477 1.747
1.50 225 23.357 27.575 1.694 0.0494 0.0323 0.0542 0.0329 0.00482 0.00062 1.754
1.47 300 23.391 27.699 1.765 0.0510 0.0337 0.0542 0.0329 0.00323 –0.00083 1.757
1.42 400 23.437 27.845 1.870 0.0534 0.0358 0.0542 0.0329 0.00080 –0.00294 1.760
1.37 454 23.461 27.891 1.948 0.0564 0.0374 0.0542 0.0329 –0.00119 –0.00446 1.762
1.33 504 23.484 27.937 2.016 0.0571 0.0387 0.0542 0.0329 –0.00293 –0.00580 1.764
© ANT International 2018
Part II. Hydride transformation strains as a function of temperature and composition based on invariant plane
strain transformation mechanism.
− T − − ̅ − , − , − ̅ −
(H/Zr) (C) − − , − , −
− − − −
(Å /atom Zr) (Å /atom Zr) (10 (10
3
6
3
6
m /mol H) m /mol H)
3
3
1.61 25 23.266 27.245 1.488 0.1062 0.0 0.0542 0.0329 –0.0520 0.0329 1.747
1.50 225 23.357 27.575 1.694 0.1204 0.0 0.0542 0.0329 –0.0662 0.0329 1.754
1.47 300 23.391 27.699 1.765 0.1253 0.0 0.0542 0.0329 –0.0711 0.0329 1.757
1.42 400 23.437 27.845 1.870 0.1325 0.0 0.0542 0.0329 –0.0783 0.0329 1.760
1.37 454 23.461 27.891 1.948 0.1378 0.0 0.0542 0.0329 –0.0836 0.0329 1.762
1.33 504 23.484 27.937 2.016 0.1426 0.0 0.0542 0.0329 –0.0884 0.0329 1.764
© ANT International 2018
Ω − = √3 α
2
Ω −ℎ = 4 3 −ℎ
̅
−ℎ (Ω −ℎ − Ω − )/
−ℎ −ℎ −ℎ
Copyright © Advanced Nuclear Technology International Europe AB, ANT International, 2019.